OpenCV Python 如何找到图像中点与轮廓之间的最短距离
我们可以使用cv2.pointPolygonTest()函数计算图像上点与轮廓之间的最短距离,将轮廓上的点的坐标和点的坐标作为参数传递给该函数。在应用cv2.pointPolygonTest()函数之前,我们需要计算图像中的轮廓。我们可以按照以下步骤来找到图像中给定点与对象轮廓之间的最短距离-
- 导入所需的库。在以下所有Python示例中,所需的库是OpenCV。确保您已经安装它。
-
使用cv2.imread()读取输入图像。使用该方法读取的RGB图像是BGR格式的。可选地将读取的BGR图像赋值给img。
-
现在使用cv2.cvtColor()函数将BGR图像转换为灰度图像,如下所示。可选地将转换后的灰度图像赋值给gray。
-
对灰度图像应用阈值处理,将其转换为二值图像。调整第二个参数(threshValue)以获得更好的二值图像。
-
在二值图像中找到轮廓。
-
选择第一个轮廓作为cnt,或循环遍历所有轮廓。
-
使用cv2.pointPolygonTest()函数计算点与所选轮廓之间的最短距离。将所需的参数传递给该函数。要计算点(250,250)与轮廓cnt之间的最短距离,我们使用以下代码片段:
dist = cv2.pointPolygonTest(cnt,(250,250),True)
-
在输入图像中打印计算出的点和对象轮廓之间的最短距离。
-
在图像中绘制点和检测到的轮廓以便更好地可视化。
让我们通过一些Python示例来了解如何找到给定点和图像中对象轮廓之间的最短距离。
示例
在这个Python程序中,我们在输入图像上取了两个点(250,250)和(350,250)。我们计算了点与输入图像中轮廓之间的最短距离。输入图像只有一个对象轮廓。我们还在图像上绘制了轮廓和点,以便清楚地理解。
# import required libraries
import cv2
# load the input image
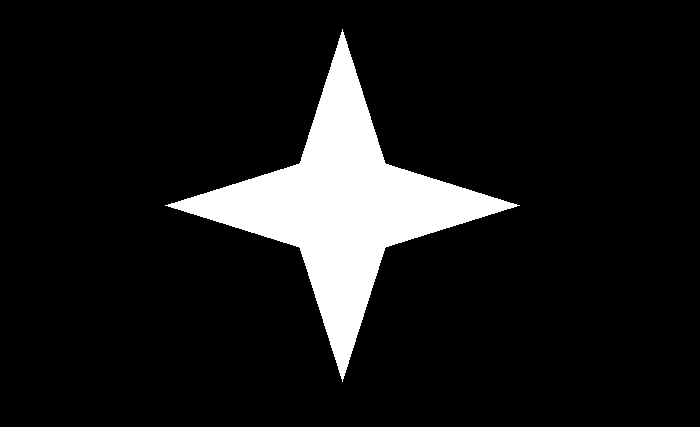
img = cv2.imread('four-point-star.png')
# convert the input image to grayscale
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# apply thresholding to convert grayscale to binary image
ret,thresh = cv2.threshold(gray,150,255,0)
# find the contours
contours,hierarchy = cv2.findContours(thresh,
cv2.RETR_TREE,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
print("Number of contours detected:", len(contours))
# select the first contour
cnt = contours[0]
# find the shortest distance from point[250,250]
dist1 = cv2.pointPolygonTest(cnt,(250,250),True)
# print the shortest distance between the point 1 and contour detected.
print('Shortest distance of Point 1 from contour:', dist1)
dist2 = cv2.pointPolygonTest(cnt,(350,250),True)
