Python return 语句
简介
Python return 语句用于从函数中返回一个值。用户只能在函数中使用 return 语句,在 Python 函数外部不能使用。return 语句包括 return 关键字和在其后将被返回的值。
return 语句的语法
def funtion_name():
statements
.
.
.
return [expression]
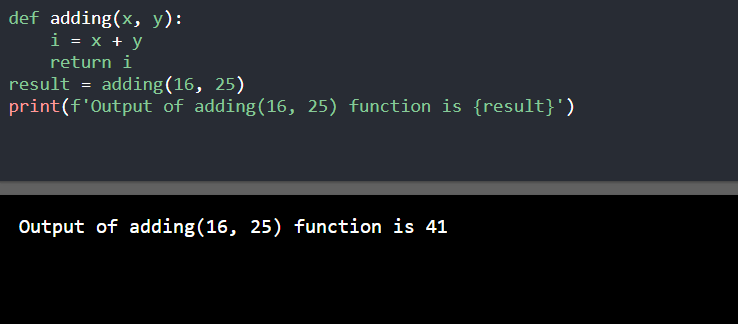
程序1
def adding(x, y):
i = x + y
return i
result = adding(16, 25)
print(f'Output of adding(16, 25) function is {result}')
输出
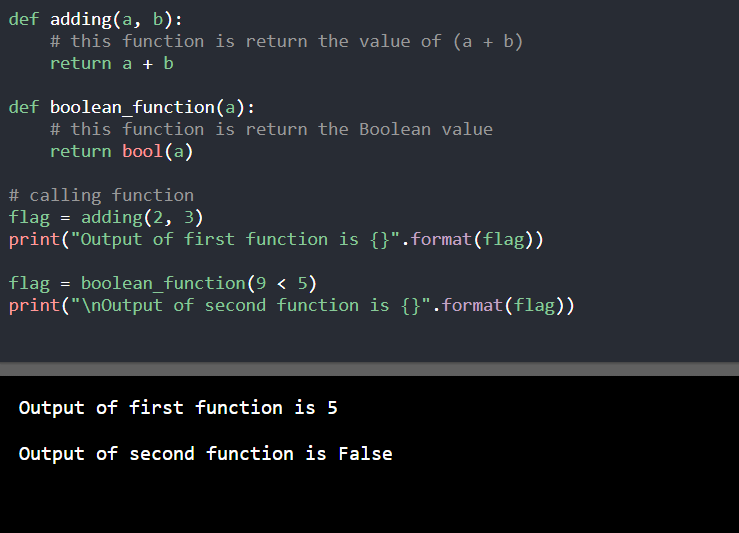
程序2
def adding(a, b):
# this function is return the value of (a + b)
return a + b
def boolean_function(a):
# this function is return the Boolean value
return bool(a)
# calling function
flag = adding(2, 3)
print("Output of first function is {}".format(flag))
flag = boolean_function(9 < 5)
print("\nOutput of second function is {}".format(flag))
输出
返回多个值
在Python编程语言中,用户可以从函数中返回多个值。下面是实现这个功能的几种方法。
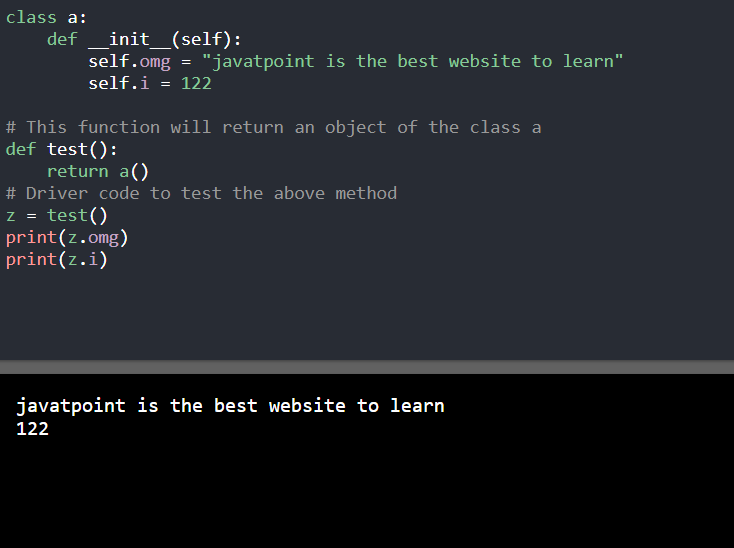
1. 使用对象: 这种方法类似于C/C++和Java。用户可以创建一个类来保存函数中的多个值,并返回该类的对象。
class a:
def __init__(self):
self.omg = "javatpoint is the best website to learn"
