在Python中建模Regula Falsi方法
在本教程中,我将展示如何借助Regula Falsi(也称为“False Position Method”)找到方程的根。让我们考虑下面所示的图形。
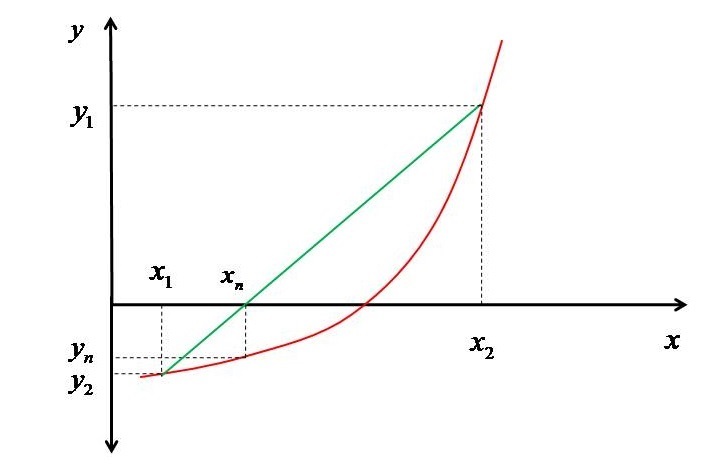
Python中Regula Falsi方法的实现
我们想要用Regula Falsi方法找出根的函数是\mathrm{𝑥^{3}}−9𝑥−5=0。初始区间被选为(-3,-1)。
导入数组使用和数据绘图的模块−
from pylab import *
定义用于求解根的多项式函数−
f=lambda x: x**3-9*x-5
这一步虽然不是必需的,但这将有助于可视化Regula Falsi(伪算法)的工作过程。以下代码将帮助绘制函数-
# Creating array of x
x=linspace(-4,4,50)
# Drawing function
figure(1,dpi=200)
plot(x,f(x))
ylim(-19,10)
plot([-4,4],[0,0],'k--')
在您预期根存在的初始区间内进行选择。我所选择的值是针对上述多项式。
# Selecting false positions x1 and x2
x1=-3
x2=-1
# Evaluating corresponding y1 and y2
y1=f(x1)
y2=f(x2)
检查初始猜测区间 (\mathrm{𝑥_{1},𝑥_{2}}) 是否正确,即判断 \mathrm{𝑦_{1}x𝑦_{2}}>0。
如果不正确,则显示适当的消息退出循环。否则,进入 while 循环。在 while 循环内,首先根据公式1计算 \mathrm{𝑥_{𝑛}} 并找到 \mathrm{𝑦_{ℎ}}。
如果 \mathrm{𝑦_{1}} 的绝对值很小,则使用最终答案 \mathrm{𝑥_{1}} 跳出 while 循环。否则,检查是否 \mathrm{y_{1}:X:y_{n}s0} 成立,如果成立,则设置 \mathrm{x_{2}=x_{n}} and \mathrm{𝑦_{2}=𝑦_{𝑛}}。否则,设置 \mathrm{𝑥_{1}=𝑥_{𝑛}} 和 \mathrm{𝑦_{1}=𝑦_{𝑛}}。
# Initial check
if y1*y2>0:
print("on the same side of x axis, Correct the Range")
exit
else:
# Plotting line joining (x1,y1) and (x2,y2)
plot([x1,x2],[y1,y2])
# Iteration counter
count=1
# Iterations
while True:
xn=x1-y1*(x2-x1)/(y2-y1)
plot([xn],[0],'o',label=f'{xn}')
yn=f(xn)
if abs(y1)<1.E-5:
print("Root= ",x1)
break
elif y1*yn<0:
x2=xn
y2=yn
plot([x1,x2],[y1,y2])
else:
x1=xn
y1=yn
plot([x1,x2],[y1,y2])
# printing few xn in legend
if count<6:
legend()
# Increasing iteration counter
count +=1
show()
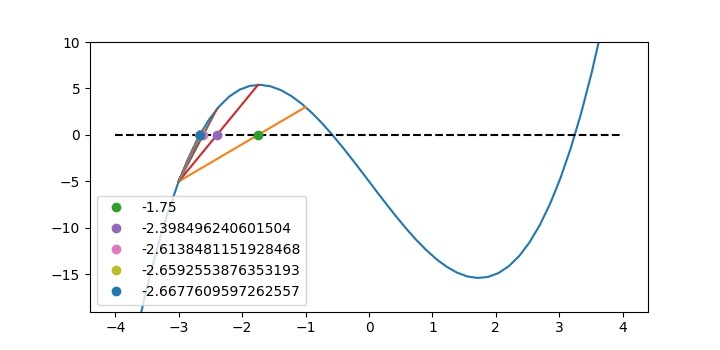
程序的输出将是−
Root= -2.669663840642225
在函数图表自身中显示的收敛到根的过程如下所示。
完整的Python代码
最终编译的代码如下:
# Importing modules for plotting and Array
from pylab import *
# Defining function using Lambda
f = lambda x: x ** 3 - 9 * x - 5
# Creating array of x using linspace
x = linspace(-4, 4, 50)
# Drawing function for better understanding of convergence
figure(1, figsize=(7.20,3.50))
plot(x, f(x))
ylim(-19, 10)
plot([-4, 4], [0, 0], 'k--')
# Selecting false position interval x1 and x2
x1 = -3
x2 = -1
# Evaluating the values at x1 and x2 viz. y1 and y2
y1 = f(x1)
y2 = f(x2)
# Initial check for gussed interval
if y1 * y2 > 0:
print("on the same side of x axis, Correct the Range")
exit
else:
# Plotting line joining (x1,y1) and (x2,y2)
plot([x1, x2], [y1, y2])
# Iteration counter
count = 1
# Iterations
while True:
xn = x1 - y1 * (x2 - x1) / (y2 - y1)
plot([xn], [0], 'o', label=f'{xn}')
yn = f(xn)
if abs(y1) < 1.E-5:
print("Root= ", x1)
break
elif y1 * yn < 0:
x2 = xn
y2 = yn
plot([x1, x2], [y1, y2])
else:
x1 = xn
y1 = yn
plot([x1, x2], [y1, y2])
# printing few xn
if count < 6:
legend()
# Incrementing counter
count += 1
show()
对于其他根,我们需要采用其他的初始集合 \mathrm{x_{1}} 和 \mathrm{x_{2}}。你可以尝试使用(-1, 1)和(2, 4)。
结论
在本教程中,你学习了如何在Python中建模Regula Falsi方法。你也学到了初始猜测区间的选择有多么重要。
 极客笔记
极客笔记