如何使用Python写入文本文件
在本教程中,我们将解释用户如何使用Python语言写入文本文件。
Python有一个内置的函数来创建、写入或读取文件。它可以处理两种类型的文件:普通文本文件和二进制文件。
- 普通文本文件: 在文本文件中,文本的每一行都以特殊字符“行尾”(EOL)终止。在Python中,默认情况下是换行符(’\n’)。
- 二进制文件: 在二进制文件中,没有行以特殊字符终止,数据在转换为机器二进制语言之后存储。
示例:(展示用户如何使用Python写入文本文件)
with open ('writeme.txt', 'w') as file:
file.write('writeme')
在文本文件中进行写入的步骤
使用Python在文本文件中进行写入时,用户需要按照以下步骤操作:
- 步骤1: 用户需要使用open()函数打开要写入或追加的文本文件。
- 步骤2: 用户可以使用write()或writelines()函数在文本文件中进行写入。
- 步骤3: 用户可以使用close()函数关闭文本文件。
语法: 打开文件
file = open (path_to_the_file, mode)
open()函数可以接受各种参数。但用户必须关注前两个:
- “path_to_the_file”参数用于指定用户要打开以写入的文本文件的路径。
- mode参数用于指定用户要打开文本文件的模式(写入、读取等)。
为了在文本文件中进行写入,用户将使用以下模式:
| 模式 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| ‘w’ | 用于打开文本文件以写入文本。 |
| ‘a’ | 用于打开文本文件以追加文本。 |
open()函数将返回文件对象,文件对象将有两个有用的函数来写入文件中的文本:
- write()
- writelines()
write()函数用于将字符串写入文本文件中,writelines()函数用于一次将字符串列表写入文件中。
writelines()函数还可以接受可迭代对象。用户还可以传递字符串元组、字符串集等。
为将行写入文本文件,用户必须手动添加换行符。
示例1:展示用户如何在Text.txt文件中添加换行符
file.write('\n')
file.writelines('\n')
这完全取决于用户是否想要在下一行添加文本。
示例2:演示如何使用write()函数将文本列表写入文本文件中
lines_1 = ['Text', 'this is the example to show how the user can write in the text file by using Python']
with open ('text.txt', 'w') as file:
for line_1 in lines_1:
file.write(line_1)
file.write('\n')
输出:

如果文件夹中不存在text.txt文件,open()函数将创建新文件。
示例3:展示用户如何将文本字符串列表写入text.txt文件中。
lines_1 = ['Text 2', ' This is the example no. 3 to show how the user can write in the text file by using Python']
with open ('text.txt', 'w') as file:
for line_1 in lines_1:
file.writelines(line_1)
输出:
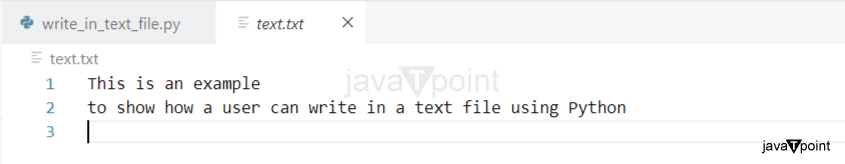
如果用户将列表的每个元素视为行,则必须使用换行符将其连接起来。
示例4:演示用户如何将换行符与文本.txt文件中的每个行元素连接起来
lines_1 = ['Text 2.', ' This is the example no. 3 to show how the user can write in the text file by using Python.']
with open ('text_2.txt', 'w') as file:
for line_1 in lines_1:
file.write('\n'.join(lines_1))
输出:

结论
在本教程中,我们解释了用户如何使用Python及其不同的函数在文本文件中编写文本。
 极客笔记
极客笔记