Python 集合
Python 集合是无序项的集合。集合中的每个元素必须是唯一的、不可变的,且集合会删除重复的元素。集合是可变的,这意味着我们可以在创建后修改它。
与Python中的其他集合不同,集合的元素没有附加索引,也就是说,我们不能通过索引直接访问集合中的任何元素。但是,我们可以一起打印它们,或者通过循环遍历集合获取元素的列表。
创建集合
可以通过使用花括号 {} 包含逗号分隔的不可变项来创建集合。Python还提供了set()方法,可以通过传递序列来创建集合。
示例1:使用花括号
Days = {"Monday", "Tuesday", "Wednesday", "Thursday", "Friday", "Saturday", "Sunday"}
print(Days)
print(type(Days))
print("looping through the set elements ... ")
for i in Days:
print(i)
输出:
{'Friday', 'Tuesday', 'Monday', 'Saturday', 'Thursday', 'Sunday', 'Wednesday'}
<class 'set'>
looping through the set elements ...
Friday
Tuesday
Monday
Saturday
Thursday
Sunday
Wednesday
示例2:使用set()方法
Days = set(["Monday", "Tuesday", "Wednesday", "Thursday", "Friday", "Saturday", "Sunday"])
print(Days)
print(type(Days))
print("looping through the set elements ... ")
for i in Days:
print(i)
输出:
{'Friday', 'Wednesday', 'Thursday', 'Saturday', 'Monday', 'Tuesday', 'Sunday'}
<class 'set'>
looping through the set elements ...
Friday
Wednesday
Thursday
Saturday
Monday
Tuesday
Sunday
它可以包含任何类型的元素,例如整数、浮点数、元组等。但是可变元素(列表、字典、集合)不能成为集合的成员。考虑以下示例。
# Creating a set which have immutable elements
set1 = {1,2,3, "JavaTpoint", 20.5, 14}
print(type(set1))
#Creating a set which have mutable element
set2 = {1,2,3,["Javatpoint",4]}
print(type(set2))
输出:
<class 'set'>
Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-5-9605bb6fbc68> in <module>
4
5 #Creating a set which holds mutable elements
----> 6 set2 = {1,2,3,["Javatpoint",4]}
7 print(type(set2))
TypeError: unhashable type: 'list'
在上面的代码中,我们创建了两个集合,其中集合 set1 具有不可变元素,而集合set2具有一个可变元素,即一个列表。在检查set2的类型时,它引发了一个错误,这意味着集合只能包含不可变元素。
创建一个空集合与创建一个空字典略有不同,因为空的花括号{}也用于创建字典。因此,Python提供了无需参数的set()方法来创建一个空集合。
# Empty curly braces will create dictionary
set3 = {}
print(type(set3))
# Empty set using set() function
set4 = set()
print(type(set4))
输出:
<class 'dict'>
<class 'set'>
让我们看看如果我们向集合中提供重复的元素会发生什么。
set5 = {1,2,4,4,5,8,9,9,10}
print("Return set with unique elements:",set5)
输出:
Return set with unique elements: {1, 2, 4, 5, 8, 9, 10}
在上述代码中,当我们打印出set5时,我们可以看到set5包含多个重复元素,因此我们需要移除set中的重复项。
向set中添加元素
Python提供了add()方法和update()方法,用于向set中添加特定的元素。add()方法用于添加单个元素,而update()方法用于添加多个元素到set中。考虑以下示例。
示例1:使用add()方法
Months = set(["January","February", "March", "April", "May", "June"])
print("\nprinting the original set ... ")
print(months)
print("\nAdding other months to the set...");
Months.add("July");
Months.add ("August");
print("\nPrinting the modified set...");
print(Months)
print("\nlooping through the set elements ... ")
for i in Months:
print(i)
输出:
printing the original set ...
{'February', 'May', 'April', 'March', 'June', 'January'}
Adding other months to the set...
Printing the modified set...
{'February', 'July', 'May', 'April', 'March', 'August', 'June', 'January'}
looping through the set elements ...
February
July
May
April
March
August
June
January
为了在集合中添加多个项目,Python提供了 update() 方法。它接受可迭代对象作为参数。
考虑以下示例。
示例2:使用update()函数
Months = set(["January","February", "March", "April", "May", "June"])
print("\nprinting the original set ... ")
print(Months)
print("\nupdating the original set ... ")
Months.update(["July","August","September","October"]);
print("\nprinting the modified set ... ")
print(Months);
输出:
printing the original set ...
{'January', 'February', 'April', 'May', 'June', 'March'}
updating the original set ...
printing the modified set ...
