Laravel 关系
Eloquent关系是Laravel中一个非常重要的功能,它允许你以一种非常简单的格式关联表格。
一对一关系
一对一关系提供不同表的列之间的一对一关系。例如,每个用户都与一篇或多篇文章相关联,但在这种关系中,我们将检索用户的一篇文章。要定义关系,我们首先需要在User模型中定义post()方法。在post()方法中,我们需要实现返回结果的hasOne()方法。
让我们通过一个例子来理解一对一的关系。
- 首先,我们在现有表中添加名为posts的新列(user_id)。在这里,user_id是外键。
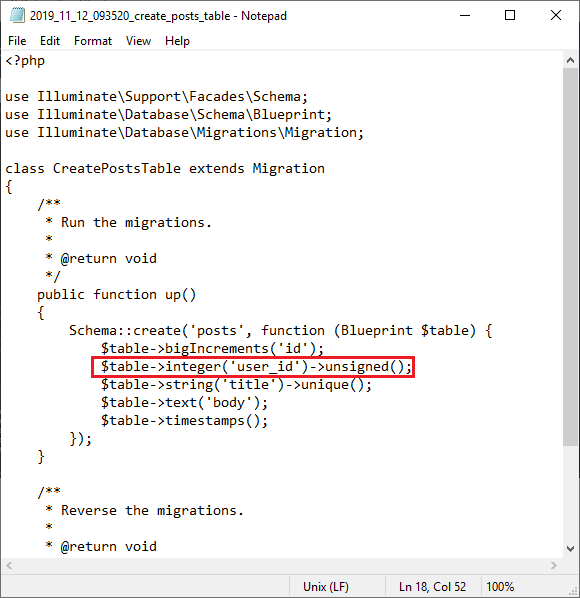
- 使用下面的命令将上述更改迁移到数据库中:php artisan migrate。
- 迁移后,posts表的结构如下图所示:
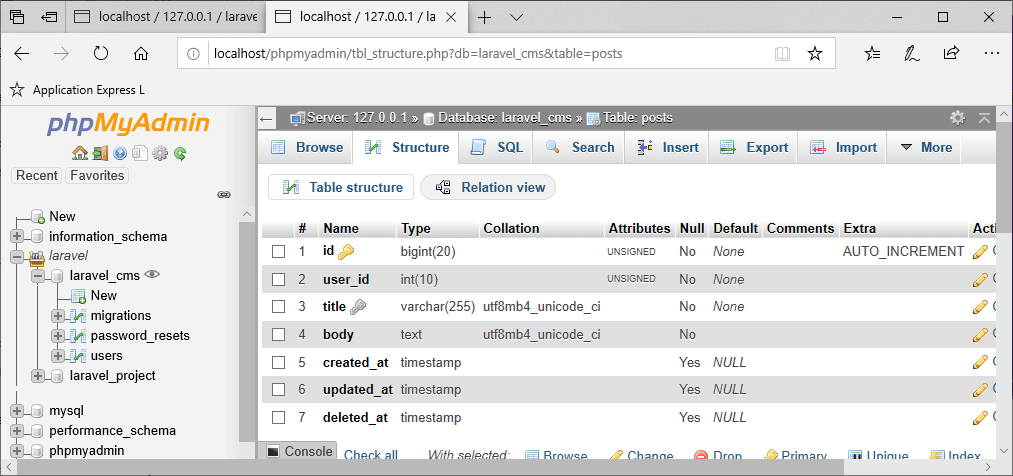
上面的截图显示user_id列成功添加。
- 打开User.php文件并将以下代码添加到User.php文件中。
public function post()
{
return $this->hasOne('App\Post');
}
在上面的代码中,我们实现了包含单个参数的hasOne()方法,即相关模型的名称。默认情况下,Post将user_id视为外键。post()方法搜索posts表(我们提到过命名空间App/ post),并查找列user_id。我们可以通过提供一个外键作为第二个参数来重写这个约定。它可以重写为:
return $this->hasOne(‘App\Post’,foreign_key)
- 现在,我们将在web.php文件中添加路由。
<?php
use App\User;
Route::get('/user',function()
{
return User::find(1)->post;
}
);
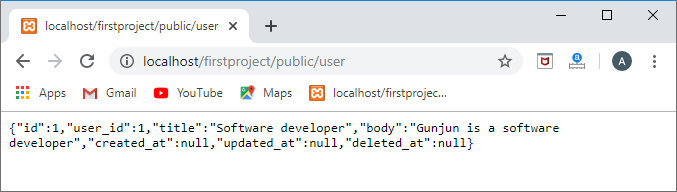
上面的代码是找到id为1的用户,然后实现帖子,以找到user_id等于1的用户的帖子。
输出
逆关系
逆关系是指一对一关系的逆关系。在上面的代码中,我们检索了属于特定用户的帖子。现在,我们根据帖子检索用户信息。让我们通过一个例子来理解这一点。
- 首先,我们在web.php文件中创建路由。
<?php
use App\Post;
Route::get('/post/user',function()
{
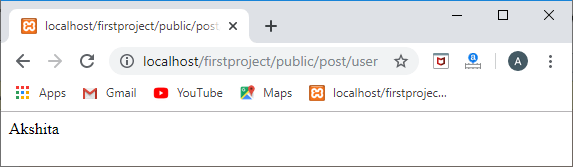
return Post::find(1)->user->name;
});
- 打开我们之前创建的Post.php文件(model)。
<?php
namespace App;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\SoftDeletes;
class Post extends Model
{
use SoftDeletes;
protected table='posts';
protectedprimaryKey='id';
protected fillable=
[
'title',
'body'
];
protecteddates=['deleted_at'];
public function user()
{
return $this->belongsTo('App\User');
}
}
输出
一对多关系
Laravel还提供了一对多关系。
- 首先,我们定义一个路由,用来找出单个用户的所有文章。
Route::get('/posts',function(){
