ElectronJS中的HTTP REST API调用
我们可以选择从各种库中,如request、axios或fetch, 发送请求到我们的HTTP REST API端点。这样做可以让我们与API中的数据进行交互,并在ElectronJS应用程序中显示它。
ElectronJS是一个开源项目,由OpenJS Foundation和一群贡献者积极维护。我们可以使用HTML、JavaScript和CSS等Web技术来构建跨平台的桌面应用程序。
在本教程中,我们将学习如何在ElectronJS应用程序中使用HTTP REST API调用。
在ElectronJS中使用HTTP REST API调用的步骤
以下是在ElectronJS中使用HTTP REST API调用的基本步骤:
步骤1 - 首先,我们必须为我们的项目安装库。例如,我们可以使用以下命令安装axios:
npm install axios
步骤2 − 之后,为了从ElectronJS应用的渲染进程进行HTTP请求并在主进程中处理响应,我们需要使用ipcMain和ipcRenderer模块建立两个进程之间的通信。
在main.js文件中,我们可以为由渲染进程触发的事件设置监听器。例如 −
const { ipcMain } = require('electron');
ipcMain.on('get-data', (event, url) => {
// Handle the request here
});
在渲染进程中,我们可以使用ipcRenderer模块向主进程发送请求。举个示例−
const { ipcRenderer } = require('electron');
ipcRenderer.send('get-data', 'https://example.com/api/data');
步骤3 − 现在,我们可以使用库来对我们的REST API进行HTTP请求。
使用内置的 ‘net’ 模块进行HTTP请求
我们可以使用Electron.js中的内置net模块来进行HTTP请求。net模块提供了一个低级网络接口,可用于创建和与TCP服务器和客户端进行交互。虽然可以使用此模块来进行HTTP请求,但需要更多的工作和对HTTP协议的低级知识。
当涉及到进行HTTP请求时,Node.js的net模块相对于原生模块提供了许多优点。以下是使用net模块的一些好处−
- net模块支持wpad协议和代理pac配置文件。
-
它可以自动为HTTPS请求创建隧道。
-
该模块支持基本、摘要、NTLM、Kerberos或negotiate认证方案用于验证代理。
-
net模块还支持类似于Fiddler的用于访问控制和监视的代理。
以下是使用net模块进行HTTP请求的示例−
const net = require('net');
// Define the request
const request = `GET / HTTP/1.1\r
Host: example.com\r
\r
`;
// Create a TCP socket and connect to the server
const socket = net.createConnection({ host: 'example.com', port: 80 }, () => {
// Send the request to the server
socket.write(request);
});
// Receive the response from the server
socket.on('data', (data) => {
console.log(data.toString());
});
// Handle errors
socket.on('error', (err) => {
console.error(err);
});
示例
在这个示例中,我们使用axios库来发出一个HTTP请求到一个REST API。代码分为三部分:main.js、index.js和index.html。
在主进程中,应用程序监听来自渲染器进程的fetch-data事件。当接收到该事件时,它使用axios库向”https://catfact.ninja/fact” URL发出一个HTTP请求。在接收到响应数据后,主进程将使用响应数据将fetch-data-response事件发送回渲染器进程。
在渲染器进程中,index.js文件监听fetch-data-response事件,并使用响应数据更新HTML文档中的响应元素。然后,它向主进程发送fetch-data事件来触发HTTP请求。
最后,index.html文件包含应用程序UI的HTML代码,其中包括一个头部、一个响应div和一个加载index.js文件的脚本标签。
main.js
const { app, BrowserWindow, ipcMain } = require('electron');
const axios = require('axios');
function createWindow () {
const win = new BrowserWindow({
width: 800,
height: 600,
webPreferences: {
nodeIntegration: true,
contextIsolation: false
}
})
win.loadFile('index.html')
ipcMain.on('fetch-data', async (event, args) => {
try {
const response = await axios.get('https://catfact.ninja/fact');
event.reply('fetch-data-response', response.data);
} catch (error) {
console.error(error);
}
});
}
app.whenReady().then(createWindow);
index.js
const { ipcRenderer } = require('electron');
const responseElement = document.getElementById('response');
ipcRenderer.on('fetch-data-response', (event, data) => {
responseElement.innerHTML = JSON.stringify(data);
});
ipcRenderer.send('fetch-data');
index.html
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>My Electron App</title>
<style>
body{
text-align: center;
padding: 1rem;
}
p{
color: green;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1> HTTP Request Response: </h1>
<p id = "response" > </p>
<script src = "./index.js" > </script>
</body>
</html>
输出
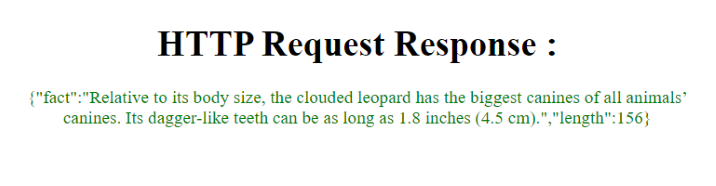
示例
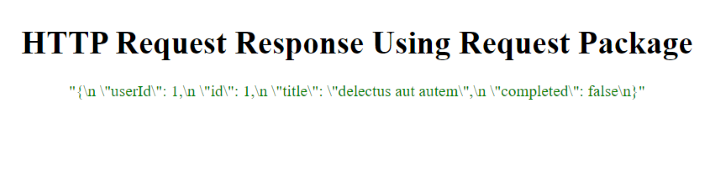
这个示例是一个使用 Electron.js 的应用程序,它使用 request 包向外部 API 发起 HTTP 请求。
这个应用程序由三个部分组成−
在 main.js 文件中,使用 request 包发起 HTTP 请求到外部 API,并使用 IPC 将响应发送到渲染进程。
index.js 文件负责接收来自主进程的响应,并更新 HTML 来显示响应内容。
而 index.html 文件是加载到 Electron.js 窗口中的 HTML 文件。它显示来自外部 API 的 HTTP 响应。
main.js
const { app, BrowserWindow, ipcMain } = require('electron');
const request = require('request');
function createWindow () {
const win = new BrowserWindow({
width: 800,
height: 600,
webPreferences: {
nodeIntegration: true,
contextIsolation: false
}
})
win.loadFile('index.html')
ipcMain.on('fetch-data', (event, args) => {
request('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/todos/1', (error, response, body) => {
if (error) {
console.error(error);
return;
}
event.reply('fetch-data-response', body);
});
});
}
app.whenReady().then(createWindow);
index.js
const { ipcRenderer } = require('electron');
const responseElement = document.getElementById('response');
ipcRenderer.on('fetch-data-response', (event, data) => {
responseElement.innerHTML = JSON.stringify(data);
});
ipcRenderer.send('fetch-data');
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset = "UTF-8">
<title> My Electron App </title>
<style>
body{
text-align: center;
padding: 1rem;
}
p{
color: green;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1> HTTP Request Response Using Request Package </h1>
<p id = "response"> </p>
<script src= "./index.js" ></script>
</body>
</html>
输出
本教程教会了我们在ElectronJS应用程序中使用HTTP REST API调用。我们讨论了安装和使用像Axios,Request或Fetch这样的库。
然后,我们通过两个示例演示了如何使用不同的库向REST API发出HTTP请求,并在ElectronJS应用程序中显示响应数据。
总的来说,通过在ElectronJS应用程序中使用HTTP REST API调用,我们可以与远程服务器的数据进行交互,并在应用程序中显示它,从而使我们能够构建功能强大且灵活的跨平台桌面应用程序。
 极客笔记
极客笔记