C++ 广度优先搜索BFS代码
BFS是什么
广度优先搜索(BFS)是一种用于遍历或搜索图的算法。它从给定的顶点开始,并在遍历下一层顶点之前探索所有相邻的顶点。BFS用于在图中找到两个顶点之间的最短路径,或者找到图的连通分量。它还用于拓扑排序,即有向无环图(DAG)中顶点的线性顺序,对于每条从顶点u到顶点v的边,u在排序中位于v之前。
在本教程中,我们将学习如何在C++中实现BFS。我们将首先了解BFS的概念及其时间复杂度。然后,我们将看到如何使用邻接表表示图,并使用BFS算法遍历图。
BFS的概念
BFS是一种用于遍历或搜索图的算法。它从给定的顶点开始,并在遍历下一层顶点之前探索所有相邻的顶点。该算法维护一个待访问的顶点队列,从源顶点开始。每一步,它从队列中移除一个顶点,并将其未访问的相邻顶点加入队列。这个过程一直持续到队列中没有更多的顶点需要访问为止。
BFS算法的时间复杂度为O(V + E),其中V是顶点数,E是图中的边数。这使得BFS在边数接近顶点数的稠密图中更适用。
在C++中表示一个图
有几种方法可以在C++中表示图。一种常见的表示方法是使用邻接表,它是与给定顶点相邻的所有顶点的列表。例如,考虑以下具有5个顶点的图:+
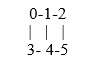
我们可以使用邻接表表示这个图,如下所示:
vector> adj_list = {
{1, 3}, // vertex 0 has neighbors 1 and 3
{0, 4}, // vertex 1 has neighbors 0 and 4
{1, 5}, // vertex 2 has neighbors 1 and 5
{0, 4}, // vertex 3 has neighbors 0 and 4
{1, 3, 5}, // vertex 4 has neighbors 1, 3, and 5
{2, 4} // vertex 5 has neighbors 2 and 4
};
这里,adj_list[i]是一个包含顶点i的邻居的向量。
在C++中实现BFS
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
// This function performs a BFS search on a graph represented as an adjacency list.
// The graph is assumed to be undirected.
//
// Parameters:
// - adj_list: a vector of vectors representing the adjacency list of the graph
// - start: the index of the starting vertex
// - target: the index of the target vertex (optional)
//
// Returns:
// - a vector of integers representing the BFS traversal order of the graph,
// starting from the start vertex
// - an empty vector if the target vertex is not found (when the target is specified)
vector bfs(const vector>& adj_list, int start, int target = -1)
{
int n = adj_list.size();
vector visited(n, false); // a boolean array to track visited vertices
vector order; // a vector to store the BFS traversal order
queue q; // a queue to hold the vertices to be visited
q.push(start); // add the starting vertex to the queue
visited[start] = true; // mark the starting vertex as visited
while (!q.empty())
{
int u = q.front(); // get the next vertex in the queue
q.pop(); // remove the vertex from the queue
order.push_back(u); // add the vertex to the traversal order
// add all the unvisited neighbors of u to the queue
for (int v : adj_list[u])
{
if (!visited[v])
{
q.push(v);
visited[v] = true;
}
}
}
if (target != -1 && !visited[target])
{
// the target vertex was not found, return an empty vector
return {};
}
return order;
}
int main()
{
// create an adjacency list for a graph with 5 vertices
vector> adj_list = {
{1, 2}, // vertex 0 has neighbors 1 and 2
{0, 3, 4}, // vertex 1 has neighbors 0, 3, and 4
{0, 4}, // vertex 2 has neighbors 0 and 4
{1, 4}, // vertex 3 has neighbors 1 and 4
{1, 2, 3} // vertex 4 has neighbors 1, 2, and 3
};
// perform a BFS search starting from vertex 0
vector order = bfs(adj_list, 0);
// print the traversal order
cout << "BFS traversal order: ";
for (int i : order)
{
cout << i << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
输出:
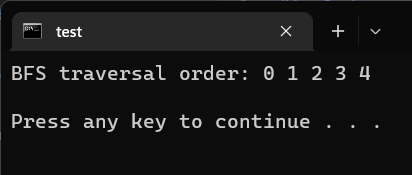
解释:
在这段代码中,我们首先定义了bfs()函数,它接受一个邻接表adj_list,一个起始顶点start和一个可选的目标顶点target。bfs()函数初始化一个boolean数组visited来跟踪访问过的顶点,还有一个vector order来存储BFS遍历顺序。它还创建了一个队列q来保存要访问的顶点。
然后,函数将起始顶点添加到队列中并标记为已访问。然后进入一个循环,直到队列为空为止。循环的每次迭代都会从队列中删除下一个顶点并将其添加到遍历顺序中。然后它将所有未访问的邻居添加到队列中并将它们标记为已访问。
最后,如果指定了目标顶点且未找到该顶点,则函数返回一个空向量。否则,它返回遍历顺序。
在main()函数中,我们创建了一个具有5个顶点的图的邻接表。然后,我们从顶点0开始执行BFS搜索,并将遍历顺序存储在order向量中。最后,我们将遍历顺序打印到控制台。
 极客笔记
极客笔记