user=User::find(1);
foreach(user->posts as post){
echopost->title."<br>";
}
});
- 将以下代码添加到User.php(model)文件中。
public function posts()
{
return $this->hasMany('App\Post','user_id');
}
输出
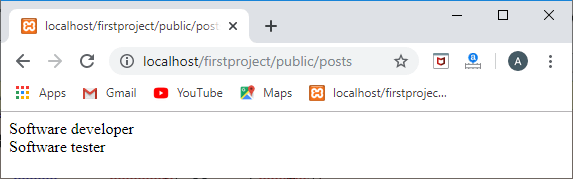
多对多关系
多对多关系比一对一关系和一对多关系更复杂。为了定义多对多关系,我们需要创建一个数据透视表。透视表基本上是一个关联两个表的查找表。例如,一个用户可能有不同的角色,这些角色可以被其他用户共享,例如许多用户可以具有“Admin”的角色。要定义用户和角色之间的关系,需要创建3个表:user、roles和role_user。在我们的数据库中,已经创建了user表;我们需要创建两个表,即roles表和pivot表(roles_user)。
- 首先,我们创建Role模型。我们使用以下命令来创建模型:
php artisan make:model Role -m
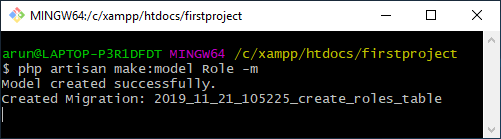
上面的屏幕显示已经创建了roles表。create_roles_table.php已经在database/migration目录下创建。该文件的结构如下所示:
<?php
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Schema;
use Illuminate\Database\Schema\Blueprint;
use Illuminate\Database\Migrations\Migration;
class CreateRolesTable extends Migration
{
/**
* Run the migrations.
*
* @return void
*/
public function up()
{
Schema::create('roles', function (Blueprint table) {table->bigIncrements('id');
table->string('name');table->timestamps();
});
}
/**
* Reverse the migrations.
*
* @return void
*/
public function down()
{
Schema::dropIfExists('roles');
}
}
在上面的代码中,我们添加了名为name的新列。name列定义了用户角色的名称。
- 现在,我们有两个表,roles表和users表。为了关联这两个表,我们需要创建一个数据透视表——roles_user表。
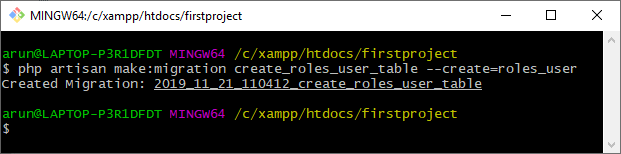
上面的截图显示了roles_user表已经创建。create_roles_user_table的结构如下:
<?php
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Schema;
use Illuminate\Database\Schema\Blueprint;
use Illuminate\Database\Migrations\Migration;
class CreateRolesUserTable extends Migration
{
/**
* Run the migrations.
