NumPy Ndarray数组
Ndarray是在numpy中定义的n维数组对象,它存储了相同类型元素的集合。换句话说,我们可以将ndarray定义为数据类型(dtype)对象的集合。
可以使用从0开始的索引访问ndarray对象。数组对象的每个元素在内存中占用相同大小。
创建ndarray对象
可以使用numpy模块的array例程创建ndarray对象。为此,我们需要导入numpy。
>>> a = numpy.array
考虑下面的图片。
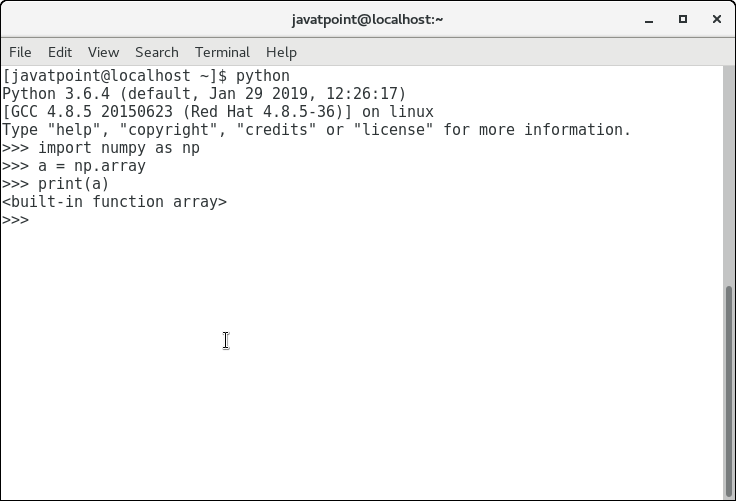
我们还可以将一个集合对象传递给数组例程,以创建等效的n维数组。语法如下所示。
>>> numpy.array(object, dtype = None, copy = True, order = None, subok = False, ndmin = 0)
参数在下表中描述。
| 序号 | 参数 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | object | 它代表集合对象。可以是列表、元组、字典、集合等。 |
| 2 | dtype | 通过更改此选项为指定类型,可以更改数组元素的数据类型。默认为none。 |
| 3 | copy | 这是可选的。默认情况下,它为true,这意味着对象已被复制。 |
| 4 | order | 此选项可以分配3个可能的值。它可以是C(列顺序)、R(行顺序)或A(任意)。 |
| 5 | subok | 返回的数组默认将为基类数组。我们可以通过将此选项设置为true来更改为子类通过。 |
| 6 | ndmin | 它表示结果数组的最小维度。 |
使用列表创建数组,使用以下语法。
>>> a = numpy.array([1, 2, 3])
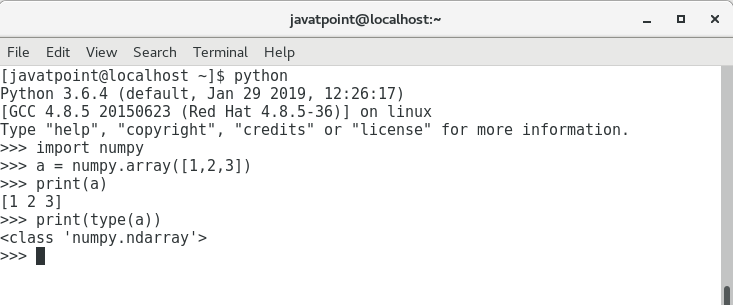
要创建一个多维数组对象,请使用以下语法。
>>> a = numpy.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])

改变数组元素的数据类型,需要在集合名称后面提及数据类型的名称。
>>> a = numpy.array([1, 3, 5, 7], complex)
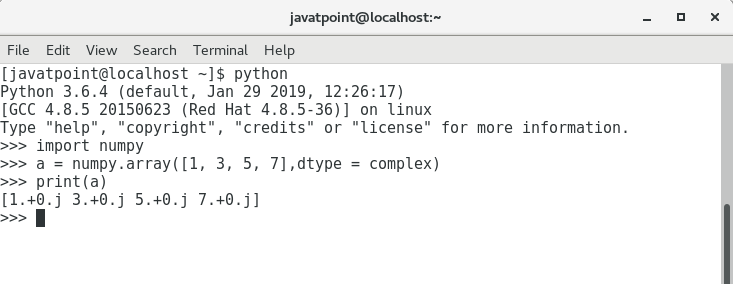
寻找数组的维度
可以使用 ndim 函数来寻找数组的维度。
>>> import numpy as np
>>> arr = np.array([[1, 2, 3, 4], [4, 5, 6, 7], [9, 10, 11, 23]])
>>> print(arr.ndim)
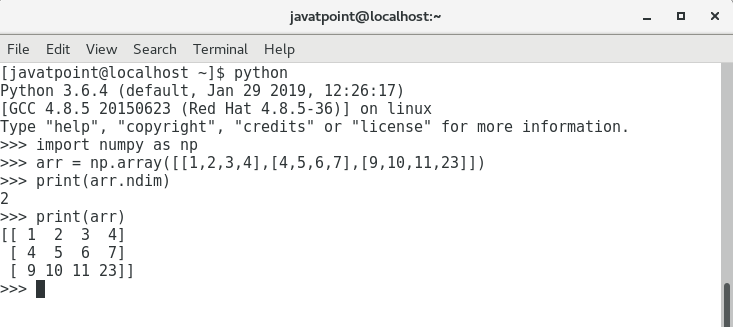
查找每个数组元素的大小
itemsize函数用于获取每个数组项的大小。它返回每个数组元素占用的字节数。
考虑下面的示例。
示例
#finding the size of each item in the array
import numpy as np
a = np.array([[1,2,3]])
print("Each item contains",a.itemsize,"bytes")
输出:
Each item contains 8 bytes.
找到每个数组项的数据类型
要检查每个数组项的数据类型,可以使用dtype函数。考虑以下示例来检查数组项的数据类型。
示例
#finding the data type of each array item
import numpy as np
a = np.array([[1,2,3]])
print("Each item is of the type",a.dtype)
输出结果:
Each item is of the type int64
寻找数组的形状和大小
为了获取数组的形状和大小,使用与numpy数组相关的size和shape函数。
考虑以下示例。
示例
import numpy as np
a = np.array([[1,2,3,4,5,6,7]])
print("Array Size:",a.size)
print("Shape:",a.shape)
输出:
Array Size: 7
Shape: (1, 7)
重新调整数组对象
通过数组的形状,我们指的是多维数组的行数和列数。然而,numpy模块提供了一种通过改变多维数组的行数和列数来重新调整数组的方法。
与ndarray对象关联的reshape()函数用于重新调整数组。它接受两个参数,表示数组的新形状的行数和列数。
让我们重新调整以下图像中给出的数组。

