Matplotlib X轴设置为弧度坐标已经学习了怎么样在X轴上显示弧度,可以解决这个特殊的问题,不过有时候X轴上坐标也想使用角度来显示,又需要怎么样做呢?其实有了前面的basic_units.py模块,可以轻松地解决,无后顾之忧。如果你不能导入此文件,记得把它保存在例子源码目录下,这样导入就不会出错了。
前面使用的cos函数来画曲线,如果想使用sin函数来画曲线,发现不行了,因为basic_units.py模块里没有实现这个函数,那么就不能使用它了。这时只能自己动手参考cos函数来实现,其实也是很简单的,比如cos函数实现如下:
def cos(x):
if np.iterable(x):
return [math.cos(val.convert_to(radians).get_value()) for val in x]
else:
return math.cos(x.convert_to(radians).get_value())
可见只要把上面math.cos换成math.sin就可以了。np.iterable(x)是用来判断变量x是否是一个可以迭代的数组,如果是迭代数组就需要一个一个地计算,采用列表解释来执行。如果不是,只需要计算一次就行了。因此sin函数的代码如下:
def sin(x):
if np.iterable(x):
return [math.sin(val.convert_to(radians).get_value()) for val in x]
else:
return math.sin(x.convert_to(radians).get_value())
有了sin函数,就可以使用了,如下来调用:
ax.plot(rad_x, bu.sin(rad_x), ls = ‘-’, lw = 3, color = ‘b’, xunits = bu.degrees)
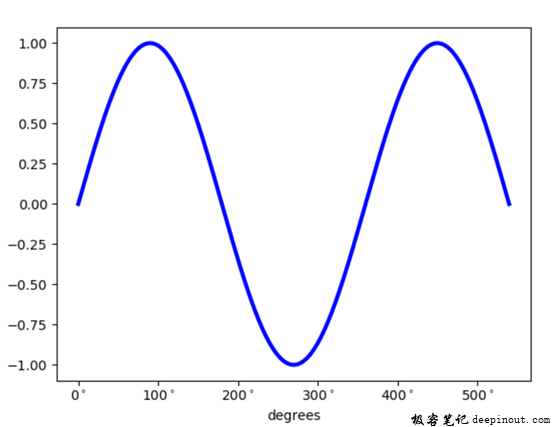
在这行代码里,与前文大体是一样的,主要区别在两点,一是把cos函数改为sin函数了;二是把radians改为bu.degrees,就可以进行角度单位在X轴上显示了,结果如下图:
整个完整的代码如下:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import basic_units as bu
#
fig, ax = plt.subplots() #创建子图
#
x = np.linspace(0, 3*np.pi, 500)
rad_x = [i*bu.radians for i in x]
#显示角度
ax.plot(rad_x, bu.sin(rad_x), ls = '-', lw = 3, color = 'b', xunits = bu.degrees)
plt.show()
新更新的basic_units.py源码如下:
"""
===========
Basic Units
===========
"""
import math
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.units as units
import matplotlib.ticker as ticker
class ProxyDelegate:
def __init__(self, fn_name, proxy_type):
self.proxy_type = proxy_type
self.fn_name = fn_name
def __get__(self, obj, objtype=None):
return self.proxy_type(self.fn_name, obj)
class TaggedValueMeta(type):
def __init__(self, name, bases, dict):
for fn_name in self._proxies:
if not hasattr(self, fn_name):
setattr(self, fn_name,
ProxyDelegate(fn_name, self._proxies[fn_name]))
class PassThroughProxy:
def __init__(self, fn_name, obj):
self.fn_name = fn_name
self.target = obj.proxy_target
def __call__(self, *args):
fn = getattr(self.target, self.fn_name)
ret = fn(*args)
return ret
class ConvertArgsProxy(PassThroughProxy):
def __init__(self, fn_name, obj):
super().__init__(fn_name, obj)
self.unit = obj.unit
def __call__(self, *args):
converted_args = []
for a in args:
try:
converted_args.append(a.convert_to(self.unit))
except AttributeError:
converted_args.append(TaggedValue(a, self.unit))
converted_args = tuple([c.get_value() for c in converted_args])
return super().__call__(*converted_args)
class ConvertReturnProxy(PassThroughProxy):
def __init__(self, fn_name, obj):
super().__init__(fn_name, obj)
self.unit = obj.unit
def __call__(self, *args):
ret = super().__call__(*args)
return (NotImplemented if ret is NotImplemented
else TaggedValue(ret, self.unit))
class ConvertAllProxy(PassThroughProxy):
def __init__(self, fn_name, obj):
super().__init__(fn_name, obj)
self.unit = obj.unit
def __call__(self, *args):
converted_args = []
arg_units = [self.unit]
for a in args:
if hasattr(a, 'get_unit') and not hasattr(a, 'convert_to'):
# if this arg has a unit type but no conversion ability,
# this operation is prohibited
return NotImplemented
if hasattr(a, 'convert_to'):
try:
a = a.convert_to(self.unit)
except Exception:
pass
arg_units.append(a.get_unit())
converted_args.append(a.get_value())
else:
converted_args.append(a)
if hasattr(a, 'get_unit'):
arg_units.append(a.get_unit())