{'January', 'February', 'April', 'August', 'October', 'May', 'June', 'July', 'September', 'March'}
从集合中删除项
Python提供了discard()方法和remove()方法,可用于从集合中删除项。这两个函数之间的区别在于,如果使用discard()函数时,如果项在集合中不存在,则集合保持不变,而remove()方法会引发错误。
考虑以下示例。
示例1 使用discard()方法
months = set(["January","February", "March", "April", "May", "June"])
print("\nprinting the original set ... ")
print(months)
print("\nRemoving some months from the set...");
months.discard("January");
months.discard("May");
print("\nPrinting the modified set...");
print(months)
print("\nlooping through the set elements ... ")
for i in months:
print(i)
输出:
printing the original set ...
{'February', 'January', 'March', 'April', 'June', 'May'}
Removing some months from the set...
Printing the modified set...
{'February', 'March', 'April', 'June'}
looping through the set elements ...
February
March
April
June
Python还提供了 remove() 方法来从集合中移除项目。考虑以下示例使用 remove() 方法来移除项目。
示例2 使用remove()函数
months = set(["January","February", "March", "April", "May", "June"])
print("\nprinting the original set ... ")
print(months)
print("\nRemoving some months from the set...");
months.remove("January");
months.remove("May");
print("\nPrinting the modified set...");
print(months)
输出:
printing the original set ...
{'February', 'June', 'April', 'May', 'January', 'March'}
Removing some months from the set...
Printing the modified set...
{'February', 'June', 'April', 'March'}
我们还可以使用pop()方法来删除元素。通常,pop()方法总是删除最后一个元素,但是由于集合是无序的,我们无法确定将从集合删除哪个元素。
考虑以下示例,使用pop()方法从集合中删除元素。
Months = set(["January","February", "March", "April", "May", "June"])
print("\nprinting the original set ... ")
print(Months)
print("\nRemoving some months from the set...");
Months.pop();
Months.pop();
print("\nPrinting the modified set...");
print(Months)
输出:
printing the original set ...
{'June', 'January', 'May', 'April', 'February', 'March'}
Removing some months from the set...
Printing the modified set...
{'May', 'April', 'February', 'March'}
在上述代码中, Month 集合的最后一个元素是 March ,但是pop()方法删除了 June和January ,因为集合是无序的,并且pop()方法无法确定集合的最后一个元素。
Python提供了clear()方法来从集合中删除所有项。
考虑以下例子。
Months = set(["January","February", "March", "April", "May", "June"])
print("\nprinting the original set ... ")
print(Months)
print("\nRemoving all the items from the set...");
Months.clear()
print("\nPrinting the modified set...")
print(Months)
输出:
printing the original set ...
{'January', 'May', 'June', 'April', 'March', 'February'}
Removing all the items from the set...
Printing the modified set...
set()
discard()和remove()的区别
尽管discard()和remove()方法执行的任务相同,但是discard()和remove()之间有一个主要区别。
如果使用discard()从集合中删除的键不存在于集合中,Python将不会报错。程序将保持其控制流程。
另一方面,如果使用remove()从集合中删除的项不存在于集合中,Python将引发一个错误。
请考虑以下示例。
示例-
Months = set(["January","February", "March", "April", "May", "June"])
print("\nprinting the original set ... ")
print(Months)
print("\nRemoving items through discard() method...");
Months.discard("Feb"); #will not give an error although the key feb is not available in the set
print("\nprinting the modified set...")
print(Months)
print("\nRemoving items through remove() method...");
Months.remove("Jan") #will give an error as the key jan is not available in the set.
print("\nPrinting the modified set...")
print(Months)
输出:
printing the original set ...
{'March', 'January', 'April', 'June', 'February', 'May'}
Removing items through discard() method...
printing the modified set...
{'March', 'January', 'April', 'June', 'February', 'May'}
Removing items through remove() method...