*
* @return void
*/
public function up()
{
Schema::create('roles_user', function (Blueprint table) {table->bigIncrements('id');
table->integer('user_id');table->integer('role_id');
$table->timestamps();
});
}
/**
* Reverse the migrations.
*
* @return void
*/
public function down()
{
Schema::dropIfExists('roles_user');
}
}
在上面的代码中,我们添加了两个新列,user_id和role_id。
- 使用下面给出的命令迁移上述所有更改:
php artisan migrate
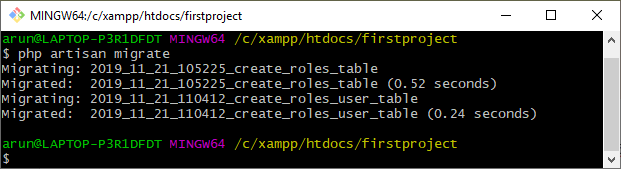
- 下面的屏幕显示了创建的所有3个表,即roles、roles_user和users.
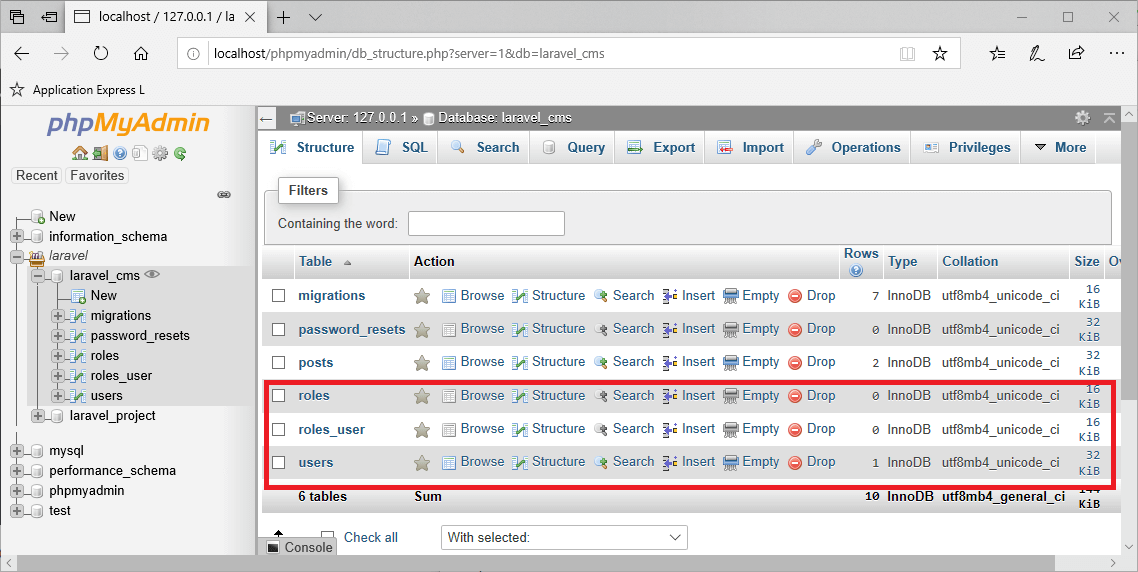
roles表中的数据:
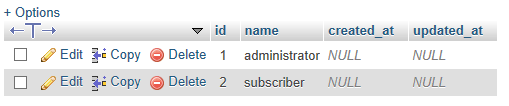
users表中的数据:
roles_user表中的数据:
- 现在,我们定义路由。
web.php
Route::get('/roles/{id}',function(id){user=User::find(id);
foreach(user->role as role)
{ returnrole->name;
}
});
- 我们在User.php文件中添加以下代码,关联这两个表。
public function role()
{
return $this->belongsToMany('App\Role','roles_user');
}
在上面的代码中,belongsToMany()方法包含两个参数,App\Role是使用Role模型的命名空间,roles_user是关联两个表的pivot表的名称。belongsToMany()方法也可以这样写:
belongsToMany(‘App\Role’,’roles_user’,’user_id’,’role_id’);
上面这行代码还包含两个参数:user_id和role_id。user_id是users表的外键,role_id是roles表的外键。
输出
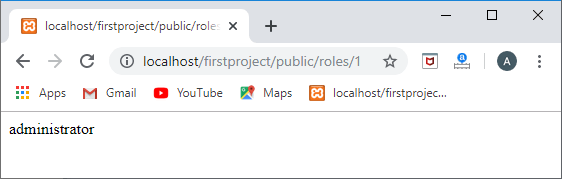
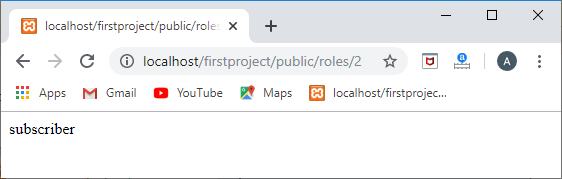
访问中间数据表
在多对多关系中,我们需要创建中间表。现在,我们来看看如何检索这个数据透视表。
<?php
Use App\User;
Route::get('/pivot',function(){
user=User::find(1);
foreach(user->role as role)
{ returnrole->pivot;
}
});
在上面的模型中,我们检索id等于1的用户。然后,使用foreach循环,我们检索在pivot属性中分配的角色模型.