else:
arg_units.append(None)
converted_args = tuple(converted_args)
ret = super().__call__(*converted_args)
if ret is NotImplemented:
return NotImplemented
ret_unit = unit_resolver(self.fn_name, arg_units)
if ret_unit is NotImplemented:
return NotImplemented
return TaggedValue(ret, ret_unit)
class TaggedValue(metaclass=TaggedValueMeta):
_proxies = {'__add__': ConvertAllProxy,
'__sub__': ConvertAllProxy,
'__mul__': ConvertAllProxy,
'__rmul__': ConvertAllProxy,
'__cmp__': ConvertAllProxy,
'__lt__': ConvertAllProxy,
'__gt__': ConvertAllProxy,
'__len__': PassThroughProxy}
def __new__(cls, value, unit):
# generate a new subclass for value
value_class = type(value)
try:
subcls = type(f'TaggedValue_of_{value_class.__name__}',
(cls, value_class), {})
return object.__new__(subcls)
except TypeError:
return object.__new__(cls)
def __init__(self, value, unit):
self.value = value
self.unit = unit
self.proxy_target = self.value
def __getattribute__(self, name):
if name.startswith('__'):
return object.__getattribute__(self, name)
variable = object.__getattribute__(self, 'value')
if hasattr(variable, name) and name not in self.__class__.__dict__:
return getattr(variable, name)
return object.__getattribute__(self, name)
def __array__(self, dtype=object):
return np.asarray(self.value).astype(dtype)
def __array_wrap__(self, array, context):
return TaggedValue(array, self.unit)
def __repr__(self):
return 'TaggedValue({!r}, {!r})'.format(self.value, self.unit)
def __str__(self):
return str(self.value) + ' in ' + str(self.unit)
def __len__(self):
return len(self.value)
def __iter__(self):
# Return a generator expression rather than use `yield`, so that
# TypeError is raised by iter(self) if appropriate when checking for
# iterability.
return (TaggedValue(inner, self.unit) for inner in self.value)
def get_compressed_copy(self, mask):
new_value = np.ma.masked_array(self.value, mask=mask).compressed()
return TaggedValue(new_value, self.unit)
def convert_to(self, unit):
if unit == self.unit or not unit:
return self
try:
new_value = self.unit.convert_value_to(self.value, unit)
except AttributeError:
new_value = self
return TaggedValue(new_value, unit)
def get_value(self):
return self.value
def get_unit(self):
return self.unit
class BasicUnit:
def __init__(self, name, fullname=None):
self.name = name
if fullname is None:
fullname = name
self.fullname = fullname
self.conversions = dict()
def __repr__(self):
return f'BasicUnit({self.name})'
def __str__(self):
return self.fullname
def __call__(self, value):
return TaggedValue(value, self)
def __mul__(self, rhs):
value = rhs
unit = self
if hasattr(rhs, 'get_unit'):
value = rhs.get_value()
unit = rhs.get_unit()
unit = unit_resolver('__mul__', (self, unit))
if unit is NotImplemented:
return NotImplemented
return TaggedValue(value, unit)
def __rmul__(self, lhs):
return self*lhs
def __array_wrap__(self, array, context):
return TaggedValue(array, self)
def __array__(self, t=None, context=None):
ret = np.array([1])
if t is not None:
return ret.astype(t)
else:
return ret
def add_conversion_factor(self, unit, factor):
def convert(x):
return x*factor
self.conversions[unit] = convert
def add_conversion_fn(self, unit, fn):
self.conversions[unit] = fn
def get_conversion_fn(self, unit):
return self.conversions[unit]
