我们知道做实验,以及写各种报告,很多时候都需要与弧度打交道,因为很多现象都具有周期性,而周期性的数据往往就需要使用三角函数。比如我们日常使用的交流电,通常交流电(简称AC)波形为正弦曲线。交流电可以有效传输电力。但实际上还有应用其他的波形,例如三角形波、正方形波。生活中使用的市电就是具有正弦波形的交流电。由于电源的基础是正弦波,那么在做各种电器实验时,往往就引入正弦波的干扰因素,而分析这种情况时,就需要使用弧度来显示数据,显示数据时,需要把X轴设置为弧度坐标,显示弧度的单位PI。由于PI是一个特殊的符号,要在坐标轴显示,不是那么容易的事情,需要使用一些特殊的技巧。不过,如果你学习过前面的文章,也许会了,因为就是使用公式显示的方式来改写坐轴的标签。这个过程,如果自己来写代码实现,还是需要一些时间和技巧的,幸运的是,已经有人写好了代码,我们直接来使用吧。
这份代码是来源于matplotlib的例子,它的github地址:
https://github.com/matplotlib/matplotlib/blob/master/examples/units/basic_units.py
整个源码如下:
"""
===========
Basic Units
===========
"""
import math
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.units as units
import matplotlib.ticker as ticker
class ProxyDelegate:
def __init__(self, fn_name, proxy_type):
self.proxy_type = proxy_type
self.fn_name = fn_name
def __get__(self, obj, objtype=None):
return self.proxy_type(self.fn_name, obj)
class TaggedValueMeta(type):
def __init__(self, name, bases, dict):
for fn_name in self._proxies:
if not hasattr(self, fn_name):
setattr(self, fn_name,
ProxyDelegate(fn_name, self._proxies[fn_name]))
class PassThroughProxy:
def __init__(self, fn_name, obj):
self.fn_name = fn_name
self.target = obj.proxy_target
def __call__(self, *args):
fn = getattr(self.target, self.fn_name)
ret = fn(*args)
return ret
class ConvertArgsProxy(PassThroughProxy):
def __init__(self, fn_name, obj):
super().__init__(fn_name, obj)
self.unit = obj.unit
def __call__(self, *args):
converted_args = []
for a in args:
try:
converted_args.append(a.convert_to(self.unit))
except AttributeError:
converted_args.append(TaggedValue(a, self.unit))
converted_args = tuple([c.get_value() for c in converted_args])
return super().__call__(*converted_args)
class ConvertReturnProxy(PassThroughProxy):
def __init__(self, fn_name, obj):
super().__init__(fn_name, obj)
self.unit = obj.unit
def __call__(self, *args):
ret = super().__call__(*args)
return (NotImplemented if ret is NotImplemented
else TaggedValue(ret, self.unit))
class ConvertAllProxy(PassThroughProxy):
def __init__(self, fn_name, obj):
super().__init__(fn_name, obj)
self.unit = obj.unit
def __call__(self, *args):
converted_args = []
arg_units = [self.unit]
for a in args:
if hasattr(a, 'get_unit') and not hasattr(a, 'convert_to'):
# if this arg has a unit type but no conversion ability,
# this operation is prohibited
return NotImplemented
if hasattr(a, 'convert_to'):
try:
a = a.convert_to(self.unit)
except Exception:
pass
arg_units.append(a.get_unit())
converted_args.append(a.get_value())
else:
converted_args.append(a)
if hasattr(a, 'get_unit'):
arg_units.append(a.get_unit())
else:
arg_units.append(None)
converted_args = tuple(converted_args)
ret = super().__call__(*converted_args)
if ret is NotImplemented:
return NotImplemented
ret_unit = unit_resolver(self.fn_name, arg_units)
if ret_unit is NotImplemented:
return NotImplemented
return TaggedValue(ret, ret_unit)
class TaggedValue(metaclass=TaggedValueMeta):
_proxies = {'__add__': ConvertAllProxy,
'__sub__': ConvertAllProxy,
'__mul__': ConvertAllProxy,
'__rmul__': ConvertAllProxy,
'__cmp__': ConvertAllProxy,
'__lt__': ConvertAllProxy,
'__gt__': ConvertAllProxy,
'__len__': PassThroughProxy}
def __new__(cls, value, unit):
# generate a new subclass for value
value_class = type(value)
try:
subcls = type(f'TaggedValue_of_{value_class.__name__}',
(cls, value_class), {})
return object.__new__(subcls)
except TypeError:
return object.__new__(cls)
def __init__(self, value, unit):
self.value = value
self.unit = unit
self.proxy_target = self.value
def __getattribute__(self, name):
if name.startswith('__'):
return object.__getattribute__(self, name)
variable = object.__getattribute__(self, 'value')
if hasattr(variable, name) and name not in self.__class__.__dict__:
return getattr(variable, name)
return object.__getattribute__(self, name)
def __array__(self, dtype=object):
return np.asarray(self.value).astype(dtype)
def __array_wrap__(self, array, context):
return TaggedValue(array, self.unit)
def __repr__(self):
return 'TaggedValue({!r}, {!r})'.format(self.value, self.unit)
def __str__(self):
return str(self.value) + ' in ' + str(self.unit)
def __len__(self):
return len(self.value)
def __iter__(self):