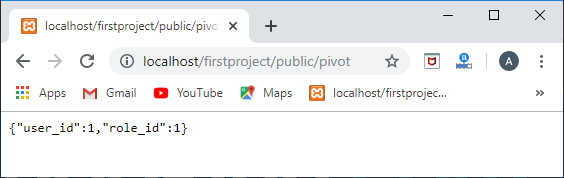
如果我们想从数据透视表中检索特定的列,
public function role()
{
return $this->belongsToMany('App\Role','roles_user')->withPivot('created_at');
}
web.php
Route::get('/pivot',function(){
user=User::find(1);
foreach(user->role as role)
{ returnrole->pivot->created_at;
}
});
输出
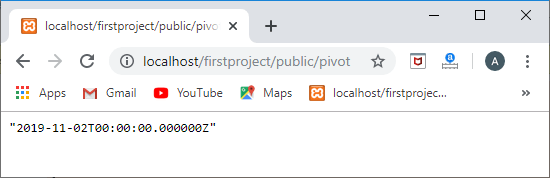
有许多通过
“有许多通过”关系提供了一种方便的方式来访问远程或中间关系。例如,我们有三个表:users、posts和country表。现在,我们想通过User模型找到属于该国家的帖子。
让我们通过一个例子来理解。
- country表在数据库中不可用。我们首先使用数据库迁移创建country模型.
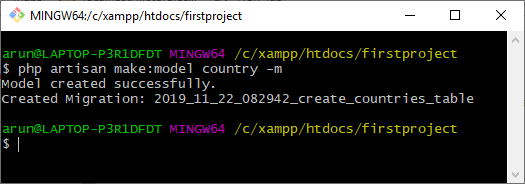
- 在country表中添加
name列。
<?php
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Schema;
use Illuminate\Database\Schema\Blueprint;
use Illuminate\Database\Migrations\Migration;
class CreateCountriesTable extends Migration
{
/**
* Run the migrations.
*
* @return void
*/
public function up()
{
Schema::create('countries', function (Blueprint table) {table->bigIncrements('id');
table->string('name');table->timestamps();
});
}
/**
* Reverse the migrations.
*
* @return void
*/
public function down()
{
Schema::dropIfExists('countries');
}
}
- 使用下面的命令迁移上述更改:
php artisan migrate - 现在,我们在users表中添加新列
country_id。使用下面给出的命令:
php artisan make:migration add_new_column_column_id -table=users; - —执行上述命令后,在“database/migrations”目录下创建add_new_column_column_id文件。
<?php
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Schema;
use Illuminate\Database\Schema\Blueprint;
use Illuminate\Database\Migrations\Migration;
class AddNewColumnColumnId extends Migration
{
/**
* Run the migrations.
*
* @return void
*/
public function up()
{
Schema::table('users', function (Blueprint table) {table->integer('country_id')->unsigned;
});
}
/**
* Reverse the migrations.
