OpenCV Python 使用ORB和BFmatcher匹配两个图像的关键点
为了匹配两个图像的关键点,我们使用 ORB(Oriented FAST and Rotated BRIEF) 来检测和计算特征关键点和描述符,并使用 Brute Force 匹配器在两个图像中匹配描述符。
步骤
要使用ORB特征检测器和Brute Force匹配器匹配两个图像的关键点,可以按照以下步骤进行:
- 导入所需的库 OpenCV , Matplotlib 和 NumPy 。确保您已经安装了它们。
- 使用 cv2.imread() 方法读取两个输入图像作为灰度图像。指定图像的完整路径。
- 使用默认值初始化ORB对象 orb=cv2.ORB_create() 。
- 使用 orb.detectAndCompute() 在两个输入图像中检测和计算关键点’kp1’和’kp2’以及描述符’des1’和’des2’。
- 创建一个BFmatcher对象 bf = cv2.BFMatcher() ,并使用此BFmatcher对象 bf.match(des1, des2) 匹配描述符。它返回匹配项。按照其距离对匹配项进行排序。
- 使用 cv2.drawMatches() 在原始输入图像上绘制匹配项。
- 可视化关键点匹配。
让我们看一些示例,使用ORB特征检测器和Brute Force匹配器来匹配两个图像的关键点。
输入图像
我们在下面的示例中使用以下图像作为输入文件。
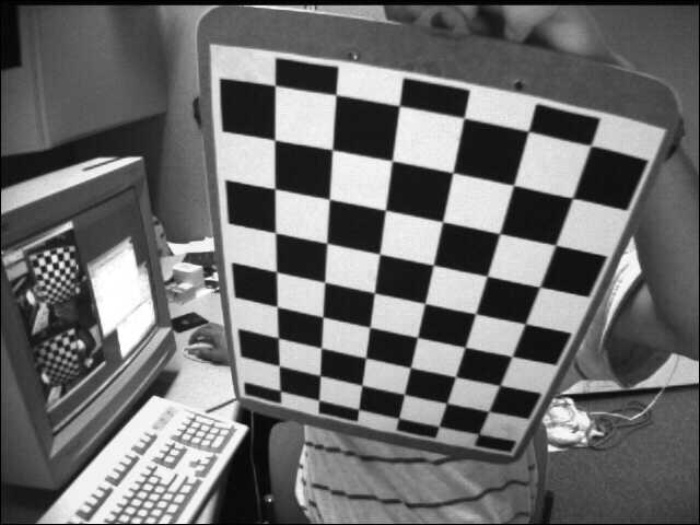
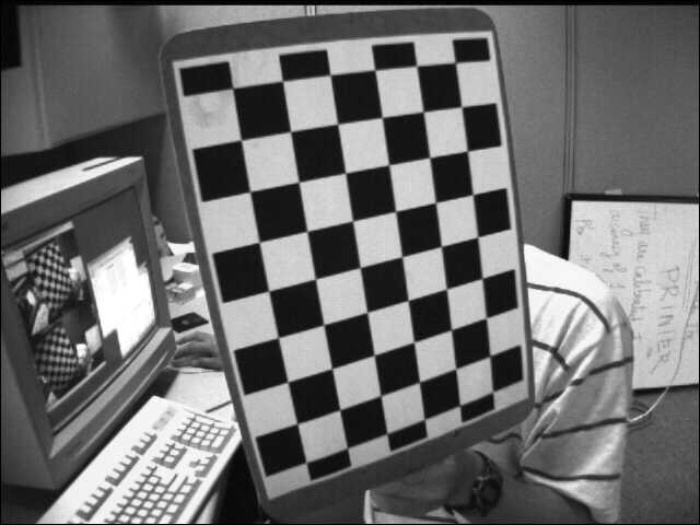


示例
在此示例中,我们使用ORB算法检测两个输入图像的关键点和描述符,并使用Brute Force匹配器匹配描述符。同时,我们绘制了最佳的50个关键点匹配项。在此示例中,我们向 drawMatches() 传递 flags=2 以绘制匹配项。
# import required libraries
import numpy as np
import cv2
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
# read two input images as grayscale
img1 = cv2.imread('left02.jpg',0)
img2 = cv2.imread('left14.jpg',0)
# Initiate ORB detector
orb = cv2.ORB_create()
# detect and compute the keypoints and descriptors with ORB
kp1, des1 = orb.detectAndCompute(img1,None)
kp2, des2 = orb.detectAndCompute(img2,None)
# create BFMatcher object
bf = cv2.BFMatcher(cv2.NORM_HAMMING, crossCheck=True)
