TypeScript 类
在像Java这样的面向对象编程语言中,类是用来创建可重用组件的基本实体。它是具有共同属性的一组对象。从面向对象的角度来看,类是用来创建对象的模板或蓝图。它是一个逻辑实体。
类定义可以包含以下属性:
- 字段: 在类中声明的变量。
- 方法: 代表对象的操作。
- 构造函数: 负责在内存中初始化对象。
- 嵌套类和接口: 表示一个类可以包含另一个类。
TypeScript是一种面向对象的JavaScript语言,因此支持类、接口、多态、数据绑定等面向对象编程特性。JavaScript ES5 或 更早版本 不支持类。TypeScript从 ES6 和 更高版本 开始支持该特性。TypeScript对使用类有 内置 支持,因为它基于ES6版本的JavaScript。如今,许多开发人员使用基于类的面向对象编程语言,并将它们编译成JavaScript,以便在所有主要浏览器和平台上运行。
声明类的语法
在TypeScript中,使用class关键字来声明类。我们可以使用以下语法创建类:
class <class_name>{
field;
method;
}
示例
class Student {
studCode: number;
studName: string;
constructor(code: number, name: string) {
this.studName = name;
this.studCode = code;
}
getGrade() : string {
return "A+" ;
}
}
TypeScript编译器将上述类转换为以下JavaScript代码。
var Student = /** @class */ (function () {
function Student(code, name) {
this.studName = name;
this.studCode = code;
}
Student.prototype.getGrade = function () {
return "A+";
};
return Student;
}());
创建一个类的对象
通过使用 new 关键字和 类名 来创建一个类的对象。new关键字在运行时为对象创建分配内存。所有的对象都在堆内存区域中获得内存。我们可以按照以下方式创建一个对象。
语法
let object_name = new class_name(parameter)
- new关键字: 它用于在内存中实例化对象。
- 表达式的右侧调用构造函数,该函数可以传递值。
示例
//Creating an object or instance
let obj = new Student();
对象初始化
对象初始化指的是将数据存储到对象中。有三种方法可以初始化一个对象。它们是:
1. 通过引用变量
示例
//Creating an object or instance
let obj = new Student();
//Initializing an object by reference variable
obj.id = 101;
obj.name = "Virat Kohli";
2. 通过方法
方法类似于用于公开对象行为的函数。
方法的优势
- 代码的可重用性
- 代码的优化
示例
//Defining a Student class.
class Student {
//defining fields
id: number;
name:string;
//creating method or function
display():void {
console.log("Student ID is: "+this.id)
console.log("Student ID is: "+this.name)
}
}
//Creating an object or instance
let obj = new Student();
obj.id = 101;
obj.name = "Virat Kohli";
obj.display();
输出:
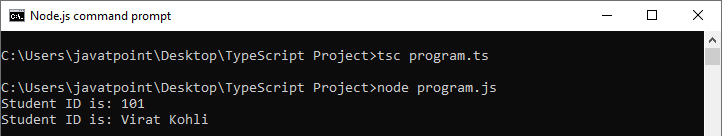
3. 通过构造函数
构造函数用于 初始化 一个对象。在TypeScript中,构造方法总是使用名称” constructor “来定义。在构造函数中,我们可以使用 this 关键字来访问类的成员。
注意:并非必须在类中始终使用构造函数。
示例:
//defining constructor
constructor(id: number, name:string) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
构造函数、方法和对象的示例:
//Defining a Student class.
class Student {
//defining fields
id: number;
name:string;
//defining constructor
constructor(id: number, name:string) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
//creating method or function
display():void {
console.log("Function displays Student ID is: "+this.id)
console.log("Function displays Student ID is: "+this.name)
}
}
//Creating an object or instance
let obj = new Student(101, "Virat Kohli")
//access the field
console.log("Reading attribute value of Student as: " +obj.id,)
console.log("Reading attribute value of Student as: " +obj.name)
//access the method or function
obj.display()
输出:
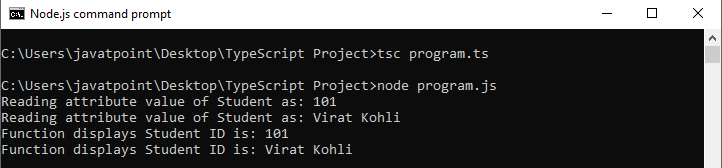
没有构造函数的示例
//Defining a Student class.
class Student {
//defining fields
id: number;
name:string;
}
//Creating an object or instance
let obj = new Student();
// Initializing an object
obj.id = 101;
obj.name = "Virat Kohli";
//access the field
console.log("Student ID: " +obj.id,);
console.log("Student Name: " +obj.name);
输出:
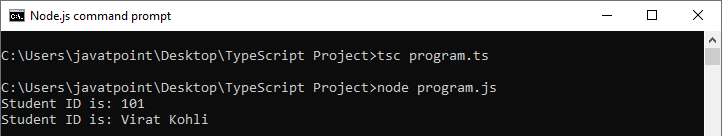
数据隐藏
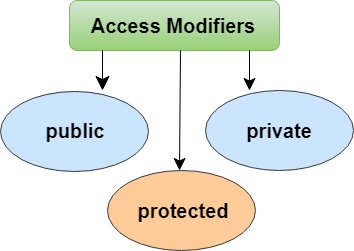
这是一种用于隐藏内部对象细节的技术。一个类可以控制其数据成员对其他类成员的可见性。这种能力被称为封装或数据隐藏。面向对象编程使用访问修饰符的概念来实现封装。访问修饰符定义了类数据成员在其定义类之外的可见性。
TypeScript支持三种类型的访问修饰符。它们是:
 极客笔记
极客笔记