使用MobileNet进行图像识别
介绍
通过图像来识别物体或特征的过程被称为图像识别。图像识别在医学成像、汽车、安全和检测缺陷等不同领域都有应用。
什么是MobileNet以及为什么它如此受欢迎
MobileNet是使用深度可分离卷积开发的深度学习CNN模型。与同样深度的其他模型相比,该模型大大减少了参数数量。该模型轻巧且经过优化,可在移动设备和边缘设备上运行。到目前为止,已发布了三个版本的MobileNet,即MobileNet v1、v2和v3。MobileNet是由Google开发的。
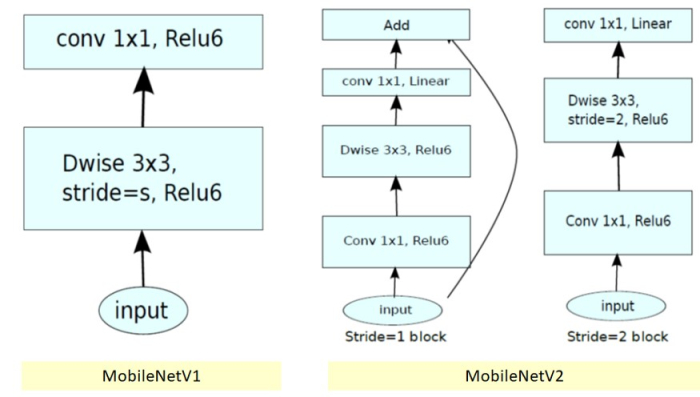
让我们稍微了解一下已经存在于机器学习领域已经有一段时间的MobileNet V1和V2。
MobileNetV2相对于MobileNet V1提供了两个全面的特性。它们是:
- MobileNetV2在层之间使用了线性瓶颈。它通过不允许非线性破坏太多信息来保留信息。
-
瓶颈之间的短连接
MobileNetv2的架构
| 输入 | 操作符 | T | C | N | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2242 X 3 | conv2d | - | 32 | 1 | 2 |
| 112 2 X 32 | bottleneck | 1 | 16 | 1 | 1 |
| 112 2 X 16 | bottleneck | 6 | 24 | 2 | 2 |
| 562 X 24 | bottleneck | 6 | 32 | 3 | 2 |
| 282 X 32 | bottleneck | 6 | 64 | 4 | 2 |
| 142 X 64 | bottleneck | 6 | 96 | 3 | 1 |
| 142 X 96 | bottleneck | 6 | 160 | 3 | 2 |
| 72 X 160 | bottleneck | 6 | 320 | 1 | 1 |
| 72 X 320 | conv2d 1×1 1 | − | 1280 | 1 | 1 |
| 72 X 1280 | avgpool 7×7 | − | − | 1 | − |
| 1 X1 X 1280 | conv2d 1×1 | − | k | − | − |
MobileNet v1和MobileNet V2的比较
| SIZE | MOBILENETV1 | MOBILENETV2 | SHUFFLENET (2X,G=3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 112X112 | 64/1600 | 16/400 | 32/800 |
| 56×56 | 128/800 | 32/200 | 48/300 |
| 28×28 | 256/400 | 64/100 | 400/600K |
| 14×14 | 512/200 | 160/62 | 800/310 |
| 7×7 | 1024/199 | 320/32 | 1600/156 |
| 1×1 | 1024/2 | 1280/2 | 1600/3 |
| max | 1600K | 400K | 600K |
图像识别的代码实现
示例
## MOBILENET
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow import keras
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense, Activation
from tensorflow.keras.metrics import categorical_crossentropy
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing import image
from tensorflow.keras.models import Model
from tensorflow.keras.optimizers import Adam
from tensorflow.keras.applications import imagenet_utils
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from IPython.display import Image,display
%matplotlib inline
mobile = tf.keras.applications.mobilenet.MobileNet()
def format_image(file):
image_path = '/content/images/'
img = image.load_img(image_path + file, target_size=(224, 224))
img_array = image.img_to_array(img)
img_array_exp_dims = np.expand_dims(img_array, axis=0)
return tf.keras.applications.mobilenet.preprocess_input(img_array_exp_dims)
display(Image(filename='/content/images/image.jpg', width=300,height=200))
preprocessed_img = format_image('image.jpg')
prediction_results = mobile.predict(preprocessed_img)
results = imagenet_utils.decode_predictions(prediction_results)
print(results)
输出
[[('n02279972', 'monarch', 0.58884907), ('n02281406', 'sulphur_butterfly',
0.18508224), ('n02277742', 'ringlet', 0.15471826), ('n02281787', 'lycaenid', 0.04744451),
('n02276258', 'admiral', 0.01013135)]]
MobileNet相比其他网络的优势
- MobileNet具有更高的分类准确度和较少的参数。
-
MobileNet小巧,延迟低,功耗优化,非常适合移动和嵌入式设备。
-
它们是用于分割和目标检测的高效特征提取器。
图像识别的好处
-
用于自动驾驶车辆和机器人来检测障碍物。
-
在OCR技术中广泛应用于从图像中提取信息。
-
交通车道检测。
-
人脸检测和考勤系统。
-
图像字幕和标记,在社交媒体网站中非常有用。
结论
图像识别已经成为每个物体检测和视频相关任务的初步任务。随着已经可用的大量预训练模型和架构,图像识别在与视觉相关的当前人工智能领域非常重要。
 极客笔记
极客笔记