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "set.py", line 9, in
Months.remove("Jan")
KeyError: 'Jan'
Python Set操作
可以对集合执行数学操作,例如并集、交集、差集和对称差。Python提供了使用运算符或方法执行这些操作的功能。我们如下所述描述这些操作。
两个集合的并集
要在Python中将两个或多个集合合并为一个集合,请使用union()函数。每个合并集合的独特特征都存在于最终集合中。作为参数,可以传递一个或多个集合给union()函数。如果只有一个集合,函数将返回所提供的集合的副本。如果作为参数提供了多个集合,该方法将返回一个包含所有参数中不同项的新集合。
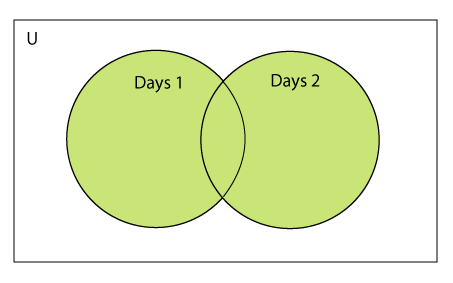
考虑以下示例来计算两个集合的并集。
示例1:使用并集|运算符
Days1 = {"Monday","Tuesday","Wednesday","Thursday", "Sunday"}
Days2 = {"Friday","Saturday","Sunday"}
print(Days1|Days2) #printing the union of the sets
输出:
{'Friday', 'Sunday', 'Saturday', 'Tuesday', 'Wednesday', 'Monday', 'Thursday'}
Python 还提供 union() 方法,该方法也可以用于计算两个集合的并集。考虑以下示例。
示例2:使用union()方法
Days1 = {"Monday","Tuesday","Wednesday","Thursday"}
Days2 = {"Friday","Saturday","Sunday"}
print(Days1.union(Days2)) #printing the union of the sets
输出:
{'Friday', 'Monday', 'Tuesday', 'Thursday', 'Wednesday', 'Sunday', 'Saturday'}
现在,我们还可以使用union()函数创建两个以上集合的并集,例如:
程序:
# Create three sets
set1 = {1, 2, 3}
set2 = {2, 3, 4}
set3 = {3, 4, 5}
# Find the common elements between the three sets
common_elements = set1.union(set2, set3)
# Print the common elements
print(common_elements)
输出:
{1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
两个集合的交集
为了发现Python中两个或多个集合中的共同之处,可以使用intersection()函数。只有在所有进行比较的集合中出现的项目会被包含在最终的集合中。一个或多个集合也可以作为intersection()函数的参数。如果只有一个集合,函数会返回提供的那个集合的副本。如果作为参数提供了多个集合,该方法会返回一个只包含所有进行比较的集合中的元素的新集合。
可以通过 and &运算符或intersection()函数来执行两个集合的交集。两个集合的交集被定义为在两个集合中都出现的元素的集合。
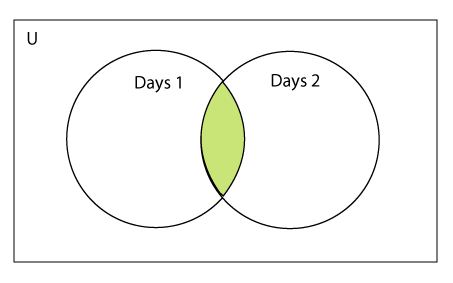
考虑以下示例。
**示例1:使用 &运算符 **
Days1 = {"Monday","Tuesday", "Wednesday", "Thursday"}
Days2 = {"Monday","Tuesday","Sunday", "Friday"}
print(Days1&Days2) #prints the intersection of the two sets
输出:
{'Monday', 'Tuesday'}
示例2:使用intersection()方法
set1 = {"Devansh","John", "David", "Martin"}
set2 = {"Steve", "Milan", "David", "Martin"}
print(set1.intersection(set2)) #prints the intersection of the two sets
输出结果:
{'Martin', 'David'}
示例3:
set1 = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7}
set2 = {1,2,20,32,5,9}
set3 = set1.intersection(set2)
print(set3)
输出:
{1,2,5}
同样地,与union函数相同,我们可以同时执行多个集合的交集操作,
例如:
程序
# Create three sets
set1 = {1, 2, 3}
set2 = {2, 3, 4}
set3 = {3, 4, 5}
# Find the common elements between the three sets
common_elements = set1.intersection(set2, set3)
# Print the common elements
print(common_elements)
输出:
{3}
intersection_update()方法
intersection_update()方法从原始集合中移除不在两个集合(如果指定了多个集合,则为所有集合)中出现的项。
intersection_update()方法与intersection()方法不同,因为它通过移除不需要的项来修改原始集合,而intersection()方法则返回一个新的集合。