*
* @return void
*/
public function down()
{
Schema::table('users', function (Blueprint table) {table->dropColumn('country_id');
});
}
}
在上面的代码中,我们在users表中添加了一列。
要将上述更改迁移到数据库中,
php artisan migrate
- 打开country.php(model)文件。我们将使用country模型提取特定country的帖子。
country.php
<?php
namespace App;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;
class country extends Model
{
public function posts(){
return $this->hasManyThrough('App\Post','App\User','country_id','user_id');
}
}
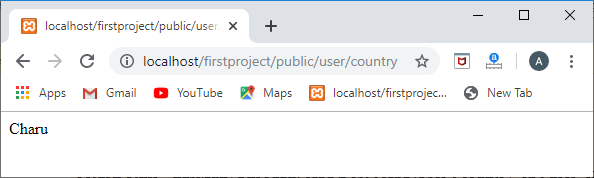
- .现在,我们添加一个路由,用于提取特定country的帖子
Route::get('/user/country',function()
{
country=country::find(1); foreach(country->posts as post) { returnpost->title;
}
});
输出
多态的关系
一对多(多态)
多态关系类似于一对多关系。当一个模型属于一个关联上的多个模型类型时,称为一对一多态关系。例如,我们有三个表,posts、users和photo表,其中photo表表示用户和posts表的多态关系。
让我们通过一个例子来理解这种关系。
- 在前一个主题中,我们已经创建了users和posts表。现在,我们创建一个照片表.
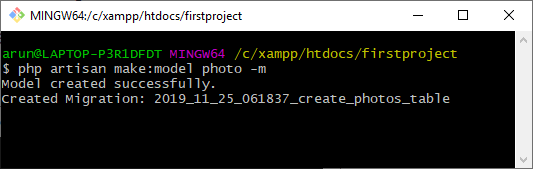
打开migrations文件夹中创建的create_photos_table.php文件.
<?php
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Schema;
use Illuminate\Database\Schema\Blueprint;
use Illuminate\Database\Migrations\Migration;
class CreatePhotosTable extends Migration
{
/**
* Run the migrations.
*
* @return void
*/
public function up()
{
Schema::create('photos', function (Blueprint table) {table->bigIncrements('id');
table->string('path');table->integer('imageable_id');
table->string('imageable_type');table->timestamps();
});
}
/**
* Reverse the migrations.
*
* @return void
*/
public function down()
{
Schema::dropIfExists('photos');
}
}
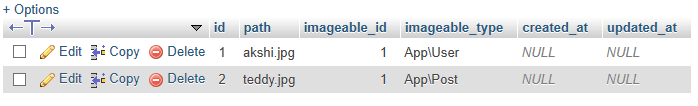
在上面的代码中,我们添加了三列,path, imageable_id和imageable_type。路径决定了图像的路径,imageable_id是用户或帖子的id值,而imageable_type是模型的类名。
- 我们将从之前创建的posts表中删除user_id列。
- 查看数据库表。
posts表中的数据

users表可用数据:

photo表中的可用数据:
- 打开Photo模型文件。
<?php
namespace App;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;
class photo extends Model
{
//
public function imageable()
{
return $this->morphTo();
}}
- 在User模型文件中添加以下代码。
public function photos()
{
return $this->morphMany('App\Photo','imageable');
}
- 在Post模型文件中添加以下代码。
public function photos()
{
return $this->morphMany('App\Photo','imageable');
}
- 现在,我们将为用户和帖子创建路由。
// Route for the users.
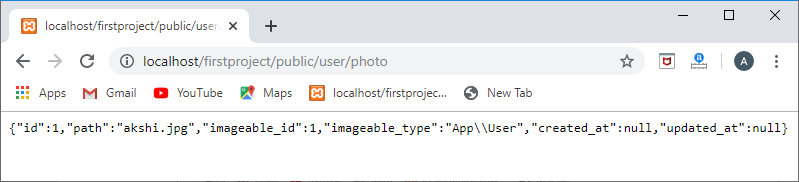
Route::get('/user/photo',function(){
user=User::find(1);
foreach(user->photos as photo)
{ returnphoto;
}
});
// Route defined for the posts.