# Return a generator expression rather than use `yield`, so that
# TypeError is raised by iter(self) if appropriate when checking for
# iterability.
return (TaggedValue(inner, self.unit) for inner in self.value)
def get_compressed_copy(self, mask):
new_value = np.ma.masked_array(self.value, mask=mask).compressed()
return TaggedValue(new_value, self.unit)
def convert_to(self, unit):
if unit == self.unit or not unit:
return self
try:
new_value = self.unit.convert_value_to(self.value, unit)
except AttributeError:
new_value = self
return TaggedValue(new_value, unit)
def get_value(self):
return self.value
def get_unit(self):
return self.unit
class BasicUnit:
def __init__(self, name, fullname=None):
self.name = name
if fullname is None:
fullname = name
self.fullname = fullname
self.conversions = dict()
def __repr__(self):
return f'BasicUnit({self.name})'
def __str__(self):
return self.fullname
def __call__(self, value):
return TaggedValue(value, self)
def __mul__(self, rhs):
value = rhs
unit = self
if hasattr(rhs, 'get_unit'):
value = rhs.get_value()
unit = rhs.get_unit()
unit = unit_resolver('__mul__', (self, unit))
if unit is NotImplemented:
return NotImplemented
return TaggedValue(value, unit)
def __rmul__(self, lhs):
return self*lhs
def __array_wrap__(self, array, context):
return TaggedValue(array, self)
def __array__(self, t=None, context=None):
ret = np.array([1])
if t is not None:
return ret.astype(t)
else:
return ret
def add_conversion_factor(self, unit, factor):
def convert(x):
return x*factor
self.conversions[unit] = convert
def add_conversion_fn(self, unit, fn):
self.conversions[unit] = fn
def get_conversion_fn(self, unit):
return self.conversions[unit]
def convert_value_to(self, value, unit):
conversion_fn = self.conversions[unit]
ret = conversion_fn(value)
return ret
def get_unit(self):
return self
class UnitResolver:
def addition_rule(self, units):
for unit_1, unit_2 in zip(units[:-1], units[1:]):
if unit_1 != unit_2:
return NotImplemented
return units[0]
def multiplication_rule(self, units):
non_null = [u for u in units if u]
if len(non_null) > 1:
return NotImplemented
return non_null[0]
op_dict = {
'__mul__': multiplication_rule,
'__rmul__': multiplication_rule,
'__add__': addition_rule,
'__radd__': addition_rule,
'__sub__': addition_rule,
'__rsub__': addition_rule}
def __call__(self, operation, units):
if operation not in self.op_dict:
return NotImplemented
return self.op_dict[operation](self, units)
unit_resolver = UnitResolver()
cm = BasicUnit('cm', 'centimeters')
inch = BasicUnit('inch', 'inches')
inch.add_conversion_factor(cm, 2.54)
cm.add_conversion_factor(inch, 1/2.54)
radians = BasicUnit('rad', 'radians')
degrees = BasicUnit('deg', 'degrees')
radians.add_conversion_factor(degrees, 180.0/np.pi)
degrees.add_conversion_factor(radians, np.pi/180.0)
secs = BasicUnit('s', 'seconds')
hertz = BasicUnit('Hz', 'Hertz')
minutes = BasicUnit('min', 'minutes')
secs.add_conversion_fn(hertz, lambda x: 1./x)
secs.add_conversion_factor(minutes, 1/60.0)
# radians formatting
def rad_fn(x, pos=None):
if x >= 0:
n = int((x / np.pi) * 2.0 + 0.25)
else:
n = int((x / np.pi) * 2.0 - 0.25)
if n == 0:
return '0'
elif n == 1:
return r'\pi/2'
elif n == 2:
return r'\pi'
elif n == -1:
return r'-\pi/2'
elif n == -2:
return r'-\pi'
elif n % 2 == 0:
return fr'{n//2}\pi'
else:
return fr'{n}\pi/2'
class BasicUnitConverter(units.ConversionInterface):
@staticmethod
def axisinfo(unit, axis):
"""Return AxisInfo instance for x and unit."""
