如何在OpenCV Python中查找图像轮廓的边界矩形?
对象的边界矩形是在图像中围绕对象绘制的矩形。有两种方法可以找到边界矩形:
OpenCV −
直立边界矩形
直立边界矩形是一个直立矩形,因为它不考虑对象的旋转。可以使用函数 cv2.boundingRect() 计算它。其语法如下:
x,y,w,h = cv2.boundingRect(cnt)
img = cv2.rectangle(img,(x,y),(x+w,y+h),(0,255,0),2)
在这里,“ cnt ”是轮廓点的数组。它返回边界矩形的左上角坐标( x , y )和宽度和高度( w , h )。
旋转矩形
它考虑对象的旋转并绘制一个最小面积的矩形。通过函数 cv2.minAreaRect() 找到旋转矩形。它返回左上角坐标( x , y )、宽度( width )、高度( height )和旋转角度。通过函数 cv2.boxPoints() 获取矩形的4个角点。
rect = cv2.minAreaRect(cnt)
box = cv2.boxPoints(rect)
box = np.int0(box)
img = cv2.drawContours(img,[box],0,(0,255,255),2)
步骤
您可以使用以下步骤来计算给定函数的雅可比矩阵:-
- 导入所需的库。所需的库是 OpenCV 和 NumPy 。
-
加载输入图像。将输入图像转换为灰度图像。
-
对灰度图像应用阈值处理以创建二值图像。
-
找到图像中物体的轮廓。
-
使用上述轮廓计算直角边界矩形。在图像上画出矩形。
-
计算旋转边界矩形并在图像上绘制它。
-
显示带有直角和旋转边界矩形的图像。
我们将使用以下图像作为 输入文件 在以下示例中。
示例1
在下面的Python代码中,我们计算直角边界矩形。
# import required libraries
import cv2
# read the input image
img = cv2.imread('approx.png')
# convert the image to grayscale
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# apply thresholding on the gray image to create a binary image
ret,thresh = cv2.threshold(gray,127,255,0)
# find the contours
contours, _ = cv2.findContours(thresh,cv2.RETR_TREE,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
# take the first contour
cnt = contours[0]
# compute the bounding rectangle of the contour
x,y,w,h = cv2.boundingRect(cnt)
# draw contour
img = cv2.drawContours(img,[cnt],0,(0,255,255),2)
# draw the bounding rectangle
img = cv2.rectangle(img,(x,y),(x+w,y+h),(0,255,0),2)
# display the image with bounding rectangle drawn on it
cv2.imshow("Bounding Rectangle", img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
输出结果
当您执行上述代码时,它将产生以下输出窗口。
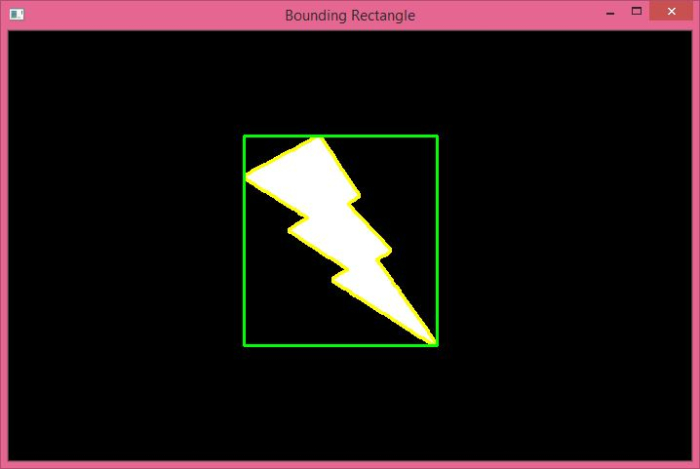
在上面的输出中,绿色矩形显示了直边界矩形。
现在,让我们计算一个包围最小面积的旋转边界矩形。请参考以下示例。
示例2
在下面的Python代码中,我们同时计算直边界矩形和旋转边界矩形。通过比较输出窗口来清楚理解两种类型边界矩形之间的区别。
import cv2
import numpy as np
img = cv2.imread('approx.png')
img1 = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
ret,thresh = cv2.threshold(img1,127,255,0)
contours,_ = cv2.findContours(thresh, cv2.RETR_TREE,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
# print("Number of contours detected:", len(contours))
cnt = contours[0]
# compute straight bounding rectangle
x,y,w,h = cv2.boundingRect(cnt)
img = cv2.drawContours(img,[cnt],0,(255,255,0),2)
img = cv2.rectangle(img,(x,y),(x+w,y+h),(0,255,0),2)
# compute rotated rectangle (minimum area)
rect = cv2.minAreaRect(cnt)
box = cv2.boxPoints(rect)
box = np.int0(box)
# draw minimum area rectangle (rotated rectangle)
img = cv2.drawContours(img,[box],0,(0,255,255),2)
cv2.imshow("Bounding Rectangles", img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
输出
当你执行上述代码时,它将产生以下输出窗口。
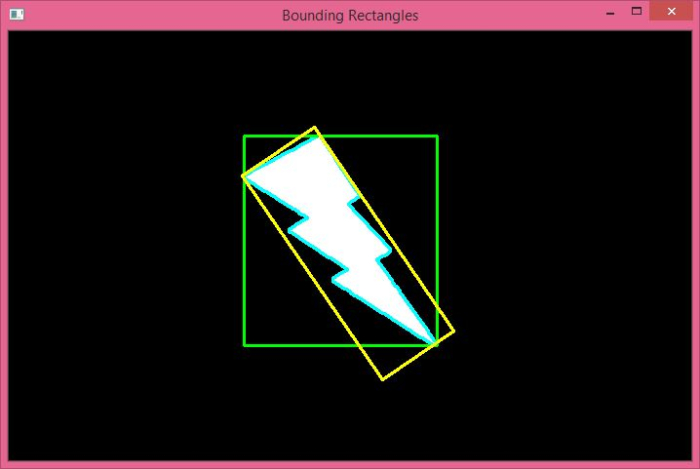
在上述输出中,绿色矩形是直边界矩形,黄色矩形是具有最小面积的旋转矩形。请注意两个矩形之间的差异。
 极客笔记
极客笔记