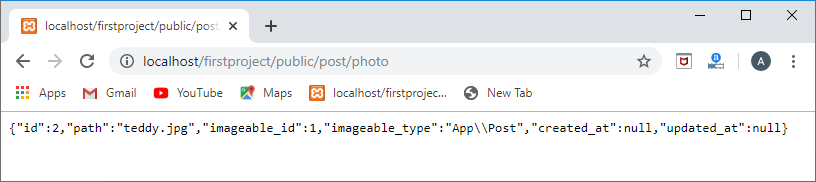
Route::get('/post/photo',function(){
post=Post::find(1);
foreach(post->photos as photo)
{ returnphoto;
}
});
输出
一对多(多态)关系的逆
在本主题中,我们将执行一对多多态关系的逆操作。到目前为止,我们已经找到了用户和帖子的图像,现在我们找到了图像的所有者。
让我们通过一个例子来理解。
我们需要在web.php文件中创建路由。
Route::get('/photo/{id}', function(id)
{photo=Photo::findOrFail(id); returnphoto->imageable;
});
在上面的代码中,Photo::findOrFail($id)方法确定给定id的照片是否存在。如果存在,则通过$photo->imageable语句返回图像的详细信息。
输出
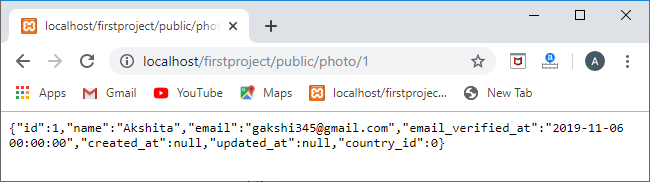
上面的输出显示了图像的细节。
多对多多态关系
在多对多多态关系中,目标模型由多个模型共享的唯一记录组成。例如,标签表共享视频和帖子表之间的多态关系。标签表由标签的唯一列表组成,这些标签由表、视频和帖子表共享。
让我们通过一个例子来理解。
- 首先,我们使用数据库迁移创建模型,命名为Audio, Tag,和Taggable。
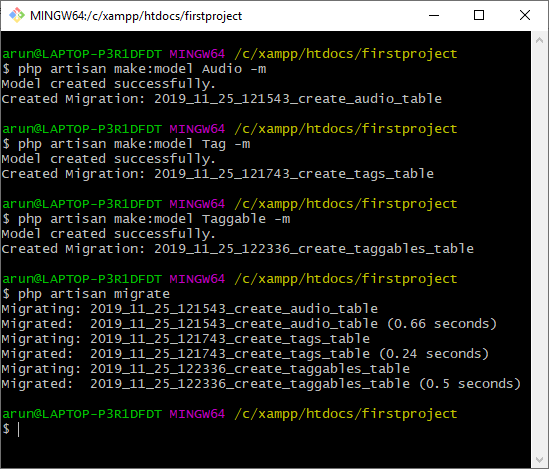
- 创建模型后,我们将编辑它们的迁移文件。
打开名为“create_audio_table”的音频表迁移文件。
<?php
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Schema;
use Illuminate\Database\Schema\Blueprint;
use Illuminate\Database\Migrations\Migration;
class CreateAudioTable extends Migration
{
/**
* Run the migrations.
*
* @return void
*/
public function up()
{
Schema::create('audio', function (Blueprint table) {table->bigIncrements('id');
table->string('name');table->timestamps();
});
}
/**
* Reverse the migrations.
*
* @return void
*/
public function down()
{
Schema::dropIfExists('audio');
}
}
在上面的代码中,我们使用命令$table->string(‘name’);在音频表中创建了name列。
打开名为create_tag_table 的Tag模型迁移文件。
<?php
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Schema;
use Illuminate\Database\Schema\Blueprint;
use Illuminate\Database\Migrations\Migration;
class CreateTagsTable extends Migration
{
/**
* Run the migrations.
*
* @return void
*/
public function up()
{
Schema::create('tags', function (Blueprint table) {table->bigIncrements('id');
table->string('name');table->timestamps();
});
}
/**
* Reverse the migrations.
*
* @return void
*/
public function down()
{
Schema::dropIfExists('tags');
}
}
在上面的代码中,我们使用命令$table->string(‘name’);在tags表中创建了name列。
打开名为“create_taggables_table”的Taggable模型迁移文件。
<?php
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Schema;
use Illuminate\Database\Schema\Blueprint;
use Illuminate\Database\Migrations\Migration;
class CreateTaggablesTable extends Migration
{
/**
* Run the migrations.
*
* @return void
*/
public function up()
{
Schema::create('taggables', function (Blueprint table) {table->bigIncrements('id');
table->integer('tag_id');table->integer('taggable_id');
table->string('taggable_type');table->timestamps();
});
}
/**
* Reverse the migrations.
