使用OpenCV Python旋转图像而不裁剪边缘
旋转图像是图像编辑中最基本的操作。Python的OpenCV库提供了cv2.getRotationMatrix2D()和cv2.rotate()方法,可以非常容易地实现这个任务。
cv2.rotate()方法可以将图像仅旋转0度、90度、180度或270度,而cv2.getRotationMatrix2D()方法可以将图像旋转到任意指定的角度。在下面的文章中,我们将使用OpenCV Python旋转图像而不裁剪或切除边缘。
使用cv2.getRotationMatrix2D()方法来旋转图像需要遵循以下三个步骤:
- 首先,我们需要获取旋转的中心点。
-
其次,通过使用getRotationMatrix2D()方法,我们需要创建2D旋转矩阵。
-
最后,通过在OpenCV中使用warpAffine()函数,我们需要对图像应用仿射变换,以纠正图像的几何失真或变形。
使用Cv2.getRotationMatrix2D()函数
这个函数创建了输入图像数组的变换矩阵,因此它将被用于旋转图像。如果角度参数的值为正数,则图像会以逆时针方向旋转。如果您想要顺时针旋转图像,则角度必须为负数。
语法
cv2.getRotationMatrix2D(center, angle, scale)
参数
- center : 输入图像旋转的中心点。
- angle : 旋转的角度,单位为度。
- scale : 等轴缩放因子。根据提供的值对图像进行放大或缩小。
示例
让我们通过使用 math 模块的三角函数来举个示例,来旋转图像。
import cv2
import math
def rotate_image(array, angle):
height, width = array.shape[:2]
image_center = (width / 2, height / 2)
rotation_mat = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D(image_center, angle, 1)
radians = math.radians(angle)
sin = math.sin(radians)
cos = math.cos(radians)
bound_w = int((height * abs(sin)) + (width * abs(cos)))
bound_h = int((height * abs(cos)) + (width * abs(sin)))
rotation_mat[0, 2] += ((bound_w / 2) - image_center[0])
rotation_mat[1, 2] += ((bound_h / 2) - image_center[1])
rotated_mat = cv2.warpAffine(array, rotation_mat, (bound_w, bound_h))
return rotated_mat
img = cv2.imread('Images/car.jpg',1)
rotated_image = rotate_image(img, 256)
cv2.imshow('Rotated image', rotated_image)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
输入图像

输出
下面显示旋转后的图像。

成功将输入图像旋转到256度角度。
示例
在此示例中,我们将使用cv2.getRotationMatrix2D()和python内置的abs()函数旋转图像。
import cv2
def rotate_image(arr, angle):
height, width = arr.shape[:2]
# get the image centers
image_center = (width/2, height/2)
rotation_arr = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D(image_center, angle, 1)
abs_cos = abs(rotation_arr[0,0])
abs_sin = abs(rotation_arr[0,1])
bound_w = int(height * abs_sin + width * abs_cos)
bound_h = int(height * abs_cos + width * abs_sin)
rotation_arr[0, 2] += bound_w/2 - image_center[0]
rotation_arr[1, 2] += bound_h/2 - image_center[1]
rotated_mat = cv2.warpAffine(arr, rotation_arr, (bound_w, bound_h))
return rotated_arr
img = cv2.imread('Images/cat.jpg',1)
rotated_image = rotate_image(img, 197)
cv2.imshow('Original image', img)
cv2.imshow('Rotated image', rotated_image)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
原始图片

旋转后图片
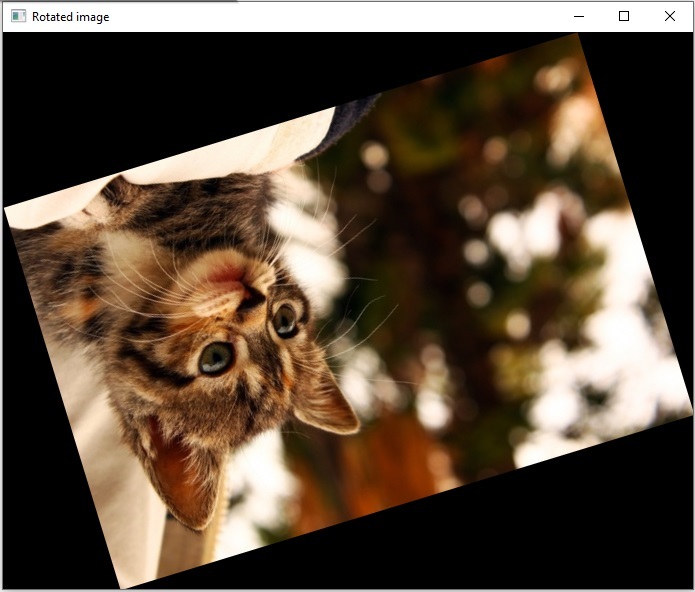
成功将输入的图片旋转到197度角。
cv2.rotate()
cv2.rotate()函数以90度的倍数(0或90或180或270度)旋转图像帧。该函数使用rotateCode= 0或1或2参数以三种不同的方式旋转图像。
语法
cv2.cv.rotate( src, rotateCode[, dst] )
参数
- src:输入图像
-
rotateCode:指定图像如何旋转
-
dst:输出图像,大小和深度与输入图像相同
返回值
返回旋转后的图像。
示例
在这个示例中,输入图像“Fruits.jpg”将被逆时针旋转90度。
import cv2
import numpy as np
img = cv2.imread('Images/logo.jpg',1)
rotated_image = cv2.rotate(img,rotateCode = 2)
cv2.imshow('Original image', img)
cv2.imshow('Rotated image', rotated_image)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
原始图像

旋转图像

使用np.rot90()函数
numpy.rot90()方法用于将数组旋转90度。如果仅需要将输入旋转90度,则这是一种简单且更容易的方法。
示例
在此示例中,我们将使用850X315尺寸的矩形图像“car.jpg”作为输入。
import cv2
import numpy as np
img = cv2.imread('Images/car.jpg',1)
rotated_image = np.rot90(img)
cv2.imwrite('Rotated image.jpg', rotated_image)
cv2.imshow('InputImage', img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
原始图像

旋转后的图像
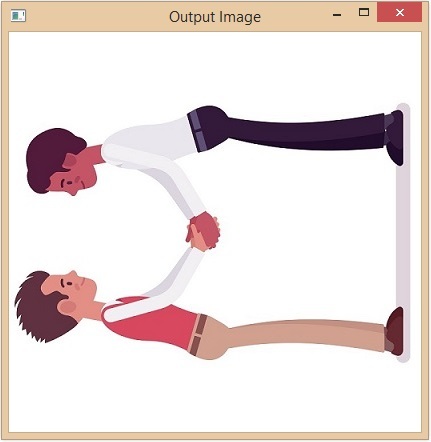

该方法从第一个轴向第二个轴方向旋转数组,因此给定的图像将逆时针方向旋转。
 极客笔记
极客笔记