Python中的菜单驱动程序
菜单驱动程序介绍
菜单驱动程序 是一个从用户那里获取输入的程序,通过显示选项列表(称为菜单)供用户选择选项。处理菜单驱动程序的系统很普通,从由微处理器控制的洗衣机到自动取款机(ATM)。以ATM为例,用户按下单个按键来指示交易类型(是否需要现金收据,是否需要账户对账单)。对于许多情况,用户按下单个按键以指示提款金额。
菜单驱动系统有两种好处:首先,通过单击按键来输入,减少了用户误操作的机会。其次,菜单驱动系统限制了字符范围,使得输入变得无歧义。因此,这两个特点使整个系统非常用户友好。
在接下来的教程中,我们将介绍一些采用 菜单驱动程序 编写的 Python 程序。这些程序将让我们了解菜单驱动程序的不同方面,以及Python编程语言的不同库和模块。
那么,让我们开始吧。
使用函数计算不同形状的参数和面积
程序:
# defining functions
def p_circle(radius):
para = 2 * 3.14 * radius
print("Parameter of Circle:", para)
def p_rectangle(height, width):
para = 2 * (height + width)
print("Parameter of Rectangle:", para)
def p_square(side):
para = 4 * side
print("Parameter of Square:", para)
def a_circle(radius):
area = 3.14 * radius * radius
print("Area of Circle:", area)
def a_rectangle(height, width):
area = height * width
print("Area of Rectangle:", area)
def a_square(side):
area = side * side
print("Area of Square:", area)
# printing the starting line
print("WELCOME TO A SIMPLE MENSURATION PROGRAM")
# creating options
while True:
print("\nMAIN MENU")
print("1. Calculate Parameter")
print("2. Calculate Area")
print("3. Exit")
choice1 = int(input("Enter the Choice:"))
if choice1 == 1:
print("\nCALCULATE PARAMETER")
print("1. Circle")
print("2. Rectangle")
print("3. Square")
print("4. Exit")
choice2 = int(input("Enter the Choice:"))
if choice2 == 1:
radius = int(input("Enter Radius of Circle:"))
p_circle(radius)
elif choice2 == 2:
height = int(input("Enter Height of Rectangle:"))
width = int(input("Enter Width of Rectangle:"))
p_rectangle(height, width)
elif choice2 == 3:
side = int(input("Enter Side of Square:"))
p_square(side)
elif choice2 == 4:
break
else:
print("Oops! Incorrect Choice.")
elif choice1 == 2:
print("\nCALCULATE AREA")
print("1. Circle")
print("2. Rectangle")
print("3. Square")
print("4. Exit")
choice3 = int(input("Enter the Choice:"))
if choice3 == 1:
radius = int(input("Enter Radius of Circle:"))
a_circle(radius)
elif choice3 == 2:
height = int(input("Enter Height of Rectangle:"))
width = int(input("Enter Width of Rectangle:"))
a_rectangle(height, width)
elif choice3 == 3:
side = int(input("Enter Side of Square:"))
a_square(side)
elif choice3 == 4:
break
else:
print("Oops! Incorrect Choice.")
elif choice1 == 3:
break
else:
print("Oops! Incorrect Choice.")
