C++ 使用优先队列实现的Dijkstra算法
在本文中,我们将看到使用C++ STL的优先队列实现Dijkstra算法。 Dijkstra算法用于在无向图中从源点到目标点寻找最短路径。
给定如下的有权边图:
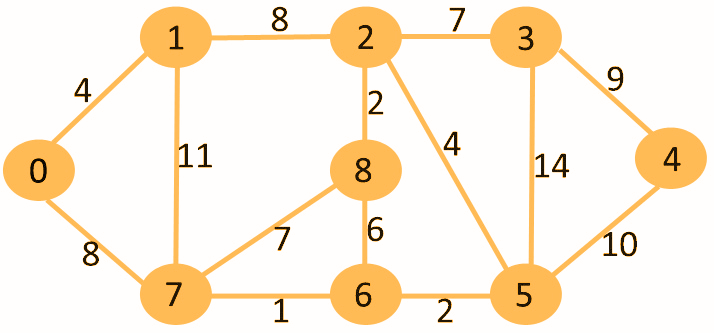
让我们考虑一个源顶点 0, 我们需要找出从源顶点到图中所有顶点的最短路径。
源顶点 = 0
| 顶点 | 距离源点的距离 |
|---|---|
| 0 | 0 从源点到目的地相同 |
| 1 | 4 直接到达1 |
| 2 | 12 路径:0 -> 1 -> 2 (8 + 4 = 12) |
| 3 | 19 路径:0 -> 1 -> 2 -> 3 (8 + 4 + 7 = 19) |
| 4 | 21 路径:0 -> 7 -> 6 -> 5 -> 4 (8 + 1 + 2 + 10 = 21) |
| 5 | 11 路径:0 -> 7 -> 6 -> 5 (8 + 1 + 2 = 11) |
| 6 | 9 路径:0 -> 7 -> 6 (8 + 1 = 9) |
| 7 | 8 路径:0 -> 7 |
| 8 | 14 路径:0 -> 1 -> 2 -> 8 (4 + 8 + 2 = 14) |
创建图结构
我们将创建一个名为Graph的类,其数据成员为:
- int v - 用于存储图中顶点的数量
- 以列表形式存储的配对 – 用于存储顶点以及与特定顶点相关的权重
< list<pair,pair>> *adj;
构造函数:
我们需要一个构造函数来分配邻接表的内存。
Graph(int vertex)
{
this->V = vertex; // Allocate the number of vertices
adj = list [vertex]; // Allocate memory for adjacency list
}
如何向图中添加边
创建的一组成对的列表有两个参数。一个参数包含顶点,另一个参数包含与之关联的权重。
由于图是双向的,我们可以将相同的权重添加到相反的顶点上。
代码:
void addanEdge(int u, int v, int w)
{
adj[u].push_back(make_pair(v,w)); // add v to w
adj[v].push_back(make_pair(u,w)); add w to v
// To add a vertex with weight associated with it
}
算法
- 标记源节点的初始距离为无穷大。
- 创建一个空的优先队列PQ。PQ的每个项目都是一个配对项(权重,顶点)。权重(或距离)被用作配对项的第一个项目,默认情况下第一个项目用于比较两个配对项。
- 将源顶点插入PQ并将其距离设为0。
- 直到定义为PQ的优先队列为空为止。执行操作a和b。
1. 从PQ中提取最小距离的顶点,记为u。
2. 循环遍历u的所有相邻顶点,并对每个顶点v执行以下操作。 // 如果通过u存在一条更短的路径到达v。 如果dist[v] > dist[u] + weight(u, v) // (v)的距离 > (u)的距离加上从u到v的权重- 更新v的距离,即执行 dist[v] = dist[u] + weight(u, v)
- 将v插入优先队列PQ(即使v已经存在)
- 循环遍历dist[]数组以打印从源到所有顶点的最短路径。
C++代码
#include
using namespace std;
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f // The distance to other vertices is initialized as infinite
// iPair ==> Integer Pair
typedef pair iPair;
class Graph // Graph structure
{
int V; // No. of vertices in the graph
list>* adj; // the list of pair to store vertex and its weight
public:
// Constructor that accept number of vertices in graph
Graph(int V) // allocate the vertex memory
{
this->V = V; // assign the vertex
adj = new list[V]; // allocate space for vertices
}
void addEdge(int u, int v, int w); // add edges in the graph
// prints shortest path from s
void shortestPathingraph(int s); // pass source vertex
};
void Graph::addEdge(int u, int v, int w) // add an edge
{
adj[u].push_back(make_pair(v, w)); // make a pair of vertex and weight and // add it to the list
adj[v].push_back(make_pair(u, w)); // add oppositely by making a pair of weight and vertex
}
// Calling function outside the Graph class
void Graph::shortestPathingraph(int src) // src is the source vertex
{
// Create a priority queue to store vertices that
// are being preprocessed.
priority_queue, greater> pq;
vector dist(V, INF); // All distance from source are infinite
pq.push(make_pair(0, src)); // push spurce node into the queue
dist[src] = 0; // distance of source will be always 0
while (!pq.empty()) { // While queue is not empty
// Extract the first minimum distance from the priority queue
// vertex label is stored in second of pair (it
// has to be done this way to keep the vertices
// sorted distance
int u = pq.top().second;
pq.pop();
// 'i' is used to get all adjacent vertices of a vertex
list>::iterator i;
for (i = adj[u].begin(); i != adj[u].end(); ++i) {
// Get vertex label and weight of current adjacent
// of u.
int v = (*i).first;
int weight = (*i).second;
// If there is shorted path to v through u.
if (dist[v] > dist[u] + weight) {
// Updating distance of v
dist[v] = dist[u] + weight;
pq.push(make_pair(dist[v], v));
}
}
}
printf("Vertex \tDistance from Source\n"); // Print the result
for (int i = 0; i < V; ++i)
printf("%d \t\t %d\n", i, dist[i]); // The shortest distance from source
}
int main()
{
int V = 9; // vertices in given graph are 9
Graph g(V); // call Constructor by creating an object of graph
g.addEdge(0, 1, 4); // add root node with neighour vertex and weight
g.addEdge(0, 7, 8);
g.addEdge(1, 2, 8);
g.addEdge(1, 7, 11);
g.addEdge(2, 3, 7);
g.addEdge(2, 8, 2);
g.addEdge(2, 5, 4);
g.addEdge(3, 4, 9);
g.addEdge(3, 5, 14);
g.addEdge(4, 5, 10);
g.addEdge(5, 6, 2);
g.addEdge(6, 7, 1);
g.addEdge(6, 8, 6);
g.addEdge(7, 8, 7);
g.shortestPathingraph(0); // call the function to find shortest path of graph
return 0; // end of main function()
}
输出
Vertex Distance from Source
0 0
1 4
2 12
3 19
4 21
5 11
6 9
7 8
8 14
 极客笔记
极客笔记