Matplotlib 绘制多个图
Python提供了一个强大的库,名为Matplotlib,它可以创建图形和图表的可视化表示。这个库的许多特性之一是能够在一个图中绘制多个图,这对比较不同数据集或可视化多个变量之间的关系非常有用。我们将探索Matplotlib中的内置方法’subplots()’,它用于绘制多个图。
在Matplotlib中绘制多个图的Python程序
在直接进入程序之前,让我们先熟悉一下Matplotlib的’subplots()’方法。
‘subplots()’方法
通过一次调用’subplots()’方法,我们可以在一个图中创建一个或多个子图。它可以合适地控制图形,并允许我们自定义它们的布局和外观。
语法
subplots(numOfrows, numOfcols)
在这里, ‘numOfrows’ 和 ‘numOfcols’ 分别指定了网格的行数和列数。
然而,根据需要,我们还可以添加一些其他的属性。
示例1
下面是一个例子,我们将绘制正弦和余弦函数的两个子图。
方法
- 首先,我们导入matplotlib和numpy库。matplotlib将用于对numpy生成的数据进行可视化。
-
使用NumPy的内置方法’linspace()’生成一个从0到10之间均匀间隔的100个值的数组。然后,分别计算x数组中每个元素的正弦和余弦值,并将它们存储在y1和y2中。
-
现在,使用’subplots()’方法创建两个垂直排列的子图。这个方法将返回一个名为’fig’的图像对象和一个包含子图轴’ax1’和’ax2’的元组。在这里,’figsize’设置了图像的大小。
-
在第一个子图ax1中,将x值与y1值进行绘制。
-
类似地,在第二个子图ax2中,将x值与y2值进行绘制。
-
使用’tight_layout()’方法调整子图之间的间距,以防止重叠。
-
最后,显示出图并退出。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# generating some random data for plotting
val = np.linspace(0, 10, 100)
pl1 = np.sin(val)
pl2 = np.cos(val)
# Creating subplots
fig, (axs1, axs2) = plt.subplots(2, 1, figsize = (6, 4))
# Plotting of the first subplot
axs1.plot(val, pl1, 'r', label = 'Sin')
axs1.set_xlabel('Axis-X')
axs1.set_ylabel('Axis-Y')
axs1.legend()
# Plotting of the second subplot
axs2.plot(val, pl2, 'b', label = 'Cos')
axs2.set_xlabel('Axis-X')
axs2.set_ylabel('Axis-Y')
axs2.legend()
# for adjusting the space between subplots
plt.tight_layout()
# to display the plots
plt.show()
输出
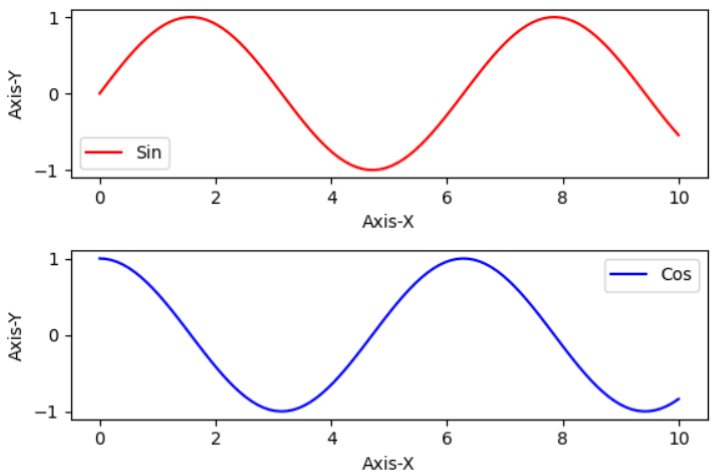
示例2
在下面的示例中,我们将更改前一个示例的代码,添加一个更多的正切函数的绘图。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# generating some random data for plotting
val = np.linspace(0, 10, 100)
pl1 = np.sin(val)
pl2 = np.cos(val)
pl3 = np.tan(val)
# Creating the subplots using above data
fig, axs = plt.subplots(2, 2, figsize = (8, 6))
# Plotting of the first subplot
axs[0, 0].plot(val, pl1, 'r', label = 'Sin')
axs[0, 0].set_xlabel('Axis-X')
axs[0, 0].set_ylabel('Axis-Y')
axs[0, 0].legend()
# To plot on the second subplot
axs[0, 1].plot(val, pl2, 'b', label = 'Cos')
axs[0, 1].set_xlabel('Axis-X')
axs[0, 1].set_ylabel('Axis-Y')
axs[0, 1].legend()
# Plotting of the third subplot
axs[1, 0].plot(val, pl3, 'g', label = 'Tan')
axs[1, 0].set_xlabel('Axis-X')
axs[1, 0].set_ylabel('Axis-Y')
axs[1, 0].legend()
# To remove the empty subplot
fig.delaxes(axs[1, 1])
# for adjusting the space between subplots
plt.tight_layout()
# Displaying all plots
plt.show()
输出
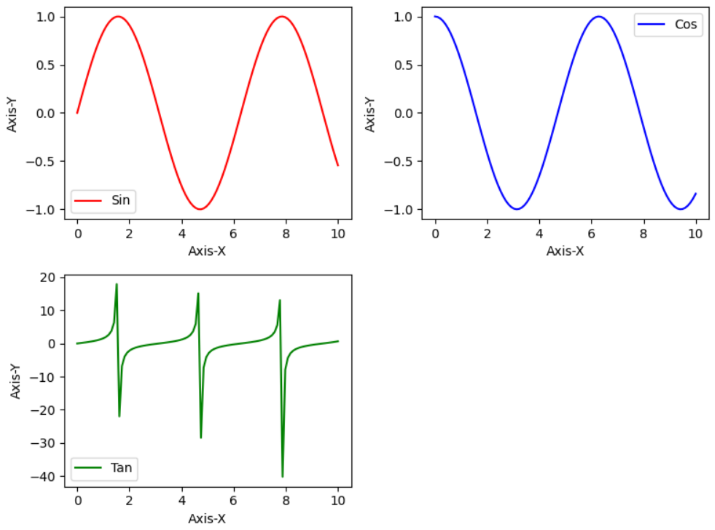
结论
我们通过介绍Matplotlib及其内置方法’subplots()’来开始本文。在接下来的部分中,我们详细解释了这个方法。同时,我们还讨论了两个示例程序,展示了’subplots()’方法在绘制多个图形中的应用。
 极客笔记
极客笔记