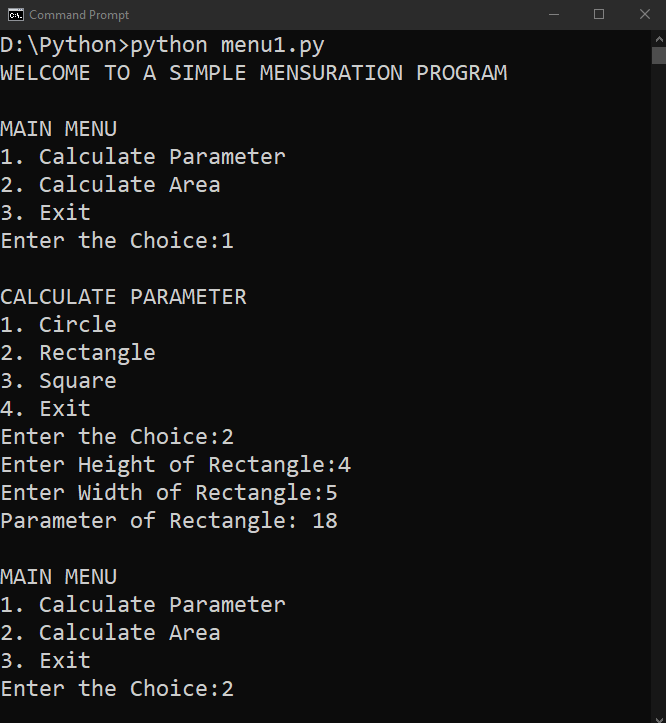
输出:
WELCOME TO A SIMPLE MENSURATION PROGRAM
MAIN MENU
1. Calculate Parameter
2. Calculate Area
3. Exit
Enter the Choice:1
CALCULATE PARAMETER
1. Circle
2. Rectangle
3. Square
4. Exit
Enter the Choice:2
Enter Height of Rectangle:4
Enter Width of Rectangle:5
Parameter of Rectangle: 18
MAIN MENU
1. Calculate Parameter
2. Calculate Area
3. Exit
Enter the Choice:2
CALCULATE AREA
1. Circle
2. Rectangle
3. Square
4. Exit
Enter the Choice:1
Enter Radius of Circle:2
Area of Circle: 12.56
MAIN MENU
1. Calculate Parameter
2. Calculate Area
3. Exit
Enter the Choice:5
Oops! Incorrect Choice.
MAIN MENU
1. Calculate Parameter
2. Calculate Area
3. Exit
Enter the Choice:3
说明:
在上面的示例中,我们定义了不同的函数,用于在计算后打印估计值。这些函数分别包括圆的参数和面积、矩形的参数和面积以及正方形的参数和面积。然后,我们打印了程序的标题,即: 欢迎来到简单测量程序 。在此之下,我们使用了无限的 while 循环来打印包含不同选项的主菜单。然后程序使用 if-elif-else 语句询问用户输入选择选项的整数。如果插入的整数不存在于选项列表中,程序也会引发 异常 。然后,我们创建了两个不同的子菜单,分别是 参数 选项和 面积 选项。然后,我们在这些子菜单中添加了几个描述不同形状的选项。这些选项还采用不同的整数值,表示圆的半径,矩形的高度和宽度以及正方形的边长。结果,菜单驱动的程序被成功创建,并且能够计算不同形状的参数和面积。
菜单驱动程序创建一个简单的计算器
在下面的菜单驱动程序的示例中,我们将构建一个 使用Python创建的简单计算器 。我们将使用无限的 while 循环和上述相同的函数。我们将设计一个菜单,让用户与计算器函数进行交互,例如加法、减法、乘法和除法。
让我们考虑以下程序的语法:
程序:
# defining addition function
def add(a, b):
sum = a + b
print(a, "+", b, "=", sum)
# defining subtraction function
def subtract(a, b):
difference = a - b
print(a, "-", b, "=", difference)
# defining multiplication function
def multiply(a, b):
product = a * b
print(a, "x", b, "=", product)
# defining division function
def divide(a, b):
division = a / b
print(a, "/", b, "=", division)
# printing the heading
print("WELCOME TO A SIMPLE CALCULATOR")
# using the while loop to print menu list
while True:
print("\nMENU")
print("1. Sum of two Numbers")
print("2. Difference between two Numbers")
print("3. Product of two Numbers")
print("4. Division of two Numbers")
print("5. Exit")
choice = int(input("\nEnter the Choice: "))
# using if-elif-else statement to pick different options
if choice == 1:
print( "\nADDITION\n")
a = int( input("First Number: "))
b = int( input("Second Number: "))
add(a, b)
elif choice == 2:
print( "\nSUBTRACTION\n")
a = int( input("First Number: "))
b = int( input("Second Number: "))
subtract(a, b)
elif choice == 3:
print( "\nMULTIPLICATION\n")
a = int( input("First Number: "))
b = int( input("Second Number: "))
multiply(a, b)
elif choice == 4:
print( "\nDIVISION\n")
a = int( input("First Number: "))
b = int( input("Second Number: "))
divide(a, b)
elif choice == 5:
break
else:
print( "Please Provide a valid Input!")
