在Python中建模Newton Raphson方法
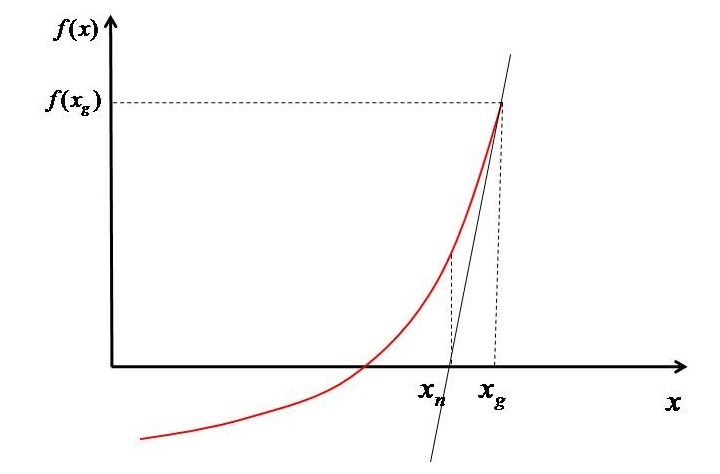
在本教程中,我将向您展示如何使用一种称为Newton Raphson方法的数值方法评估多项式或超越方程的根。这是一种迭代方法,我们从一个初始猜测(独立变量)开始,然后根据猜测评估𝑥的新值。该过程持续进行直到达到收敛。该方法通过下面的图示进行解释:
from pylab import *
只使用了一个模块,即pylab,因为它包含numpy。所以不需要单独导入它。
形成多项式及其导数函数,即𝑓(𝑥)和𝑓'(x)。
f=lambda x: x**2+4*x+3
dfdx=lambda x: 2*x+4
我使用了’lambda’,因为函数中只有一条语句。如果你愿意,你也可以使用’def’方法。
使用”linspace”函数创建一个名为”x”的数组。
# Array of x
x=linspace(-15,10,50)
现在,这一步是可选的。绘制函数时要考虑适当的定义域。我还会向您展示如何绘制切线,同时展示解的收敛情况。所以如果您对视觉效果感兴趣,可以按照这个步骤进行。
# Plotting the function
figure(1,dpi=150)
plot(x,f(x))
plot([-15,10],[0,0],'k--')
xlabel('x')
ylabel('f(x)')
假设𝑥的初始猜测用于开始第一次迭代。同时将误差(\left | x_{g}-x_{n} \right |)设置为某个大于收敛标准的值。在本文中,我将收敛标准设定为<10^{-5},但您可以根据所需的精度级别进行设置。同时将循环计数器设置为1。
# Initial Guess
xg=10
# Setting initial error and loop counter
error=1
count=1
在一个 “for” 循环内,使用上述的收敛准则解决方程(2)。同时,绘制误差和切线。切线绘制在名为 figure(1) 的图上,误差绘制在 figure(2) 上。此外,还对 x_{g} 和 f\left ( x_{g} \right ) 进行表格化,以显示不同的值。
# For printing x_g and f(x_g) at different steps
print(f"{'xg':^15}{'f(xg)':^15}")
print("===========================")
# Starting iterations
while error>1.E-5:
# Solving Eq. 1
xn=xg-f(xg)/dfdx(xg)
# Printing x_g and f(x_g)
print(f'{round(xg,5):^15}{round(f(xg),5):^15}')
# Plotting tangents
figure(1,dpi=300)
plot([xg,xn],[f(xg),0])
plot([xn,xn],[0,f(xn)],'--',label=f'xg={xg}')
legend(bbox_to_anchor=(1.01, 1),loc='upper left', borderaxespad=0)
# Evaluating error and plotting it
error=abs(xn-xg)
figure(2,dpi=300)
semilogy(count,error,'ko')
xlabel('Iteration count')
ylabel('Error')
# Setting up new value as guess for next step
xg=xn
# Incrementing the loop counter
count=count+1
# printing the final answer
print("===========================")
print("\nRoot ",round(xn,5))
show()
收敛后,打印根数。并展示图表。
在上述情况中,我选择了初始猜测为10。因此,程序输出将如下所示 –
xg f(xg)
======================================
10 143
4.04167 35.50174
1.10359 8.63228
-0.2871 1.93403
-0.85165 0.31871
-0.99042 0.01926
-0.99995 9e-05
-1.0 0.0
========================================
Root -1.0
错误图如下所示 –
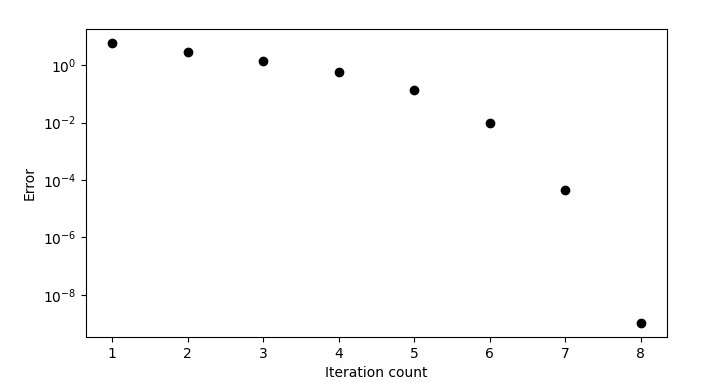
下面的图显示了具有切线的函数图。

所以对应于x_{g}=10,根为-1。对于第二个根,我们需要更改猜测值,让我们取-10。然后程序的输出将如下所示 –
