MongoDB Shell集合方法
以下是用于不同场景的MongoDB集合方法。
db.collection.aggregate(pipeline, option)
aggregate方法用于计算集合/表或视图中数据的聚合值。
Pipeline: 这是一组用于数据的质量操作或阶段的数组。它可以作为单独的参数接受pipeline,而不是作为数组的元素。如果pipeline未指定为数组,则不会指定第二个参数。
Option: 传递聚合命令的文件。只有在将pipeline指定为数组时才可用。
命令字段:
| 字段 | 类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| explain | 布尔型 | explain字段用于返回流水线处理的信息。 |
| allowDiskUse | 布尔型 | allowDiskUse字段用于允许写入临时文件。 |
| cursor | 文档型 | cursor字段指定光标的初始批量大小。该字段内的值是具有batchSize字段的文档。 |
| maxTimeMS | 非负整数 | 使用该字段指定光标上的处理操作的时间限制。 |
| bypassDocument | 验证 | bypassDocument字段可用于指定out或merge聚合阶段。它允许聚合集合方法在操作期间绕过文档验证。 |
| readConcern | 文档型 | 使用该字段可以指定读取关注级别。 |
| collation | 文档型 | collation字段指定了字符串比较的语言特定规则。 |
示例
这些示例使用包含以下文档的集合库:
{ _id: 1, book_id: "Java", ord_date: ISODate("2012-11-02T17:04:11.102Z"), status: "A", amount: 50 }
{ _id: 0, book_id: "MongoDB", ord_date: ISODate("2013-10-01T17:04:11.102Z"), status: "A", amount: 100 }
{ _id: 0.01, book_id: "DBMS", ord_date: ISODate("2013-10-12T17:04:11.102Z"), status: "D", amount: 25 }
{ _id: 2, book_id: "Python", ord_date: ISODate("2013-10-11T17:04:11.102Z"), status: "D", amount: 125 }
{ _id: 0.02, book_id: "SQL", ord_date: ISODate("2013-11-12T17:04:11.102Z"), status: "A", amount: 25 }
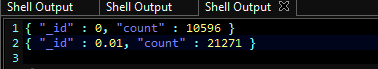
计算总和
db.library.aggregate([
{ match: { status: "A" } },
{group: { _id: "book_id", total: {count: "amount" } } },
{sort: { total: -1 } }
])
输出:
指定排序规则
db.library.aggregate(
[ { match: { status: "A" } }, {group: { _id: "ord_date", count: {count: 1 } } } ],
{ library: { locale: "fr", strength: 1 } } );
db.collection.bulkWrite()
bulkWrite()方法用于执行多个写入操作,并控制执行顺序。该方法会执行一系列的写入操作,操作默认按照特定顺序执行。
语法:
db.collection.bulkWrite(
[ <op. 1>, <op. 2>, .. ],
{
writeConcern : <document>,
ordered: <boolean>
}
)
输出:
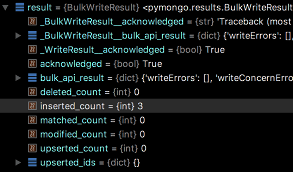
执行操作
insertOne: 将一个文档插入到集合中。
db.collection.bulkWrite( [
{ insertOne : { "document" : <document> } }
] )

updateOne: 它仅更新集合中与过滤器匹配的一个文档。
db.collection.bulkWrite( [
{ updateOne :
{
"filter": <document>,
"update": <document or pipeline>,
"upsert": <boolean>,
"collation": <document>,
"arrayFilters": [ <filterdocument1>, ... ],
"hint": <document|string>
}
}
] )
输出:
updateMany: 它会更新集合中所有匹配筛选条件的文档。
db.collection.bulkWrite( [
{ updateMany :{
"filter" : <doc.>,
"update" : <document or pipeline>,
"upsert" : <Boolean>,
"collation": <document>,
"arrayFilters": [ <filterdocument1>, ... ],
"hint": <document|string> // Available starting in 4.2.1
}
}
] )
replaceOne: 它用于替换集合中与过滤器匹配的单个文档。
db.collection.bulkWrite([
{ replaceOne :
{
"filter" : <doc.>,
"replacement" : <doc.>,
"upsert" : <boolean>,
"collation": <document>,
"hint": <document|string>
