Tkinter Text 存储Text控件内容
当使用编辑程序完成文件的编排后,下一步是将所编排的文件存储,这也将是本节的重点。
示例1
一个简单文档存储的程序,这个程序在File菜单中只包含两个功能:Save和Exit。Save可以将所编辑的文档存储在apidemos.txt,Exit则是结束此程序。程序执行时窗口标题是apidemos.com,当文档存储后窗口标题将改为所存储的文档名apidemos.txt。
from tkinter import *
def saveFile():
textContent = text.get("1.0",END)
filename = "apidemos.txt"
with open(filename,"w") as output:
output.write(textContent)
root.title(filename)
root = Tk()
root.title("apidemos.com")
root.geometry("300x180")
menubar = Menu(root) # 建立最上层菜单
# 建立菜单类别对象,并将此菜单命名为File
filemenu = Menu(menubar,tearoff=False)
menubar.add_cascade(label="File",menu=filemenu)
# 在File菜单内建立菜单列表
filemenu.add_command(label="Save",command=saveFile)
filemenu.add_command(label="Exit",command=root.destroy)
root.config(menu=menubar)
# 建立Text
text = Text(root,undo=True)
text.pack(fill=BOTH,expand=True)
text.insert(END,"Five Hundred Miles\n") # 插入时同时设置Tag
text.insert(END,"If you miss the rain I am on,\n")
text.insert(END,"You will knw that I am gone.\n")
text.insert(END,"You can hear the whistle blw\n")
text.insert(END,"A hunded miles,\n")
root.mainloop() 输出:
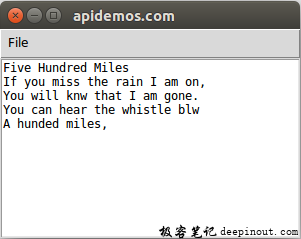
点击Save后:

下面是apidemos.txt的内容。
Five Hundred Miles
If you miss the rain I am on,
You will knw that I am gone.
You can hear the whistle blw
A hunded miles,上述程序虽然可以执行存储文档的工作,但不是GUI的设计方式,在GUI的设计中应该是启动“另存为”对话框,然后可以选择将文档存储的文件夹再输入文件名。在tkinter.f i ledialog模块中有asksaveasf i lename( )方法,我们可以使用此方法,让窗口出现对话框,再执行存储工作。
filename = asksaveasfilename()上述程序可以传回所存文档的路径(含文件夹)。
示例2
建立一个File菜单,在这个菜单内有Save As命令,执行此命令可以出现“Save as”对话框,然后可以选择文件夹以及输入文件名,最后存储文档。
from tkinter import *
from tkinter.filedialog import asksaveasfilename
def saveAsFile():
global filename
textContent = text.get("1.0",END)
filename = asksaveasfilename()
print("The file path passed back is : ",filename)
if filename == "":
return
with open(filename,"w") as output:
output.write(textContent)
root.title(filename)
filename = "apidemos"
root = Tk()
root.title(filename)
root.geometry("300x180")
menubar = Menu(root) # 建立最上层菜单
# 建立菜单类别对象,并将此菜单命名为File
filemenu = Menu(menubar,tearoff=False)
menubar.add_cascade(label="File",menu=filemenu)
# 在File菜单内建立菜单列表
filemenu.add_command(label="Save As",command=saveAsFile)
filemenu.add_separator()
filemenu.add_command(label="Exit",command=root.destroy)
root.config(menu=menubar)
# 建立Text
text = Text(root,undo=True)
text.pack(fill=BOTH,expand=True)
text.insert(END,"Five Hundred Miles\n") # 插入时同时设置Tag
text.insert(END,"If you miss the rain I am on,\n")
text.insert(END,"You will knw that I am gone.\n")
text.insert(END,"You can hear the whistle blw\n")
text.insert(END,"A hunded miles,\n")
root.mainloop() 输出:
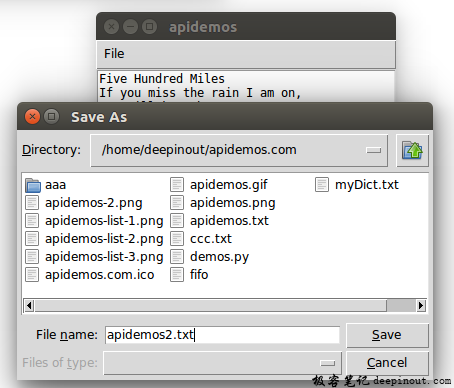
作者使用的文件名是apidemos2.txt,当单击“Save”按钮后,可以保存此文档,然后可以在窗口看到下列结果。
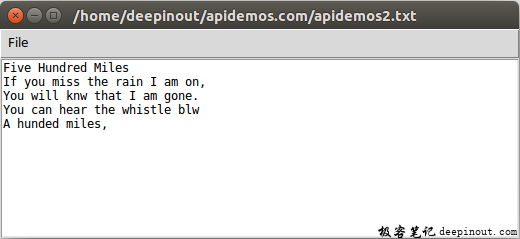
其实在正规的文字编辑程序中,需要考虑的事项有许多,例如,可以有Save命令,可以直接使用目前文件名存储文档,如果尚未存盘才出现“另存为”对话框。另外,也须考虑快捷键的使用,不过经过第16章和第17章的说明,相信读者已经有能力设计这方面的程序。
上述使用最简单的asksaveasfilename( )方法,其实在这个方法内有许多参数可以使用,例如在先前的执行结果中,必须在另存新文件对话框的文件名字段输入含扩展名的文件名,如果我们感觉所输入的文件名是txt文档,可以参考下列实例设置参数。
示例3
假设所建的文档是txt文档。
from tkinter import *
from tkinter.filedialog import asksaveasfilename
def saveAsFile():
global filename
textContent = text.get("1.0",END)
filename = asksaveasfilename(defaultextension=".txt")
print("The file path passed back is : ",filename)
if filename == "":
return
with open(filename,"w") as output:
output.write(textContent)
root.title(filename)
filename = "apidemos"
root = Tk()
root.title(filename)
root.geometry("300x180")
menubar = Menu(root) # 建立最上层菜单
# 建立菜单类别对象,并将此菜单命名为File
filemenu = Menu(menubar,tearoff=False)
menubar.add_cascade(label="File",menu=filemenu)
# 在File菜单内建立菜单列表
filemenu.add_command(label="Save As",command=saveAsFile)
filemenu.add_separator()
filemenu.add_command(label="Exit",command=root.destroy)
root.config(menu=menubar)
# 建立Text
text = Text(root,undo=True)
text.pack(fill=BOTH,expand=True)
text.insert(END,"Five Hundred Miles\n") # 插入时同时设置Tag
text.insert(END,"If you miss the rain I am on,\n")
text.insert(END,"You will knw that I am gone.\n")
text.insert(END,"You can hear the whistle blw\n")
text.insert(END,"A hunded miles,\n")
root.mainloop() 输出:
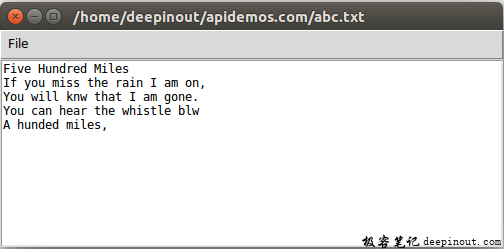
另存为时,我们只输入了abc,自动保存为abc.txt
 极客笔记
极客笔记