C++ 集合数组
数组被定义为以连续方式存储的数据项的集合。数组存储相同类型的不同变量。由于它们存储在连续位置,因此更容易访问这些变量。
例如
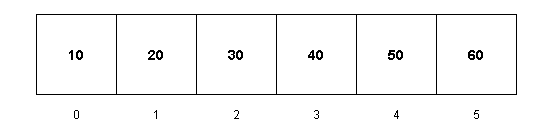
这是一个包含六个元素的数组。假设数组的名称是arr[]。现在,如果我们想要访问这些元素,它们可以访问到0到n-1的索引。这里,n是数组的大小。
Arr[0] = 10
Arr[1] = 20
Arr[2] = 30
Arr[3] = 40
Arr[4] = 50
Arr[5] = 60
集合
集合是一种关联容器,其中的元素是唯一的。与数组不同,添加到集合中的值在添加后不能修改。然而,如果我们想要更新集合中的值,我们可以先删除它,然后再输入修改后的值。
语法
set<data_type> variable_name
示例
set<int> s —– 一组整数值的集合
set<char> c —- 一组字符值的集合
集合的数组
当我们说一个集合的数组时,它是一个具有固定行数的二维数组。每一行可以有可变长度。
在集合的数组中,每个数组索引存储一个集合。可以通过迭代器访问该集合。
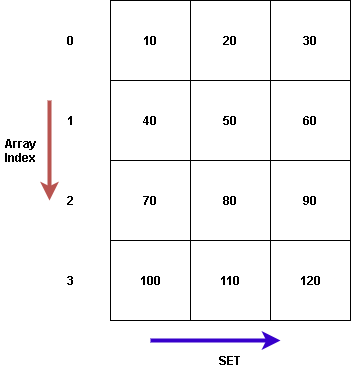
set<data_type> variable_name[size_of_array]
示例
set<int> s[3] —-> 大小为3的整型set数组
插入操作在set数组中
插入操作使用insert()函数,因为每一行都是一个set。所以我们使用set数组进行插入操作,使用以下方法 –
set_variable[行号].insert(元素)
示例
s[0].insert(10) —-> 在第1行插入10
s[1].insert(20)—-> 在第2行插入20
代码
#include
using namespace std;
#define ROW 3
#define COL 4
int main()
{
set s[ROW]; // Create an array of sets
int num = 10; // Initial element to be inserted
for (int i = 0; i < ROW; i++) { // iterate in row
// Insert the column elements
for (int j = 0; j < COL; j++) {
s[i].insert(num);
num += 10;
}
}
// Display the array of sets
for (int i = 0; i < ROW; i++) {
cout << "Row " << i + 1 << " = "
<< "Elements at index " << i << ": ";
// Print the array of sets
for (auto x : s[i])
cout << x << " ";
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
输出
Row 1 = Elements at index 0: 10 20 30 40
Row 2 = Elements at index 1: 50 60 70 80
Row 3 = Elements at index 2: 90 100 110 120
在一个集合数组中的删除操作
当我们说在这里删除元素时,我们是从集合中移除该元素。从集合中移除元素的函数是 erase() 。
代码
在这个示例中,我们从集合3中移除了一个元素,从集合2中移除了一个元素。记住,集合索引是i-1,因为数组索引从0开始。
#include
using namespace std;
// Fixing rows and column
#define ROW 3
#define COL 4
int main()
{
set s[ROW]; // Create array of set
int num = 10;
// Put elements in the set at a increment of 10
for (int i = 0; i < ROW; i++) {
// insert the column elements
for (int j = 0; j < COL; j++) {
s[i].insert(num);
num += 10;
}
}
cout << "Before removal elements are:"
<< endl;
// Print elements after insertion
for (int i = 0; i < ROW; i++) {
cout << "Elements at index "
<< i << ": ";
for (auto x : s[i])
cout << x << " ";
cout << endl;
}
s[2].erase(100); // Erase 100 from row 3 which means set 3
s[1].erase(50); // Erase 50 from row 2 which means set 2
cout << endl
<< "After removal elements are:" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < ROW; i++) {
cout << "Elements at index " << i << ": ";
// Print the current set
for (auto x : s[i])
cout << x << " ";
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
输出
Before removal elements are:
Elements at index 0: 10 20 30 40
Elements at index 1: 50 60 70 80
Elements at index 2: 90 100 110 120
After removal elements are:
Elements at index 0: 10 20 30 40
Elements at index 1: 60 70 80
Elements at index 2: 90 110 120
在数组集合中进行遍历操作
当我们遍历数组集合时,我们会通过每个集合迭代并打印出该集合中的所有元素。迭代器用于遍历集合元素。
代码
在下面的示例中,我们创建一个有两行的数组集合。第一行的集合中有三个元素,第二行的集合中有两个元素。
要遍历数组集合,我们运行一个外部循环来处理行。在内部循环中,我们使用迭代器来打印每个集合。
#include
using namespace std;
#define ROW 2 // Making a set of 2 rows
int main()
{
set s[ROW]; // create an array of sets with 2 rows
// Insertion in row 1
s[0].insert(10); // insertion in column 1
s[0].insert(15); // insertion in column 2
s[0].insert(35); // insertion in column 3
// Insertion in row 2
s[1].insert(20); // insertion in column 1
s[1].insert(30); // insertion in column 2
// Traversal in array of sets
for (int i = 0; i < ROW; i++) { // Iterate in the row
cout << "Elements at index " << i << ": ";
// Now we have to Iterate in the set of a particular row
// So use an Iterate that runs from begin of set to end of that set
for (auto it = s[i].begin(); it != s[i].end(); it++) {
// Print the set value
cout << *it << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
输出
Elements at index 0: 10 15 35
Elements at index 1: 20 30
 极客笔记
极客笔记