xg f(xg)
===========================
-10 63
-6.0625 15.50391
-4.15433 3.64112
-3.30925 0.71415
-3.03652 0.07438
-3.00064 0.00129
-3.0 0.0
===========================
Root -3.0
现在,错误图将如下所示−
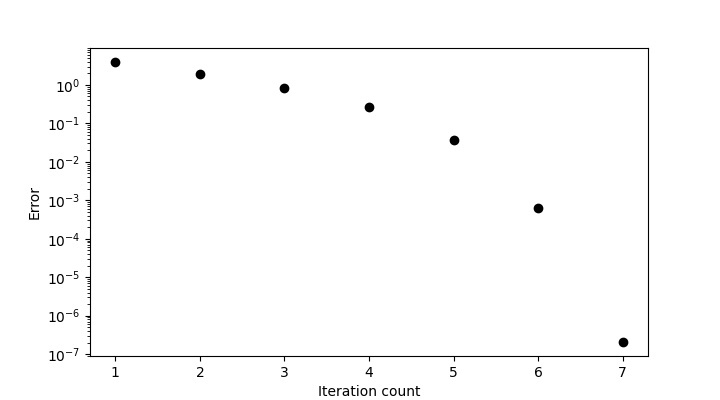
而且绘图函数将会是这样的 –
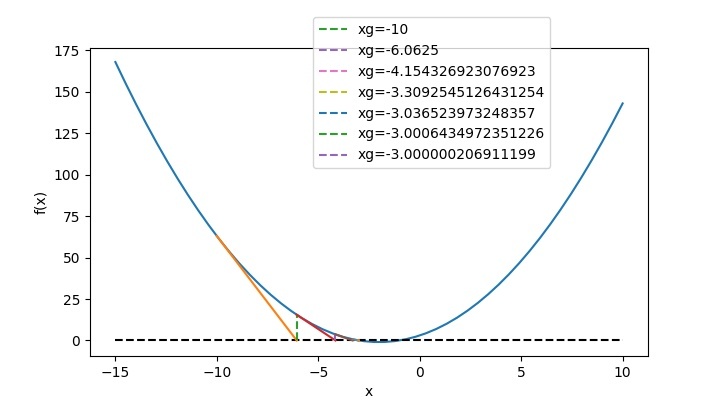
因此,对应于x_{g}=-10,根为−3。
完整的Python代码
完整代码如下−
# Importing module
from pylab import *
# Funciton for f(x) and f'(x)
f = lambda x: x ** 2 + 4 * x + 3
dfdx = lambda x: 2 * x + 4
# Array of x
x = linspace(-15, 10, 50)
# Plotting the function
figure(1, figsize=(7.20, 4.00))
plot(x, f(x))
plot([-15, 10], [0, 0], 'k--')
xlabel('x')
ylabel('f(x)')
# Initial Guess
xg = 10
# Setting initial error and loop counter
error = 1
count = 1
# For printing x_g and f(x_g) at different steps
print(f"{'xg':^15}{'f(xg)':^15}")
print("===========================")
# Starting iterations
while error > 1.E-5:
# Solving Eq. 1
xn = xg - f(xg) / dfdx(xg)
# Printing x_g and f(x_g)
print(f'{round(xg, 5):^15}{round(f(xg), 5):^15}')
# Plotting tangents
figure(1)
plot([xg, xn], [f(xg), 0])
plot([xn, xn], [0, f(xn)], '--', label=f'xg={xg}')
legend(bbox_to_anchor=(0.4, 1.1), loc='upper left', borderaxespad=0)
# Evaluating error and plotting it
error = abs(xn - xg)
figure(2, figsize=(7.20, 4.00))
semilogy(count, error, 'ko')
xlabel('Iteration count')
ylabel('Error')
# Settingup new value as guess for next step
xg = xn
# Incrementing the loop counter
count = count + 1
# printing the final answer
print("===========================")
print("\nRoot ", round(xn, 5))
show()
你可以将代码直接复制到你的Jupyter笔记本中并运行。
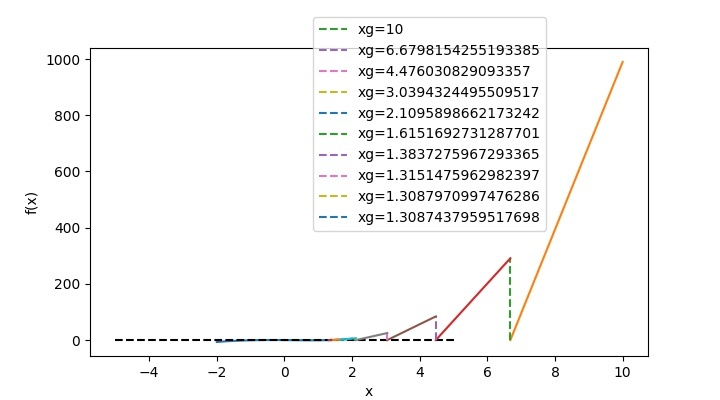
对于你选择的多项式,你可以根据上面的代码更改函数和导数多项式,并基于你的猜测值得到输出。例如,如果你想要找到方程𝑥3−sin2(𝑥)−𝑥=0的根,那么在上面的代码中,函数及其导数将被更改为−
# Function for f(x) and f'(x)
f=lambda x: x**3-(sin(x))**2-x
dfdx=lambda x: 3*x**2-2*sin(x)*cos(x)-1
然后,对于猜测值为1,程序的输出将为 −
xg f(xg)
===========================
1 -0.70807
1.64919 1.84246
1.39734 0.36083
1.31747 0.0321
1.30884 0.00036
1.30874 0.0
===========================
Root 1.30874
并且,函数图像将如下所示 –
结论
在本教程中,你学会了如何使用牛顿拉弗森方法求解方程的根。你还学会了如何绘制切线并在pyplots中展示根收敛。
 极客笔记
极客笔记