如何在OpenCV Python中对图像进行归一化?
我们使用函数cv2.normalize()在OpenCV中对图像进行归一化。此函数接受参数-src、dst、alpha、beta、norm_type、dtype和mask。其中,src和dst是输入图像和与输入图像大小相同的输出图像,alpha是范围归一化的较低范围值,beta是范围归一化的较高范围值,norm_type是归一化类型,dtype是输出的数据类型,mask是可选的操作掩码。
步骤
要归一化图像,我们可以按照以下步骤进行:
- 导入所需的库。在以下所有示例中,所需的Python库是OpenCV。请确保您已经安装了它。
-
使用cv2.imread()方法将输入图像读取为灰度图像。指定图像的完整路径和图像类型(png或jpg)。
-
在输入图像img上应用cv2.normalize()函数。传递参数src、dst、alpha、beta、norm_type、dtype和mask。
img_normalized = cv2.normalize(img, None, 0, 1.0, cv2.NORM_MINMAX, dtype=cv2.CV_32F)
-
显示归一化输出图像。
-
在Normalize之前和之后打印图像数据。尝试找出这两个图像数据之间的差异。
让我们通过一些Python示例来理解问题。
我们将使用这张图片作为下面示例中的输入文件:

示例
在这个Python程序中,我们使用最小最大归一化方法对彩色输入图像进行归一化。图像的像素值被归一化到[0,1]的范围内。
# import required library
import cv2
# read the input image in grayscale
img = cv2.imread('jeep.jpg',0)
print("Image data before Normalize:\n", img)
# Normalize the image
img_normalized = cv2.normalize(img, None, 0, 1.0,
cv2.NORM_MINMAX, dtype=cv2.CV_32F)
# visualize the normalized image
cv2.imshow('Normalized Image', img_normalized)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
print("Image data after Normalize:\n", img_normalized)
输出
运行上面的程序后,将会产生以下的输出:
Image data before Normalize:
[[ 37 37 37 ... 55 55 55]
[ 39 39 39 ... 57 56 56]
[ 39 39 39 ... 56 56 56]
...
[243 244 244 ... 82 85 86]
[242 245 245 ... 83 91 91]
[242 245 245 ... 86 94 93]]
Image data after Normalize:
[[0.14509805 0.14509805 0.14509805 ... 0.21568629 0.21568629 0.21568629]
[0.15294118 0.15294118 0.15294118 ... 0.22352943 0.21960786 0.21960786]
[0.15294118 0.15294118 0.15294118 ... 0.21960786 0.21960786 0.21960786]
...
[0.95294124 0.9568628 0.9568628 ... 0.32156864 0.33333334 0.3372549 ]
[0.9490197 0.9607844 0.9607844 ... 0.3254902 0.35686275 0.35686275]
[0.9490197 0.9607844 0.9607844 ... 0.3372549 0.36862746 0.3647059 ]]
然后我们得到以下显示归一化图像的窗口 −
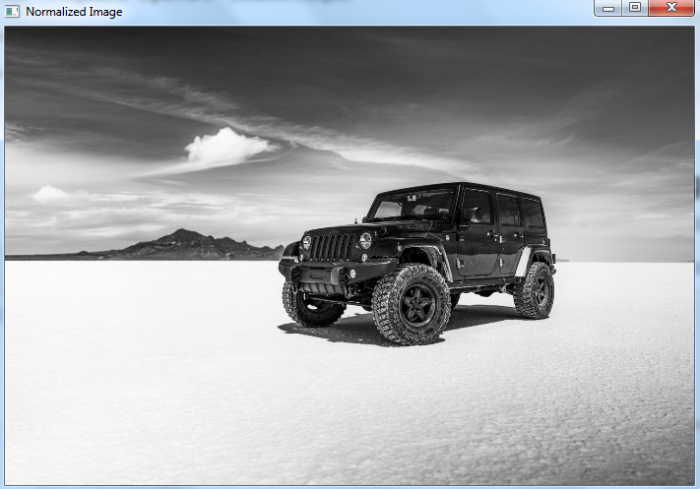
示例
在这个Python程序中,我们使用最小最大归一化对二进制输入图像进行归一化处理。归一化后的图像像素值要么是0,要么是1。
# import required library
import cv2
# read the input image as grayscale image
img = cv2.imread('jeep.jpg',0)
print("Image data before Normalize:\n", img)
# Apply threshold to create a binary image
ret,thresh = cv2.threshold(img,140,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
print("Image data after Thresholding:\n", thresh)
# normalize the binary image
img_normalized = cv2.normalize(thresh, None, 0, 1.0,
cv2.NORM_MINMAX, dtype=cv2.CV_32F)
# visualize the normalized image
cv2.imshow('Normalized Image', img_normalized)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
print("Image data after Normalize:\n", img_normalized)
输出
当您运行上述Python程序时,它将产生以下 输出 −
Image data before Normalize:
[[ 37 37 37 ... 55 55 55]
[ 39 39 39 ... 57 56 56]
[ 39 39 39 ... 56 56 56]
...
[243 244 244 ... 82 85 86]
[242 245 245 ... 83 91 91]
[242 245 245 ... 86 94 93]]
Image data after Thresholding:
[[ 0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]
[ 0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]
[ 0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]
...
[255 255 255 ... 0 0 0]
[255 255 255 ... 0 0 0]
[255 255 255 ... 0 0 0]]
Image data after Normalize:
[[0. 0. 0. ... 0. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 0. ... 0. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 0. ... 0. 0. 0.]
...
[1. 1. 1. ... 0. 0. 0.]
[1. 1. 1. ... 0. 0. 0.]
[1. 1. 1. ... 0. 0. 0.]]
我们得到了以下窗口显示的归一化二进制图像−

 极客笔记
极客笔记