def convert_value_to(self, value, unit):
conversion_fn = self.conversions[unit]
ret = conversion_fn(value)
return ret
def get_unit(self):
return self
class UnitResolver:
def addition_rule(self, units):
for unit_1, unit_2 in zip(units[:-1], units[1:]):
if unit_1 != unit_2:
return NotImplemented
return units[0]
def multiplication_rule(self, units):
non_null = [u for u in units if u]
if len(non_null) > 1:
return NotImplemented
return non_null[0]
op_dict = {
'__mul__': multiplication_rule,
'__rmul__': multiplication_rule,
'__add__': addition_rule,
'__radd__': addition_rule,
'__sub__': addition_rule,
'__rsub__': addition_rule}
def __call__(self, operation, units):
if operation not in self.op_dict:
return NotImplemented
return self.op_dict[operation](self, units)
unit_resolver = UnitResolver()
cm = BasicUnit('cm', 'centimeters')
inch = BasicUnit('inch', 'inches')
inch.add_conversion_factor(cm, 2.54)
cm.add_conversion_factor(inch, 1/2.54)
radians = BasicUnit('rad', 'radians')
degrees = BasicUnit('deg', 'degrees')
radians.add_conversion_factor(degrees, 180.0/np.pi)
degrees.add_conversion_factor(radians, np.pi/180.0)
secs = BasicUnit('s', 'seconds')
hertz = BasicUnit('Hz', 'Hertz')
minutes = BasicUnit('min', 'minutes')
secs.add_conversion_fn(hertz, lambda x: 1./x)
secs.add_conversion_factor(minutes, 1/60.0)
# radians formatting
def rad_fn(x, pos=None):
if x >= 0:
n = int((x / np.pi) * 2.0 + 0.25)
else:
n = int((x / np.pi) * 2.0 - 0.25)
if n == 0:
return '0'
elif n == 1:
return r'\pi/2'
elif n == 2:
return r'\pi'
elif n == -1:
return r'-\pi/2'
elif n == -2:
return r'-\pi'
elif n % 2 == 0:
return fr'{n//2}\pi'
else:
return fr'{n}\pi/2'
class BasicUnitConverter(units.ConversionInterface):
@staticmethod
def axisinfo(unit, axis):
"""Return AxisInfo instance for x and unit."""
if unit == radians:
return units.AxisInfo(
majloc=ticker.MultipleLocator(base=np.pi/2),
majfmt=ticker.FuncFormatter(rad_fn),
label=unit.fullname,
)
elif unit == degrees:
return units.AxisInfo(
majloc=ticker.AutoLocator(),
majfmt=ticker.FormatStrFormatter(r'%i^\circ'),
label=unit.fullname,
)
elif unit is not None:
if hasattr(unit, 'fullname'):
return units.AxisInfo(label=unit.fullname)
elif hasattr(unit, 'unit'):
return units.AxisInfo(label=unit.unit.fullname)
return None
@staticmethod
def convert(val, unit, axis):
if units.ConversionInterface.is_numlike(val):
return val
if np.iterable(val):
if isinstance(val, np.ma.MaskedArray):
val = val.astype(float).filled(np.nan)
out = np.empty(len(val))
for i, thisval in enumerate(val):
if np.ma.is_masked(thisval):
out[i] = np.nan
else:
try:
out[i] = thisval.convert_to(unit).get_value()
except AttributeError:
out[i] = thisval
return out
if np.ma.is_masked(val):
return np.nan
else:
return val.convert_to(unit).get_value()
@staticmethod
def default_units(x, axis):
"""Return the default unit for x or None."""
if np.iterable(x):
for thisx in x:
return thisx.unit
return x.unit
def cos(x):
if np.iterable(x):
return [math.cos(val.convert_to(radians).get_value()) for val in x]
else:
return math.cos(x.convert_to(radians).get_value())
def sin(x):
if np.iterable(x):
return [math.sin(val.convert_to(radians).get_value()) for val in x]
else:
return math.sin(x.convert_to(radians).get_value())
units.registry[BasicUnit] = units.registry[TaggedValue] = BasicUnitConverter()
 极客笔记
极客笔记