使用Python中的元类进行元编程
元编程可能听起来很新鲜,但如果用户以前使用过装饰器或元类,那么他们在项目中已经使用过元编程。因此,我们可以说元编程是用于操作程序的程序。
在本教程中,我们将讨论元类及其用途以及其替代方法。由于这是一个高级主题, Python 的用户在开始本教程之前建议复习“ Python中的装饰器 ”和“ Python中的面向对象编程概念 ”的基本概念。
元类
在Python中,每个模块或函数都与某种类型相关联。例如,如果用户有一个具有整数值的变量,那么它与“int”类型相关联。用户可以使用type()方法来知道任何东西的类型。
示例:
number = 13
print("Type of number is:", type(num))
list = [3, 7, 8]
print("Type of list is:", type(list))
name = "Mark Jackson"
print("Type of name is:", type(name))
输出:
Type of number is: <class 'int'>
Type of list is: <class 'list'>
Type of name is: <class 'str'>
解释-
在Python中,每种类型都由类来定义。因此,在上面的示例中,它们是’int’、’list’或’str’类类型的对象,与C语言或Java语言中的int、char和float等基本数据类型不同。用户可以通过创建该类型的类来创建新类型。例如,我们可以通过City类创建新的Object类型。
示例:
class City:
pass
City_object = City()
# now, we will print the type of object of City class
print("Type of City_object is:", type(City_object))
输出:
Type of City_object is: <class '__main__.City'>
在Python中,类也是一个对象,因此像其他对象一样,它是元类的一个实例。元类是一种特殊的类类型,负责创建类和类对象。因此,例如,如果用户想要查找”City”类的类型,他们会发现它是”type”。
示例:
class City:
pass
# now, we will print the type of the City class
print("Type of City class is:", type(City))
输出:
Type of City class is: <class 'type'>
由于类也是对象,我们可以对其进行修改。例如,用户可以像对待其他对象一样,添加或减去类中的字段或函数。
示例:
# First, we will define the class without any using any class methods or variables.
class City:
pass
# now, we will define the method variables
City.a = 65
# we will now, define the class methods
City.foo = lambda self: print('Pune')
# then, we will create the object
userobject = City()
print(userobject.a)
userobject.foo()
输出:
65
Pune
我们可以将整个元类总结为:
元类用于创建类,而这些类可以创建对象。
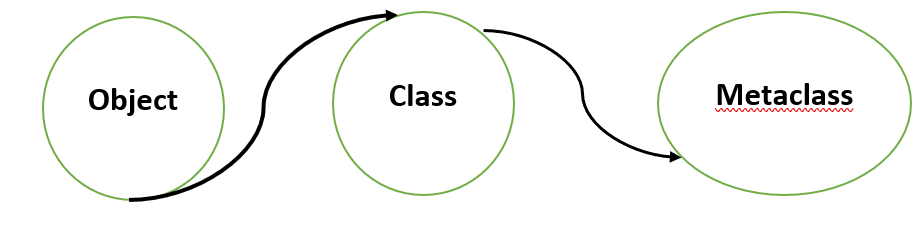
元类负责创建类,以便用户可以通过插入代码或额外操作来编写其自定义的元类,以修改类的创建方式。通常情况下,用户不需要自定义元类,但在特殊情况下是必要的。
使用元类或非元类可以解决一些问题,但有些情况下只能使用元类来解决。
如何创建自定义元类
要创建自定义元类,用户自定义的元类必须继承自type元类,并通常进行覆盖,例如:
- __new__(): new() 函数在 init() 函数之前执行。它用于创建对象并返回。用户可以覆盖此函数来控制对象的创建方式。
- __init__(): init() 函数用于初始化传递给它的已创建对象。
用户可以直接使用 type() 方法创建类。type() 方法可以以以下方式调用:
- 如前面的示例所示,用户可以使用一个参数调用它,它将返回类型。
- 用户可以使用三个参数调用它。它将创建类。以下参数将传递给它:
- 类名
- 传递以类继承的基类组成的元组
- 类字典:将作为类的局部命名空间,并填充函数和变量。
示例:
def City_method(self):
print("This is City class method!")
# we will create the base class
class Base:
def userfunction(self):
print("This is a inherited method!")
# we will create the city class dynamically by using
# type() function.
City = type('City', (Base, ), dict(a = "Mark Jackson", user_method = City_method))
# now, we will print the type of City
print("The Type of City class: ", type(City))
# we will create the instance of City class
City_object = City()
print(" The Type of City_object: ", type(City_object))
# we will now call the inherited method
City_object.userfunction()
# we will call the City class method
City_object.user_method()
# at last we will print the variable
print(City_object.a)
输出:
The Type of City class: <class 'type'>
The Type of City_object: <class '__main__.City'>
This is a inherited method!
This is City class method!
Mark Jackson
现在,让我们看看如何在不直接使用type()函数的情况下创建一个元类。例如,我们将创建一个名为MultiBases的元类,它将检查正在创建的类是否从多个基类继承。如果是这样,它将引发一个错误。
示例:
# Inside the metaclass
class MultiBases(type):
# we will override the __new__() function
def __new__(city, city_name, bases, citydict):
# if the number of base classes are greator than 1
# it will raise an error
if len(bases)>1:
raise TypeError("There are inherited multiple base classes!!!")
