Python if-else语句
决策是几乎所有编程语言中最重要的方面。顾名思义,决策允许我们针对特定的条件运行特定的代码块。在这里,决策是基于特定条件的有效性进行的。条件检查是决策制定的基础。
在Python中,使用以下语句进行决策制定。
| 语句 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| If语句 | If语句用于测试特定的条件。如果条件为真,则执行一段代码块(if-block)。 |
| If-else语句 | If-else语句与if语句类似,只是它还提供了用于检查条件为假时的代码块。如果if语句中的条件为假,则执行else语句。 |
| 嵌套if语句 | 嵌套if语句使我们能够在外部if语句内部使用if-else语句。 |
Python中的缩进
为了编程方便和简单性,Python不允许使用圆括号来标记代码块的级别。在Python中,缩进用于声明一个代码块。如果两个语句处于相同的缩进级别,则它们属于同一个代码块。
通常,在Python中使用四个空格进行缩进是一种典型的缩进量。
缩进是Python语言中最常用的部分,因为它声明了代码块。一个代码块中的所有语句都以相同级别的缩进进行缩进。我们将看到实际的缩进如何在Python中进行决策制定和其他事情。
if语句
if语句用于测试特定条件,如果条件为真,则执行一段被称为if-block的代码块。if语句的条件可以是任何有效的逻辑表达式,该表达式可以求值为真或假。
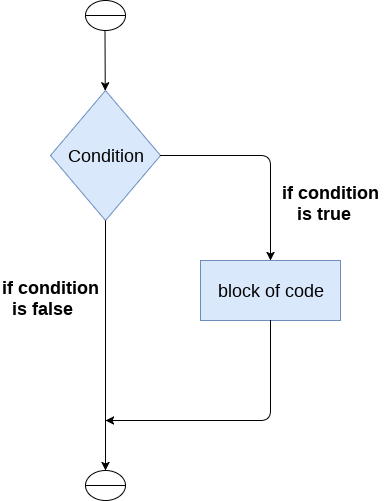
if语句的语法如下所示:
if expression:
statement
示例 1
# Simple Python program to understand the if statement
num = int(input("enter the number:"))
# Here, we are taking an integer num and taking input dynamically
if num%2 == 0:
# Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block
print("The Given number is an even number")
输出:
enter the number: 10
The Given number is an even number
示例2:编写程序打印三个数字中的最大值
# Simple Python Program to print the largest of the three numbers.
a = int (input("Enter a: "));
b = int (input("Enter b: "));
c = int (input("Enter c: "));
if a>b and a>c:
# Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block
print ("From the above three numbers given a is largest");
if b>a and b>c:
# Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block
print ("From the above three numbers given b is largest");
if c>a and c>b:
# Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block
print ("From the above three numbers given c is largest");
输出:
Enter a: 100
Enter b: 120
Enter c: 130
From the above three numbers given c is largest
if-else语句
if-else语句结合了if语句和else语句,在条件不满足时执行else块。
如果条件为真,则执行if块。否则,执行else块。
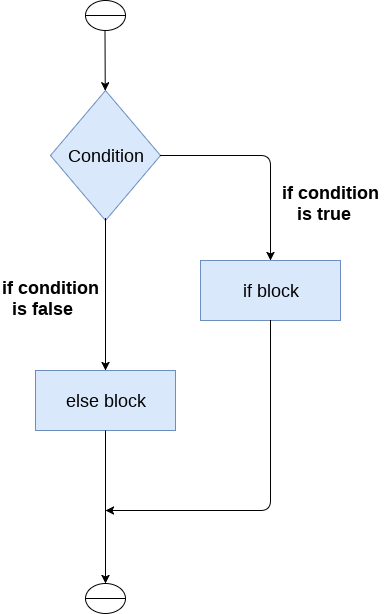
if-else语句的语法如下所示:
if condition:
#block of statements
else:
#another block of statements (else-block)
示例1:检查一个人是否有资格投票
# Simple Python Program to check whether a person is eligible to vote or not.
age = int (input("Enter your age: "))
# Here, we are taking an integer num and taking input dynamically
if age>=18:
# Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block
print("You are eligible to vote !!");
else:
print("Sorry! you have to wait !!");
输出:
Enter your age: 90
You are eligible to vote !!
示例2:检查一个数字是否为偶数
# Simple Python Program to check whether a number is even or not.
num = int(input("enter the number:"))
# Here, we are taking an integer num and taking input dynamically
if num%2 == 0:
# Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block
print("The Given number is an even number")
else:
print("The Given Number is an odd number")
输出:
enter the number: 10
The Given number is even number
elif语句
elif语句使我们能够检查多个条件,并根据其中一个条件的真实性执行特定的代码块。根据需要,我们的程序中可以有任意数量的elif语句。但是,使用elif是可选的。
elif语句在C语言中类似于if-else-if梯形语句。它必须跟在if语句之后。
elif语句的语法如下所示:
if expression 1:
# block of statements
elif expression 2:
# block of statements
elif expression 3:
# block of statements
else:
# block of statements

示例 1
# Simple Python program to understand elif statement
number = int(input("Enter the number?"))
# Here, we are taking an integer number and taking input dynamically
if number==10:
# Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block
print("The given number is equals to 10")
elif number==50:
# Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block
print("The given number is equal to 50");
elif number==100:
# Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block
print("The given number is equal to 100");
else:
print("The given number is not equal to 10, 50 or 100");
输出:
Enter the number?15
The given number is not equal to 10, 50 or 100
示例 2
# Simple Python program to understand elif statement
marks = int(input("Enter the marks? "))
# Here, we are taking an integer marks and taking input dynamically
if marks > 85 and marks <= 100:
# Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block
print("Congrats ! you scored grade A ...")
elif marks > 60 and marks <= 85:
# Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block
print("You scored grade B + ...")
elif marks > 40 and marks <= 60:
# Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block
print("You scored grade B ...")
elif (marks > 30 and marks <= 40):
# Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block
print("You scored grade C ...")
else:
print("Sorry you are fail ?")
输出:
Enter the marks? 89
Congrats ! you scored grade A ...
 极客笔记
极客笔记