# Match descriptors.
matches = bf.match(des1,des2)
# print(matches)
# Sort them in the order of their distance.
matches = sorted(matches, key = lambda x:x.distance)
# Draw first 50 matches.
img3 = cv2.drawMatches(img1,kp1,img2,kp2,matches[:50], None, flags=2)
plt.imshow(img3),plt.show()
输出
执行时,将产生以下 输出 −
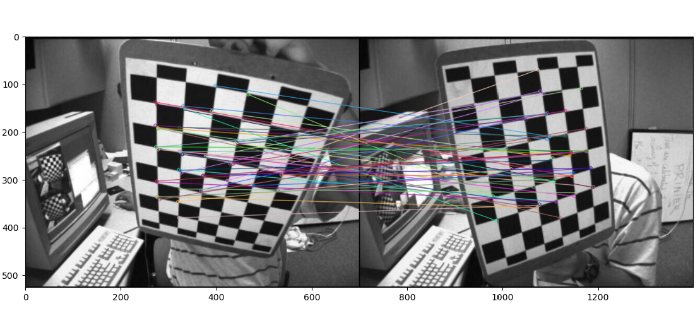
示例
在此示例中,我们使用ORB算法检测两个输入图像的关键点和描述符,并使用暴力匹配器匹配描述符。我们还绘制最佳的50个关键点匹配。在这个示例中,我们将 flags = 0 传递给 drawMatches() 来绘制匹配项。
# import required libraries
import numpy as np
import cv2
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# read two input images as grayscale
img1 = cv2.imread('left02.jpg', 0)
img2 = cv2.imread('left14.jpg', 0)
# Initiate ORB detector
orb = cv2.ORB_create()
# detect and compute the keypoints and descriptors with ORB
(kp1,des1) = orb.detectAndCompute(img1, None)
(kp2,des2) = orb.detectAndCompute(img2, None)
# create BFMatcher object
bf = cv2.BFMatcher(cv2.NORM_HAMMING, crossCheck=True)
# Match descriptors.
matches = bf.match(des1,des2)
# Sort them in the order of their distance. Least distance is better
matches = sorted(matches, key=lambda val: val.distance)
# Draw first 50 matches.
out = cv2.drawMatches(img1, kp1, img2, kp2, matches[:50], None, flags=0)
plt.imshow(out), plt.show()
输出
执行后,它将产生以下 输出 −
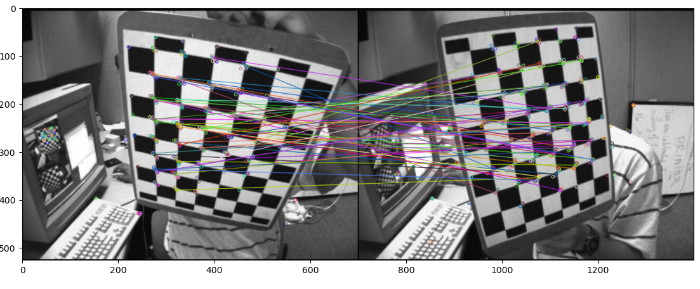
请注意两个示例中输出图像中绘制的关键点的区别。
 极客笔记
极客笔记