}
}
] )
db.collection.count(query, option)
count()方法返回与集合或视图的find方法查询匹配的文档数量。
示例:
我们将使用以下操作计算javaTpoint集合中的所有文档的数量:
db.javaTpoint.count()
现在,我们将统计javaTpoint集合中字段tut_dt大于new Date(’01/01/2015′)的所有匹配查询的文档数量
db.javaTpoint.count( { tut_dt: { $gt: new Date('01/01/2015') } } )
输出:
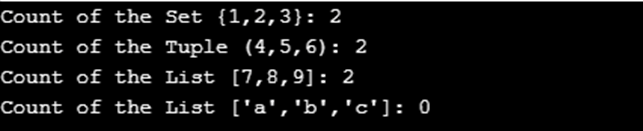
Db.collection.countDocuments(query, options)
countDocuments() 方法返回与集合或视图中的查询匹配的文档数量。它不会使用元数据返回计数。
语法:
db.collection.countDocuments( <query>, <options> )
示例:
下面的示例将计算javaTpoint集合中的所有文档的数量。
db.javaTpoint.countDocuments({})
现在,我们将计算javaTpoint集合中字段tut_dt大于new Date(’01/01/2015′)的所有与查询匹配的文档数量。
db.javaTpoint.countDocuments( { tut_dt: { $gt: new Date('01/01/2015') } } )
db.collection.estimatedDocumentCount()
estimatedDocumentCount()方法计算集合或视图中的所有文档。此方法封装了count命令。
语法:
db.collection.estimatedDocumentCount( <options> )
示例
下面的示例将检索 javaTpoint 集合中所有文档的数量:
db.javaTpoint.estimatedDocumentCount({})
db.collection.createIndex(keys, options)
键值:
对于在字段上进行升序索引,我们需要指定值为1;对于降序索引,我们需要指定值为-1。
示例
下面的示例在字段tut_Date上创建了一个升序索引。
db.collection.createIndex( { tut_Date: 1 } )
下面的示例显示了在tut_Date字段和tut_code字段上创建的复合索引。
db.collection.createIndex( { tut_Date: 1, tut_code: -1 } )
以下示例将创建一个名为category_tutorial的索引。该示例使用指定了区域设置为fr和比较强度的排序规则创建索引
db.collection.createIndex(
{ category: 1 },
{ name: "category_tutorial", collation: { locale: "fr", strength: 2 } }
)
db.collection.createIndexes()
createIndexes() 方法在集合上创建一个或多个索引。
语法:
db.collection.createIndexes( [keyPatterns, ]options)
关键模式: :它是一个包含索引特定文档的数组。所有的文档都有字段-值对。对于一个字段的升序索引,我们需要指定一个值为1,对于降序索引,我们需要指定一个值为-1。
示例
在下面的示例中,我们考虑了一个包含类似以下文档的员工集合:
{
location: {
type: "Point",
coordinates: [-73.8577, 40.8447]
},
name: "Employee",
company: "Amazon",
borough: "CA",
}
输出:
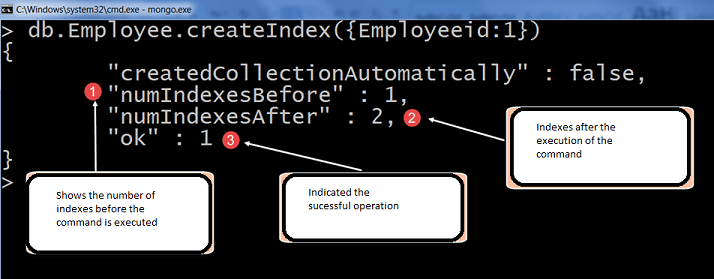
现在,下面的示例在products集合上创建了两个索引:
- 按照升序创建了一个在manufacturer字段上的索引。
- 按照升序创建了一个在category字段上的索引。
上述索引使用了一个排序规则,其中基本的法语规则和比较强度设置为2。
db.products.createIndexes( [ { "manufacturer": 1}, { "category": 1 } ],
{ collation: { locale: "fr", strength: 2 } })
db.collection.dataSize()
数据大小方法将覆盖collStats命令的输出(即db.collection.stats())。
db.collection.deleteOne()
deleteOne()方法从集合中删除一个文档。它替换与过滤器相似的第一个文档。您需要使用与唯一索引相关的字段(例如id)进行完美删除。
语法:
db.collection.deleteOne(
<filter>,
{
writeConcern: <document>,
collation: <document>
}
)
示例
订单集合具有以下结构的文档:
{
_id: objectId("563237a41a4d6859da"),
book: "",
qty: 2,
type: "buy-limit",
limit: 10,
creationts: ISODate("2015-11-01T2:30:15Z"),
expiryts: ISODate("2015-11-01T2:35:15Z"),
client: "JavaTpoint"
}
以下操作会删除 _id 为 objectId (“563237a41a4d6858 2da”) 的订单:
try {
db.orders.deleteOne( { "_id" : objectId("563237a41a4d68582da") } );
} catch (e) {
print(e);
}
输出:
 极客笔记
极客笔记