# print the shortest distance between the point 2 and contour detected.
print('Shortest distance of Point 2 from contour:', dist2)
# draw the point [250,250] on the image
cv2.circle(img, (250,250), 4, (0, 0, 255), -1)
cv2.putText(img, "Point 1", (255,255),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.6, (0, 255, 0), 2)
cv2.circle(img, (350,250), 4, (0, 0, 255), -1)
cv2.putText(img, "Point 2", (355,255),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.6, (0, 255, 0), 2)
# draw contour on the input image
cv2.drawContours(img, [cnt], -1, (0,255,255), 3)
# display the image with drawn extreme points
while True:
cv2.imshow("Extreme Points", img)
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == 27:
break
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
我们将使用这个图片作为这个程序的输入文件 –
输出
当你运行上面的程序时,它将产生以下输出 –
Number of contours detected: 1
Shortest distance of Point 1 from contour: -17.72004514666935
Shortest distance of Point 2 from contour: 31.622776601683793
我们得到以下窗口显示轮廓和两点-
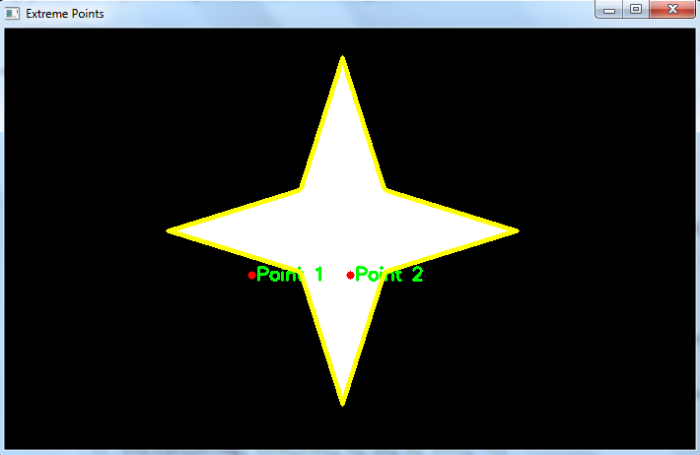
在上面的输出图像中,轮廓以黄色绘制,两个点以红色显示。点1与轮廓之间的最短距离为负数,表示该点位于轮廓外部。点2与轮廓之间的最短距离为正数,表示该点位于轮廓内部。如果最短距离为零,表示该点位于轮廓边界上。
示例
在这个Python程序中,我们在输入图像上取了一个点(350,250)。我们在输入图像中检测所有对象的轮廓。图像有三个轮廓。我们计算了点与输入图像中轮廓之间的最短距离。我们还在图像上绘制了轮廓和点,以便更清楚地理解。
# import required libraries
import cv2
# load the input image
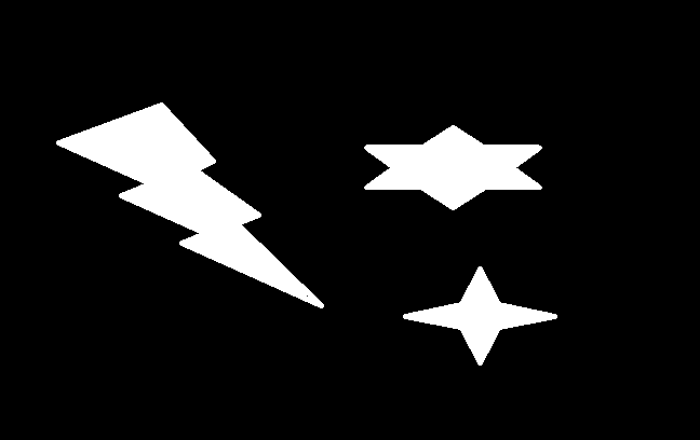
img = cv2.imread('convexhull.png')
# convert the input image to grayscale
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# apply thresholding to convert grayscale to binary image
ret,thresh = cv2.threshold(gray,100,255,0)
# find the contours
contours,hierarchy = cv2.findContours(thresh,
cv2.RETR_TREE,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
print("Number of contours detected:", len(contours))
# draw contour and shape number
for i, cnt in enumerate(contours):
M = cv2.moments(cnt)
x1, y1 = cnt[0,0]
img1 = cv2.drawContours(img, [cnt], -1, (0,255,255), 3)
cv2.putText(img, f'Contour:{i+1}', (x1, y1),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.6, (0, 255, 0), 2)
# compute shortest distance of point (350,250) from the contour
dist = cv2.pointPolygonTest(cnt,(350,250),True)
print(f'Shortest distance of Point (350,250) from contour
{i+1}:', dist)
cv2.circle(img, (350,250), 4, (0, 0, 255), -1)
cv2.imshow("Shapes", img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
我们将使用这个图像作为该程序的 输入文件 –
输出
当你运行上面的程序时,它将产生以下输出 –
Number of contours detected: 3
Shortest distance of Point (350,250) from contour 1: -83.73768566183328
Shortest distance of Point (350,250) from contour 2: -62.81719509815764
Shortest distance of Point (350,250) from contour 3: -57.27564927611035
我们得到以下窗口显示轮廓和点 −
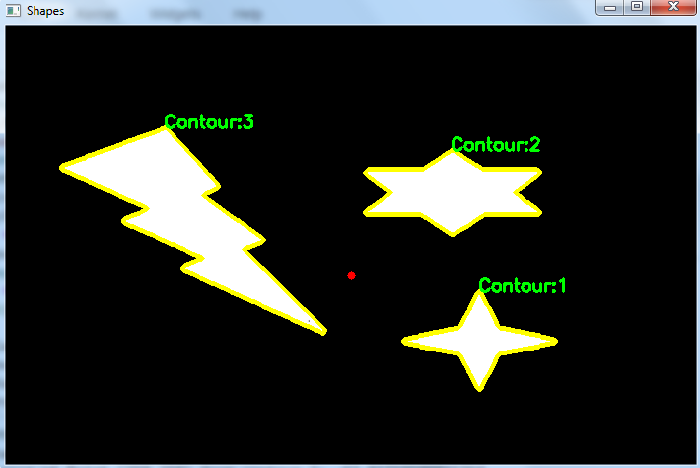
在上面的输出图像中,轮廓用黄色绘制,点用红色表示。点与轮廓之间的每个最短距离都是负数,说明该点位于每个轮廓之外。与其他距离相比,点与轮廓 3 之间的绝对距离最小。因此该点距离轮廓 3 最近。
 极客笔记
极客笔记