Python round() 函数
Python round() 方法返回浮点数 x 的四舍五入值,准确的说保留值将保留到离上一位更近的一端(四舍六入)。
精度要求高的,不建议使用该函数。
Python round() 语法
以下是 round() 方法的语法:
round( x [, n] )Python round() 参数
- x – 数字表达式。
- n – 表示从小数点位数,其中 x 需要四舍五入,默认值为 0。
Python round() 返回值
返回浮点数x的四舍五入值。
Python round() 示例1
以下展示了使用 round() 方法的实例:
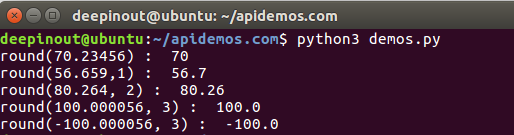
#!/usr/bin/python3
print ("round(70.23456) : ", round(70.23456))
print ("round(56.659,1) : ", round(56.659,1))
print ("round(80.264, 2) : ", round(80.264, 2))
print ("round(100.000056, 3) : ", round(100.000056, 3))
print ("round(-100.000056, 3) : ", round(-100.000056, 3))输出:
Python round() 示例2
>>> round(2.675, 2)
2.67按我们的想法返回结果应该是 2.68,可结果却是 2.67,为什么?
这跟浮点数的精度有关。我们知道在机器中浮点数不一定能精确表达,因为换算成一串 1 和 0 后可能是无限位数的,机器已经做出了截断处理。那么在机器中保存的2.675这个数字就比实际数字要小那么一点点。这一点点就导致了它离 2.67 要更近一点点,所以保留两位小数时就近似到了 2.67。
 极客笔记
极客笔记