self.i = 122
# This function will return an object of the class a
def test():
return a()
# Driver code to test the above method
z = test()
print(z.omg)
print(z.i)
输出
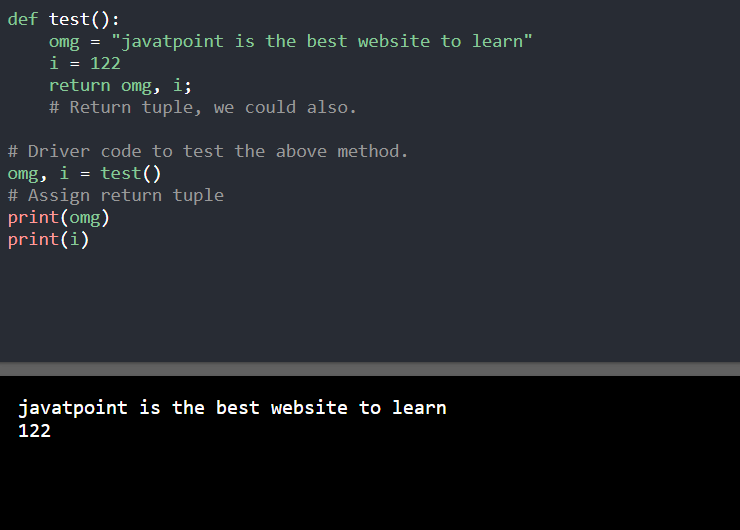
2. 使用元组: 元组与列表类似,但是元组与列表之间存在细微的差异。在元组中,对象的值不能被改变,而在列表中对象的值可以被改变。
def test():
omg = "javatpoint is the best website to learn"
i = 122
return omg, i;
# Return tuple, we could also.
# Driver code to test the above method.
omg, i = test()
# Assign return tuple
print(omg)
print(i)
输出
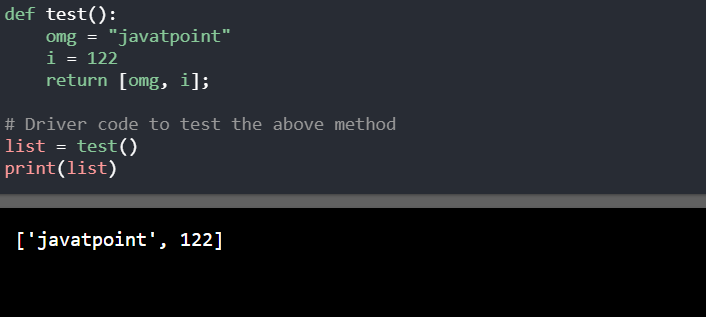
3. 使用列表: 列表类似于动态大小的数组。在列表中,用户可以将所有内容存储在一个变量中。
def test():
omg = "javatpoint"
i = 122
return [omg, i];
# Driver code to test the above method
list = test()
print(list)
输出
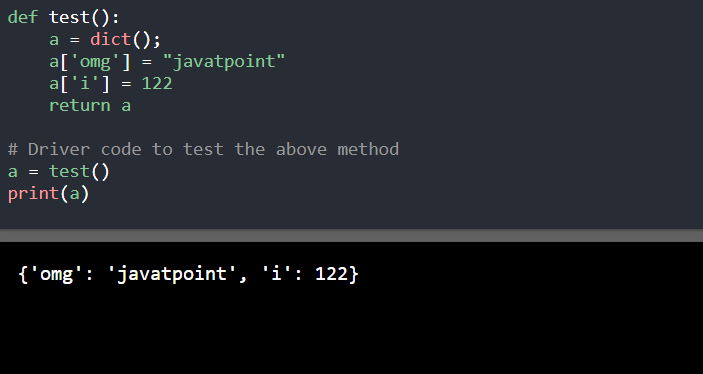
4. 使用字典: 在Python语言中,字典是一种无序的集合,用于存储散列或映射等数据值。
def test():
a = dict();
a['omg'] = "javatpoint"
a['i'] = 122
return a
# Driver code to test the above method
a = test()
print(a)
输出
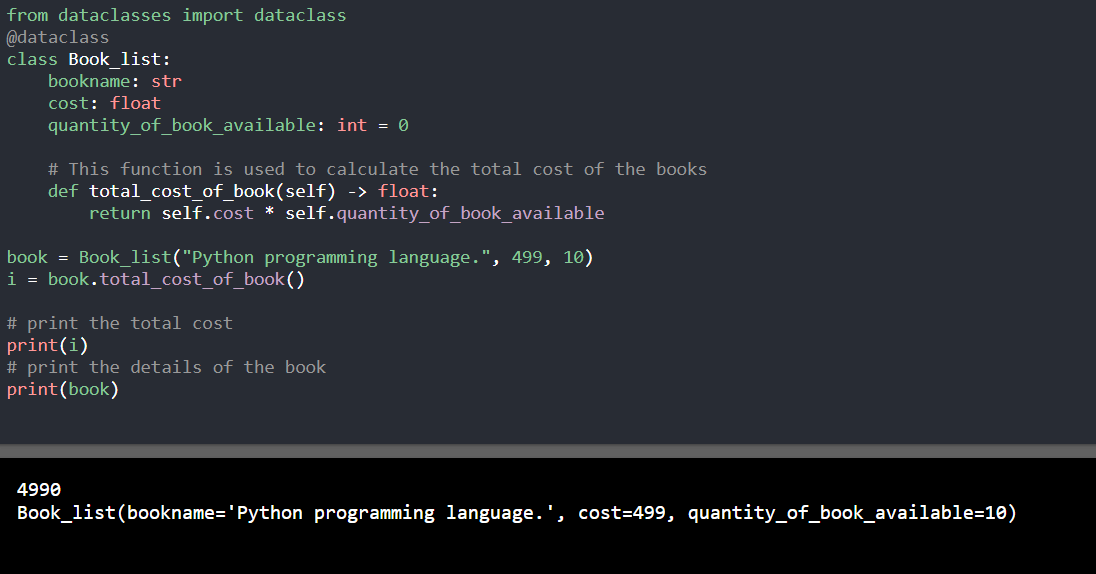