if unit == radians:
return units.AxisInfo(
majloc=ticker.MultipleLocator(base=np.pi/2),
majfmt=ticker.FuncFormatter(rad_fn),
label=unit.fullname,
)
elif unit == degrees:
return units.AxisInfo(
majloc=ticker.AutoLocator(),
majfmt=ticker.FormatStrFormatter(r'%i^\circ'),
label=unit.fullname,
)
elif unit is not None:
if hasattr(unit, 'fullname'):
return units.AxisInfo(label=unit.fullname)
elif hasattr(unit, 'unit'):
return units.AxisInfo(label=unit.unit.fullname)
return None
@staticmethod
def convert(val, unit, axis):
if units.ConversionInterface.is_numlike(val):
return val
if np.iterable(val):
if isinstance(val, np.ma.MaskedArray):
val = val.astype(float).filled(np.nan)
out = np.empty(len(val))
for i, thisval in enumerate(val):
if np.ma.is_masked(thisval):
out[i] = np.nan
else:
try:
out[i] = thisval.convert_to(unit).get_value()
except AttributeError:
out[i] = thisval
return out
if np.ma.is_masked(val):
return np.nan
else:
return val.convert_to(unit).get_value()
@staticmethod
def default_units(x, axis):
"""Return the default unit for x or None."""
if np.iterable(x):
for thisx in x:
return thisx.unit
return x.unit
def cos(x):
if np.iterable(x):
return [math.cos(val.convert_to(radians).get_value()) for val in x]
else:
return math.cos(x.convert_to(radians).get_value())
units.registry[BasicUnit] = units.registry[TaggedValue] = BasicUnitConverter()
暂时我们知道使用这个源码就可以了,先不管它里面实现的原理。下面就来实现一个X轴显示弧度的例子,如下图:
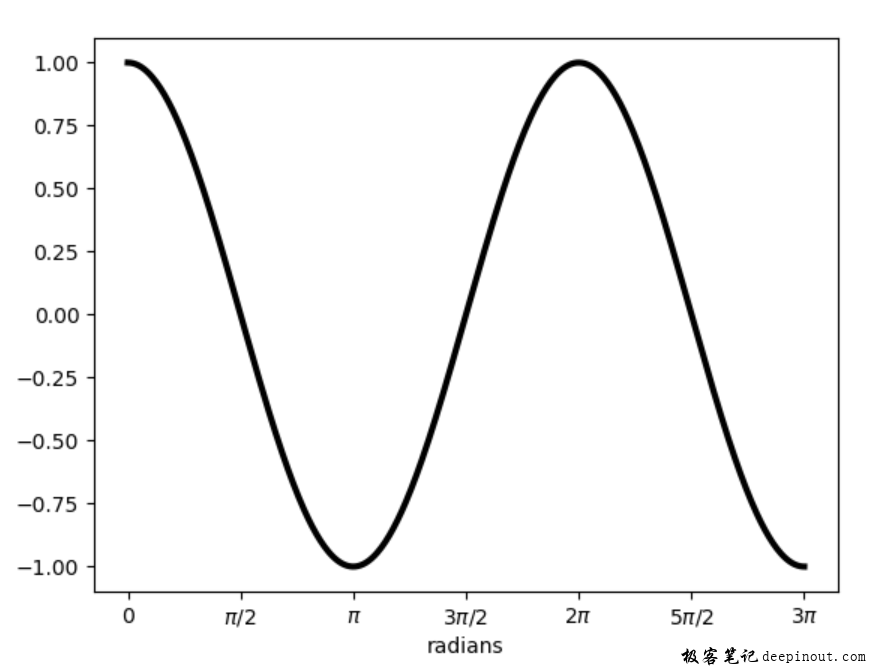
可以看到X轴的文字已经显示PI的符号,这是一个余弦函数曲线的图。其实有了basic_units.py的功能之后,实现这个显示就非常简单了,只需要下面几行代码即可:
x = np.linspace(0, 3*np.pi, 500)
rad_x = [i*bu.radians for i in x]
第一行代码是生成0到3PI的数据点,共有500个,第二行代码是把数据转换为弧度单位的数据,这样很方便转换为角度的数据。
ax.plot(rad_x, bu.cos(rad_x), ls = '-', lw = 3, color = 'k', xunits = bu.radians)
这行代码是显示余弦函数曲线,第一个参数是弧度数据,第二个参数是调用basic_units.py 的函数bu.cos计算曲线。这里特别要注意xunits = bu.radians参数,这个参数可以改变X轴的符号显示,在这里弧度,如果把它修改为degrees,就会显示角度数据。
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import basic_units as bu
#
fig, ax = plt.subplots() #创建子图
#
x = np.linspace(0, 3*np.pi, 500)
rad_x = [i*bu.radians for i in x]
#显示弧度
ax.plot(rad_x, bu.cos(rad_x), ls = '-', lw = 3, color = 'k', xunits = bu.radians)
plt.show()
 极客笔记
极客笔记