*
* @return void
*/
public function down()
{
Schema::dropIfExists('taggables');
}}
在上面的代码中,我们在taggables表中添加了三列,即tag_id、taggable_id和taggable_type。其中tag_id表示标签表的id, taggable id表示模型表的id, taggable type表示类的名称。
- 要迁移上述更改,我们使用下面给出的命令:
php artisan migrate - 查看数据库表:
audio表中的数据:

post表提供的数据:

tags表中的数据:
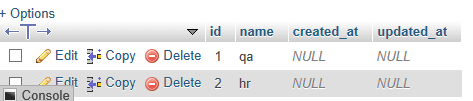
taggables表中的数据:
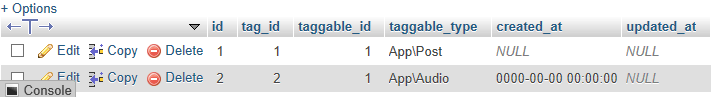
- 现在我们在模型上定义关系。
Audio.php
<?php
namespace App;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;
class Audio extends Model
{
// get all the tags from the audio.
public function tags()
{
return $this->morphToMany('App\Tag','taggable');
}
}
Post.php
namespace App;
use App\Photo;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\SoftDeletes;
class Post extends Model
{
// get all the tags from this post.
public function tags()
{
return $this->morphToMany('App\Tag','taggable');
}
}
- 现在我们定义路由。
use App\Post;
use App\Audio;
// Route for getting the tags from the Post model.
Route::get('/post/tags',function()
{
post=Post::find(1); foreach(post->tags as tag) { returntag->name;
}});
//Route for getting the tags from the Audio model.
Route::get('/audio/tags',function()
{
audio=Audio::find(1); foreach(audio->tags as tag) { returntag->name;
}});
输出
当访问post的路由时,输出将是:
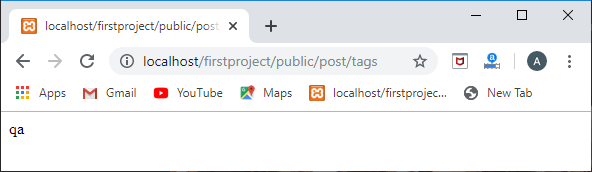
当访问音频的路由时,输出将是:
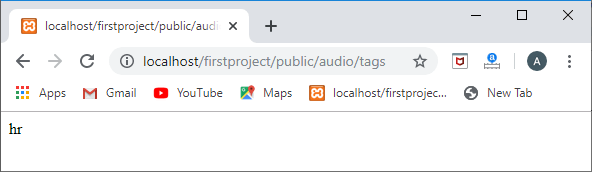
多对多(多态)关系的逆
在多对多多态关系中,我们找到了属于post和audio模型的标签。但是,在多对多(polymorphic)的反向关系中,我们将找到属于特定标签的所有帖子和音频。
让我们通过一个例子来理解。
- 首先,我们在标签模型中定义该方法。
Tag.php
<?php
namespace App;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;
class Tag extends Model
{
// get all the posts from the tag.
public function posts()
{
return this->morphedByMany('App\Post','taggable'); }
// get all the audios from the tag.
public function audios() { returnthis->morphedByMany('App\Audio','taggable');
}
}
在上面的代码中,我们定义了两个方法,posts()和audios()。在posts()方法中,获取属于指定标签的所有文章。在audios()方法中,我们获取属于指定标签的所有音频。
- 现在,我们定义路由。
use App\Tag;
// Route for getting all the posts of a tag.
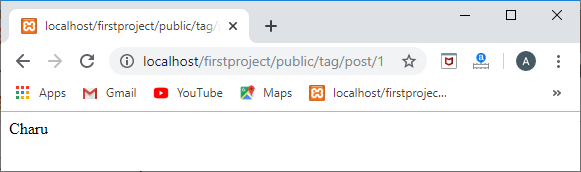
Route::get('/tag/post/{id}',function(id){tag=Tag::find(id);
foreach(tag->posts as post)
{ returnpost->title;
}
});
// Route for getting all the audios of a tag.
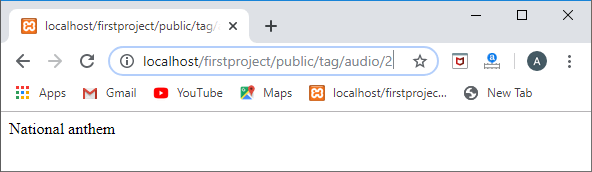
Route::get('/tag/audio/{id}',function(id){tag=Tag::find(id);
foreach(tag->audios as audio)
{ returnaudio->name;
}
});
输出
 极客笔记
极客笔记