考虑以下示例。
a = {"Devansh", "bob", "castle"}
b = {"castle", "dude", "emyway"}
c = {"fuson", "gaurav", "castle"}
a.intersection_update(b, c)
print(a)
输出:
{'castle'}
两个集合之间的差集
两个集合的差异可以通过使用减法 (-) 运算符或 intersection() 方法来计算。假设有两个集合 A 和 B,差异是 A-B,表示得到的结果集将包含 A 中不在集合 B 中的元素。
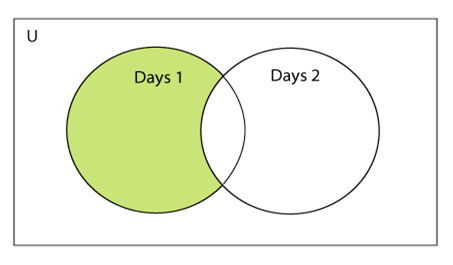
Days1 = {"Monday", "Tuesday", "Wednesday", "Thursday"}
Days2 = {"Monday", "Tuesday", "Sunday"}
print(Days1-Days2) #{"Wednesday", "Thursday" will be printed}
输出:
{'Thursday', 'Wednesday'}
例子2:使用difference()方法
Days1 = {"Monday", "Tuesday", "Wednesday", "Thursday"}
Days2 = {"Monday", "Tuesday", "Sunday"}
print(Days1.difference(Days2)) # prints the difference of the two sets Days1 and Days2
输出:
{'Thursday', 'Wednesday'}
两个集合的对称差
在Python中,集合set1和set2的对称差是指出现在一个集合中或另一个集合中但不同时出现在两个集合中的元素的集合。换句话说,它是set1和set2中的元素,但不是它们的交集。
可以使用Python的symmetric_difference()方法来计算两个集合的对称差。该方法返回一个新的集合,其中包含两个集合中任意一个但不同时出现的所有元素。考虑以下示例:
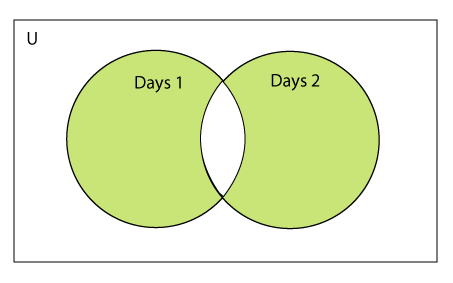
例子 – 1:使用^操作符
a = {1,2,3,4,5,6}
b = {1,2,9,8,10}
c = a^b
print(c)
输出:
{3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10}
例子 – 2:使用 symmetric_difference() 方法
a = {1,2,3,4,5,6}
b = {1,2,9,8,10}
c = a.symmetric_difference(b)
print(c)
输出:
{3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10}
集合比较
在Python中,您可以比较集合以检查它们是否相等,一个集合是否为另一个集合的子集或超集,或者两个集合是否有共同的元素。
以下是Python中可用的集合比较运算符:
==:检查两个集合是否具有相同的元素,无论其顺序如何。!=:检查两个集合是否不相等。<:检查左侧集合是否为右侧集合的真子集(即左侧集合中的所有元素也在右侧集合中,但是右侧集合还有额外的元素)。<=:检查左侧集合是否为右侧集合的子集(即左侧集合中的所有元素也在右侧集合中)。>:检查左侧集合是否为右侧集合的真超集(即右侧集合中的所有元素也在左侧集合中,但是左侧集合还有额外的元素)。>=:检查左侧集合是否为右侧集合的超集(即右侧集合中的所有元素也在左侧集合中)。考虑以下示例。
Days1 = {"Monday", "Tuesday", "Wednesday", "Thursday"}
Days2 = {"Monday", "Tuesday"}
Days3 = {"Monday", "Tuesday", "Friday"}
#Days1 is the superset of Days2 hence it will print true.
print (Days1>Days2)
#prints false since Days1 is not the subset of Days2
print (Days1
输出:
True
False
False
冻结集合
在Python中,冻结集合是内置集合数据类型的不可变版本。它类似于集合,但是一旦创建冻结集合,其内容就不能更改。
冻结集合对象是无序的唯一元素集合,就像集合一样。除了无法修改它们之外,它们可以像集合一样使用。由于它们是不可变的,冻结集合对象可以用作其他集合的元素或字典键,而标准集合则不行。
使用冻结集合对象的主要优点之一是它们是可哈希的,这意味着它们可以用作字典的键或其他集合的元素。它们的内容不会改变,因此它们的哈希值保持不变。标准集合不可哈希,因为它们可以被修改,所以它们的哈希值可以改变。
冻结集合对象支持许多相同操作,如并集、交集、差集和对称差集。它们还支持不修改冻结集合的操作,如len()、min()、max()和in。
考虑以下示例来创建冻结集合。
Frozenset = frozenset([1,2,3,4,5])
print(type(Frozenset))
print("\nprinting the content of frozen set...")
for i in Frozenset:
print(i);
Frozenset.add(6) #gives an error since we cannot change the content of Frozenset after creation
输出:
<class 'frozenset'>
printing the content of frozen set...