5. 使用数据类(Python 3.7+)
from dataclasses import dataclass
@dataclass
class Book_list:
bookname: str
cost: float
quantity_of_book_available: int = 0
# This function is used to calculate the total cost of the books
def total_cost_of_book(self) -> float:
return self.cost * self.quantity_of_book_available
book = Book_list("Python programming language.", 499, 10)
i = book.total_cost_of_book()
# print the total cost
print(i)
# print the details of the book
print(book)
输出
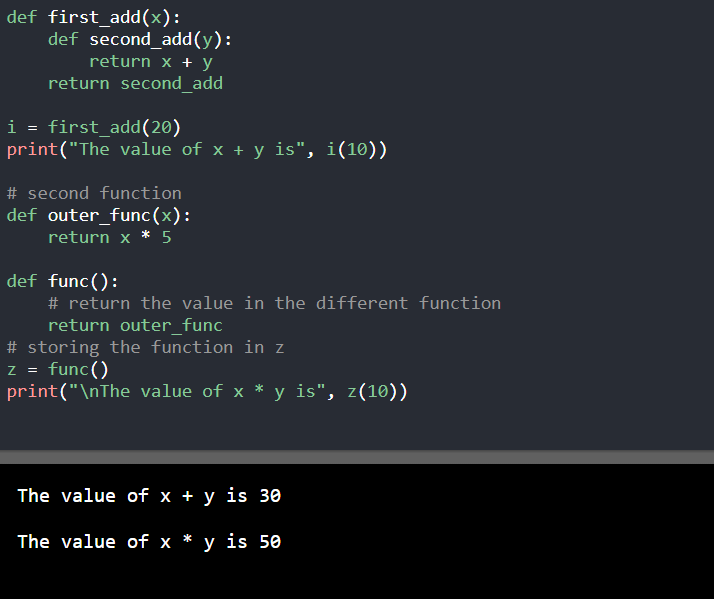
功能返回另一个函数
在Python编程语言中,函数是以对象的形式存在的。因此,用户可以从另一个函数返回一个函数。
在下面的程序中,first_add函数返回second_add函数。
def first_add(x):
def second_add(y):
return x + y
return second_add
i = first_add(20)
print("The value of x + y is", i(10))
# second function
def outer_func(x):
return x * 5
def func():
# return the value in the different function
return outer_func
# storing the function in z
z = func()
print("\nThe value of x * y is", z(10))
输出
 极客笔记
极客笔记