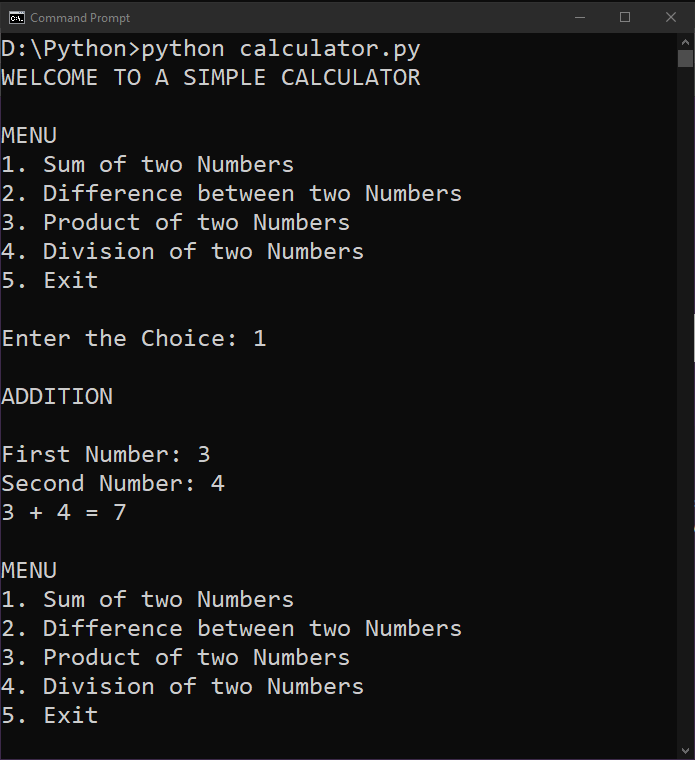
输出:
WELCOME TO A SIMPLE CALCULATOR
MENU
1. Sum of two Numbers
2. Difference between two Numbers
3. Product of two Numbers
4. Division of two Numbers
5. Exit
Enter the Choice: 1
ADDITION
First Number: 3
Second Number: 4
3 + 4 = 7
MENU
1. Sum of two Numbers
2. Difference between two Numbers
3. Product of two Numbers
4. Division of two Numbers
5. Exit
Enter the Choice: 2
SUBTRACTION
First Number: 6
Second Number: 3
6 - 3 = 3
MENU
1. Sum of two Numbers
2. Difference between two Numbers
3. Product of two Numbers
4. Division of two Numbers
5. Exit
Enter the Choice: 3
MULTIPLICATION
First Number: 8
Second Number: 2
8 x 2 = 16
MENU
1. Sum of two Numbers
2. Difference between two Numbers
3. Product of two Numbers
4. Division of two Numbers
5. Exit
Enter the Choice: 4
DIVISION
First Number: 10
Second Number: 4
10 / 4 = 2.5
MENU
1. Sum of two Numbers
2. Difference between two Numbers
3. Product of two Numbers
4. Division of two Numbers
5. Exit
Enter the Choice: 5
解释:
在上面的程序中,我们使用了几乎与上一个程序相似的过程。我们定义了各种函数,例如 add, subtract, multiply 和 divide . 然后我们使用 while 循环向用户打印菜单列表,并使用 if-elif-else 语句返回用户所需的答案。结果,成功创建了一个简单的计算器,并执行了一些基本的计算,如加法、减法、乘法和除法。
基于菜单的程序创建电话目录
在下面的基于菜单的程序中,我们将使用不同函数创建一个电话簿目录。我们将向电话簿目录中添加以下功能:
- 存储联系人的电话号码
- 使用姓名搜索联系人的电话号码
让我们在以下程序中实现这个想法:
程序:
# printing the heading of the program
print( "WELCOME TO THE PHONEBOOK DIRECTORY")
# creating a .txt file to store contact details
filename = "myphonebook.txt"
myfile = open(filename, "a+")
myfile.close
# defining main menu
def main_menu():
print( "\nMAIN MENU\n")
print( "1. Show all existing Contacts")
print( "2. Add a new Contact")
print( "3. Search the existing Contact")
print( "4. Exit")
choice = input("Enter your choice: ")
if choice == "1":
myfile = open(filename, "r+")
filecontents = myfile.read()
if len(filecontents) == 0:
print( "There is no contact in the phonebook.")