示例
import numpy as np
a = np.array([[1,2],[3,4],[5,6]])
print("printing the original array..")
print(a)
a=a.reshape(2,3)
print("printing the reshaped array..")
print(a)
输出:
printing the original array..
[[1 2]
[3 4]
[5 6]]
printing the reshaped array..
[[1 2 3]
[4 5 6]]
数组中的切片
在NumPy数组中,切片是从数组中提取一系列元素的方法。在数组中进行切片的方式与在python列表中进行切片的方式相同。
考虑以下示例来打印数组的特定元素。
示例
import numpy as np
a = np.array([[1,2],[3,4],[5,6]])
print(a[0,1])
print(a[2,0])
输出:
2
5
上面的程序从数组的第0个索引中输出第2个元素,并从数组的第2个索引中输出第0个元素。
Linspace
linspace()函数返回给定区间内均匀间隔的值。下面的示例返回在给定区间5-15上均匀分布的10个值。
示例
import numpy as np
a=np.linspace(5,15,10) #prints 10 values which are evenly spaced over the given interval 5-15
print(a)
输出:
[ 5. 6.11111111 7.22222222 8.33333333 9.44444444 10.55555556
11.66666667 12.77777778 13.88888889 15. ]
查找数组元素的最大值、最小值和总和
NumPy提供了max()、min()和sum()函数,分别用于查找数组元素的最大值、最小值和总和。
考虑下面的示例。
示例
import numpy as np
a = np.array([1,2,3,10,15,4])
print("The array:",a)
print("The maximum element:",a.max())
print("The minimum element:",a.min())
print("The sum of the elements:",a.sum())
输出:
The array: [ 1 2 3 10 15 4]
The maximum element: 15
The minimum element: 1
The sum of the elements: 35
NumPy数组的轴
一个NumPy多维数组由轴表示,其中轴-0表示列,轴-1表示行。我们可以指定轴来执行行级或列级计算,比如行或列元素的加法。

要计算每列中的最大元素、每行中的最小元素以及所有行元素的总和,请考虑以下示例。
示例
import numpy as np
a = np.array([[1,2,30],[10,15,4]])
print("The array:",a)
print("The maximum elements of columns:",a.max(axis = 0))
print("The minimum element of rows",a.min(axis = 1))
print("The sum of all rows",a.sum(axis = 1))
输出:
The array: [[1 2 30]
[10 15 4]]
The maximum elements of columns: [10 15 30]
The minimum element of rows [1 4]
The sum of all rows [33 29]
查找平方根和标准差
与numpy数组相关的sqrt()和std()函数分别用于查找数组元素的平方根和标准差。
标准差表示数组每个元素与numpy数组的平均值之间的差异程度。
考虑以下示例。
示例
import numpy as np
a = np.array([[1,2,30],[10,15,4]])
print(np.sqrt(a))
print(np.std(a))
输出:
[[1. 1.41421356 5.47722558]
[3.16227766 3.87298335 2. ]]
10.044346115546242
数组的算术运算
numpy模块允许我们直接在多维数组上进行算术运算。
在以下示例中,对两个多维数组a和b执行了算术运算。
示例
import numpy as np
a = np.array([[1,2,30],[10,15,4]])
b = np.array([[1,2,3],[12, 19, 29]])
print("Sum of array a and b\n",a+b)
print("Product of array a and b\n",a*b)
print("Division of array a and b\n",a/b)
数组连接
numpy为我们提供了垂直堆叠和水平堆叠的功能,可以将两个多维数组垂直或水平连接在一起。
考虑以下示例。
示例
import numpy as np
a = np.array([[1,2,30],[10,15,4]])
b = np.array([[1,2,3],[12, 19, 29]])
print("Arrays vertically concatenated\n",np.vstack((a,b)));
print("Arrays horizontally concatenated\n",np.hstack((a,b)))
输出:
Arrays vertically concatenated
[[ 1 2 30]
[10 15 4]
[ 1 2 3]
[12 19 29]]
Arrays horizontally concatenated
[[ 1 2 30 1 2 3]
[10 15 4 12 19 29]]
 极客笔记
极客笔记