JavaScript closest()方法
在JavaScript中,closest()方法用于检索与选择器匹配的元素的最近祖先或父元素。如果未找到祖先,该方法返回null。
此方法沿着文档树遍历元素及其父元素,遍历将继续直到找到与提供的选择器字符串匹配的第一个节点为止。
语法
targetElement.closest(selectors);
在上面的语法中, 选择器 是一个包含选择器的字符串(例如 p:hover 等),用于查找节点。
通过使用一些示例来理解这个方法。
示例1
在这个示例中,有三个div元素和一个标题,我们正在应用 closest() 方法。在这里,我们使用的选择器是 id 选择器, 后代 选择器, 子元素 选择器和 :not 选择器。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
</head>
<body>
<div id = "div1"> This is the first div element.
<h3 id = "h"> This is a heading inside the div. </h3>
<div id = "div2"> This is the div inside the div element.
<div id = "div3"> This is the div element inside the second div element. </div>
</div>
</div>
<script>
var val1 = document.getElementById("div3");
var o1 = val1.closest("#div1");
var o2 = val1.closest("div div");
var o3 = val1.closest("div > div");
var o4 = val1.closest(":not(#div3)");
console.log(o1);
console.log(o2);
console.log(o3);
console.log(o4);
</script>
</body>
</html>
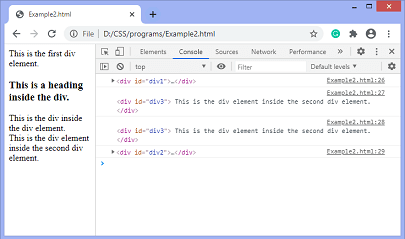
输出
在执行上述代码之后,输出将是 –
示例2
这是另一个使用JavaScript的 closest() 方法的示例。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
</head>
<body>
<div id = "div1"> This is the div element.
<p id = "p1"> This is the paragraph element inside the div element.
<h3 id = "h"> This is the child of the paragraph element.
<p id = "p2"> This is the child of heading element of the paragraph element. </p>
</h3>
</p>
</div>
<script>
var val1 = document.getElementById("p2");
var o1 = val1.closest("p");
var o2 = val1.closest("h3");
var o3 = val1.closest("div");
console.log(o1);
console.log(o2);
console.log(o3);
</script>
</body>
</html>
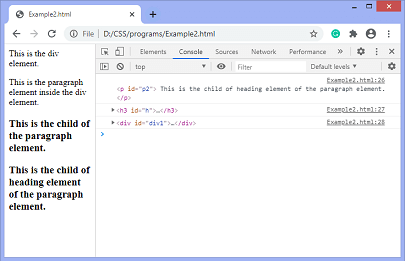
输出
在上述代码执行后,输出结果为 –
 极客笔记
极客笔记