else:
print(filecontents)
myfile.close
enter = input("Press Enter to continue ...")
main_menu()
elif choice == "2":
newcontact()
enter = input("Press Enter to continue ...")
main_menu()
elif choice == "3":
searchcontact()
enter = input("Press Enter to continue ...")
main_menu()
elif choice == "4":
print("Thank you for using Phonebook!")
else:
print( "Please provide a valid input!\n")
enter = input( "Press Enter to continue ...")
main_menu()
# defining search function
def searchcontact():
searchname = input( "Enter First name for Searching contact record: ")
remname = searchname[1:]
firstchar = searchname[0]
searchname = firstchar.upper() + remname
myfile = open(filename, "r+")
filecontents = myfile.readlines()
found = False
for line in filecontents:
if searchname in line:
print( "Your Required Contact Record is:", end = " ")
print( line)
found = True
break
if found == False:
print( "The Searched Contact is not available in the Phone Book", searchname)
# first name
def input_firstname():
first = input( "Enter your First Name: ")
remfname = first[1:]
firstchar = first[0]
return firstchar.upper() + remfname
# last name
def input_lastname():
last = input( "Enter your Last Name: ")
remlname = last[1:]
firstchar = last[0]
return firstchar.upper() + remlname
# storing the new contact details
def newcontact():
firstname = input_firstname()
lastname = input_lastname()
phoneNum = input( "Enter your Phone number: ")
emailID = input( "Enter your E-mail Address: ")
contactDetails = ("[" + firstname + " " + lastname + ", " + phoneNum + ", " + emailID + "]\n")
myfile = open(filename, "a")
myfile.write(contactDetails)
print( "The following Contact Details:\n " + contactDetails + "\nhas been stored successfully!")
main_menu()
输出:
WELCOME TO THE PHONEBOOK DIRECTORY
MAIN MENU
1. Show all existing Contacts
2. Add a new Contact
3. Search the existing Contact
4. Exit
Enter your choice: 1
There is no contact in the phonebook.
Press Enter to continue ...
MAIN MENU
1. Show all existing Contacts
2. Add a new Contact
3. Search the existing Contact
4. Exit
Enter your choice: 2
Enter your First Name: Mark
Enter your Last Name: Henry
Enter your Phone number: 1234567890
Enter your E-mail Address: stash
The following Contact Details:
[Mark Henry, 1234567890, stash]
has been stored successfully!
Press Enter to continue ...
MAIN MENU
1. Show all existing Contacts
2. Add a new Contact
3. Search the existing Contact
4. Exit
Enter your choice: 3
Enter First name for Searching contact record: Mark
Your Required Contact Record is: [Mark Henry, 1234567890, stash]
Press Enter to continue ...
MAIN MENU
1. Show all existing Contacts
2. Add a new Contact
3. Search the existing Contact
4. Exit
Enter your choice: 1
[Mark Henry, 1234567890, stash]
Press Enter to continue ...
MAIN MENU
1. Show all existing Contacts
2. Add a new Contact
3. Search the existing Contact
4. Exit
Enter your choice: 4
Thank you for using Phonebook!
解释:
在上面的菜单驱动程序中,我们创建了一个电话簿目录,可以将新联系人存储在一个文本文件中,显示已存储的联系人,并允许用户搜索已有的号码。首先,我们创建了一个文本文件来存储联系人的详细信息。然后,我们定义了各种函数来添加、显示和搜索不同的联系人。我们还创建了不同的联系人详细信息字段,例如 名字、姓氏、手机号码和电子邮件地址。 结果,程序成功完成,其输出如上所示。
结论
在上面的教程中,我们了解了菜单驱动编程的含义,并给出了一些示例。我们创建了三个不同的程序,包括测量程序、简单计算器和电话簿目录。除了这三个之外,还有许多其他程序可以创建。
 极客笔记
极客笔记