1
2
3
4
5
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "set.py", line 6, in <module>
Frozenset.add(6) #gives an error since we can change the content of Frozenset after creation
AttributeError: 'frozenset' object has no attribute 'add'
字典的不可变集合
如果我们将字典作为序列传递给frozenset()方法,它将仅获取字典的键并返回一个包含字典键作为元素的不可变集合。
考虑以下例子。
Dictionary = {"Name":"John", "Country":"USA", "ID":101}
print(type(Dictionary))
Frozenset = frozenset(Dictionary); #Frozenset will contain the keys of the dictionary
print(type(Frozenset))
for i in Frozenset:
print(i)
输出:
<class 'dict'>
<class 'frozenset'>
Name
Country
ID
设置编程示例
示例 – 1: 编写一个程序从集合中移除给定的数字。
my_set = {1,2,3,4,5,6,12,24}
n = int(input("Enter the number you want to remove"))
my_set.discard(n)
print("After Removing:",my_set)
输出:
Enter the number you want to remove:12
After Removing: {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 24}
示例 – 2: 编写一个程序将多个元素添加到集合中。
set1 = set([1,2,4,"John","CS"])
set1.update(["Apple","Mango","Grapes"])
print(set1)
输出:
{1, 2, 4, 'Apple', 'John', 'CS', 'Mango', 'Grapes'}
示例 – 3: 编写一个程序来找到两个集合之间的并集。
set1 = set(["Peter","Joseph", 65,59,96])
set2 = set(["Peter",1,2,"Joseph"])
set3 = set1.union(set2)
print(set3)
输出:
{96, 65, 2, 'Joseph', 1, 'Peter', 59}
示例- 4: 编写一个程序来找到两个集合之间的交集。
set1 = {23,44,56,67,90,45,"Javatpoint"}
set2 = {13,23,56,76,"Sachin"}
set3 = set1.intersection(set2)
print(set3)
输出:
{56, 23}
示例 – 5: 编写程序将元素添加到frozenset中。
set1 = {23,44,56,67,90,45,"Javatpoint"}
set2 = {13,23,56,76,"Sachin"}
set3 = set1.intersection(set2)
print(set3)
输出:
TypeError: 'frozenset' object does not support item assignment
上面的代码出现错误,因为frozensets是不可变的,创建后不能更改。
示例-6: 编写程序以查找issuperset,issubset和superset。
set1 = set(["Peter","James","Camroon","Ricky","Donald"])
set2 = set(["Camroon","Washington","Peter"])
set3 = set(["Peter"])
issubset = set1 >= set2
print(issubset)
issuperset = set1 <= set2
print(issuperset)
issubset = set3 <= set2
print(issubset)
issuperset = set2 >= set3
print(issuperset)
输出:
False
False
True
True
Python内置集合方法
Python包含以下用于集合的方法。
| SN | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | add(item) | 将一个项添加到集合中。如果该项已经存在于集合中,则不会产生任何影响。 |
| 2 | clear() | 从集合中删除所有项。 |
| 3 | copy() | 返回集合的浅拷贝。 |
| 4 | difference_update(….) | 通过从指定的集合中删除所有也存在于此集合中的项,修改该集合。 |
| 5 | discard(item) | 从集合中移除指定的项。 |
| 6 | intersection() | 返回一个新集合,其中只包含两个集合(如果指定了两个以上的集合,则为所有集合)共有的元素。 |
| 7 | intersection_update(….) | 从原始集合中移除那些在另一个或多个集合中不存在的项。 |
| 8 | Isdisjoint(….) | 如果两个集合没有交集,则返回True。 |
| 9 | Issubset(….) | 判断另一个集合是否包含该集合。 |
| 10 | Issuperset(….) | 判断该集合是否包含另一个集合。 |
| 11 | pop() | 移除并返回集合中的任意一个元素(最后一个元素)。如果集合为空,则引发KeyError。 |
| 12 | remove(item) | 从集合中移除一个元素;它必须是集合的成员。如果元素不是集合的成员,则引发KeyError。 |
| 13 | symmetric_difference(….) | 返回一个新集合,其中包含了当前集合与另一个集合(如果指定了另一个集合)的对称差集。 |
| 14 | symmetric_difference_update(….) | 使用当前集合与另一个集合(如果指定了另一个集合)的对称差集来更新集合。 |
| 15 | union(….) | 将多个集合的所有元素返回为一个新集合(即两个集合中的所有元素)。 |
| 16 | update() | 使用自身与其他集合的并集来更新集合。 |
 极客笔记
极客笔记