# else it will execute the __new__() function of super class, that is
# it will call the __init__() function of type class
return super().__new__(city, city_name, bases, citydict)
# the metaclass can be specified by using 'metaclass' keyword argument
# now we will use the MultiBase class for creating classes
# this will be propagated to all subclasses of Base
class Base(metaclass = MultiBases):
pass
# this will raise no error
class P(Base):
pass
# this will raise no error
class Q(Base):
pass
# this will raise no error
class R(Base):
pass
# This will raise an error!
class S(P, Q, R):
pass
输出:
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
TypeError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-2-409c90c285d5> in <module>
29 pass
30 # This will raise an error!
---> 31 class S(P, Q, R):
32 pass
<ipython-input-2-409c90c285d5> in __new__(city, city_name, bases, citydict)
6 # it will raise an error
7 if len(bases)>1:
----> 8 raise TypeError("There are inherited multiple base classes!!!")
9
10 # else it will execute the __new__() function of super class, that is
TypeError: There are inherited multiple base classes!!!
如何解决使用元类的问题
有一些问题可以通过使用元类和装饰器来解决。但有些问题只能通过使用元类来解决。例如,用户想要调试类函数,他们希望在执行类函数之前打印出其完整限定名称。
示例:
from functools import wraps
def debugg(funct):
'''decorator for debugging passed function'''
@wraps(funct)
def wrapperr(*args, **kwargs):
print("The full name of this Function:", funct.__qualname__)
return funct(*args, **kwargs)
return wrapperr
def debug_methods(clas):
'''class decorator make use of debug decorator
for debuging the class functions '''
# now we will check in the class dictionary for any callable(function)
# if there is any, replace it with debugged version
for key, value in vars(clas).items():
if callable(value):
setattr(clas, key, debugg(value))
return clas
# sample class
@debugmethods
class Calculator:
def add(self, p, q):
return p+q
def mul(self, p, q):
return p*q
def div(self, p, q):
return p/q
user_cal = Calculator()
print(user_cal.add(5, 8))
print(user_cal.mul(6, 7))
print(user_cal.div(21, 7))
输出:
The full name of this method: Calculator.add
13
The full name of this method: Calculator.mul
42
The full name of this method: Calculator.div
3.0
解释 –
上述解决方案运行正常,但是存在一个问题,即用户希望将装饰器方法应用于所有继承了 “Calculator” 类的子类。因此,在这种情况下,用户必须分别将装饰器方法应用于每个子类,就像我们在上面的示例中对 “Calculator” 类所做的那样。
现在,实际问题是类可能有很多子类,并且单独将装饰器方法应用于每个子类是具有挑战性和耗时的过程。因此,为了解决这个问题,用户必须确保每个子类都具有此调试属性,他们应该寻找基于元类的解决方案。
示例:
我们将按照正常方式创建这个类,然后立即使用 debug 方法装饰器进行包装:
from functools import wraps
def debugg(funct):
'''decorator for debugging passed function'''
@wraps(funct)
def wrapperr(*args, **kwargs):
print("The full name of this Function:", funct.__qualname__)
return funct(*args, **kwargs)
return wrapperr
def debug_methods(clas):
'''class decorator will make use of the debug decorator
to the debug class '''
for key, value in vars(clas).items():
if callable(value):
setattr(clas, key, debugg(value))
return clas
class debug_Meta(type):
'''meta class which feed created class object
to debug_method for getting debug functionality
enabled objects'''
def __new__(clas, clasname, bases, clasdict):
object = super().__new__(clas, clasname, bases, clasdict)
object = debug_methods(object)
return object
# the base class with metaclass 'debug_Meta'
# now all the subclass of this will have the applied debugging function
class Base(metaclass = debug_Meta):pass
# now, we will inherite the Base
class Calculator(Base):
def add(self, p, q):
return p+q
#and then, we will inherite the Calculator
class Calculator_adv(Calculator):
def mult(self, p, q):
return p*q
# Now Calculator_adv object will show
# the behaviour og debugging
user_cal = Calculator_adv()
print(user_cal.add(3, 7))
user_cal = Calculator_adv()
print(user_cal.mult(3, 7))
输出:
The full name of this Function: Calculator.add
10
The full name of this Function: Calculator_adv.mult
21
用户何时应该使用元类
大多数情况下,用户不会经常使用元类,因为元类主要用于复杂的情况。但是有些情况下,用户可以使用元类:
- 如上例所示,元类用于生成继承层次结构。这将影响所有的子类。如果用户遇到这样的情况,他们可以使用元类。
- 如果用户想要在创建类时自动更改类,他们可以使用元类。
- 如果用户是应用程序编程接口(API)开发人员,他们可以使用元类来实现这个目的。
结论
在本教程中,我们讨论了元类,如何自定义元类以及用户如何使用它们来解决问题和复杂的编程以及它们的替代方法。
 极客笔记
极客笔记