C++ 继承
在C++中,继承是一个对象自动获取其父对象的所有属性和行为的过程。通过这种方式,可以重用、扩展或修改在其他类中定义的属性和行为。
在C++中,继承另一个类的成员的类被称为派生类,而被继承成员的类被称为基类。派生类是基类的专门化类。
C++继承的优势
代码可重用性: 现在您可以重用父类的成员。因此,无需再次定义成员。所以类中所需的代码更少。
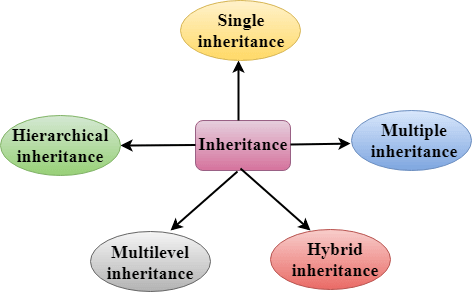
继承的类型
C++支持五种类型的继承:
- 单继承
- 多继承
- 层次继承
- 多级继承
- 混合继承
派生类
派生类是指从基类派生出来的类。
派生类的语法如下:
class derived_class_name :: visibility-mode base_class_name
{
// body of the derived class.
}
其中:
derived_class_name: 它是派生类的名称。
visibility mode: 可见性模式指定基类的特性是公开继承还是私有继承。它可以是public或private。
base_class_name: 它是基类的名称。
- 当派生类以私有方式继承基类时,基类的公有成员变为派生类的私有成员。因此,基类的公有成员只能由派生类的成员函数访问,而不能被派生类的对象访问。
- 当派生类以公有方式继承基类时,基类的公有成员也成为派生类的公有成员。因此,基类的公有成员既可以被派生类的对象访问,也可以被基类的成员函数访问。
注意:
- 在C++中,默认的可见性模式是私有。
- 基类的私有成员不会被继承。
C++单继承
单继承 被定义为只从一个基类继承的派生类。
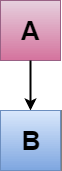
其中’A’是基类,’B’是派生类。
C++单层继承示例:继承字段
当一个类继承另一个类时,称为单层继承。让我们来看一个继承字段的单层继承示例。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Account {
public:
float salary = 60000;
};
class Programmer: public Account {
public:
float bonus = 5000;
};
int main(void) {
Programmer p1;
cout<<"Salary: "<<p1.salary<<endl;
cout<<"Bonus: "<<p1.bonus<<endl;
return 0;
}
输出:
Salary: 60000
Bonus: 5000
在上面的示例中,Employee是基类,Programmer是派生类。 C ++单层继承示例:继承方法 让我们看一个只继承方法的C ++继承的另一个示例。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Animal {
public:
void eat() {
cout<<"Eating..."<<endl;
}
};
class Dog: public Animal
{
public:
void bark(){
cout<<"Barking...";
}
};
int main(void) {
Dog d1;
d1.eat();
d1.bark();
return 0;
}
输出:
Eating...
Barking...
让我们看一个简单的例子。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A
{
int a = 4;
int b = 5;
public:
int mul()
{
int c = a*b;
return c;
}
};
class B : private A
{
public:
void display()
{
int result = mul();
std::cout <<"Multiplication of a and b is : "<<result<< std::endl;
}
};
int main()
{
B b;
b.display();
return 0;
}
输出:
Multiplication of a and b is : 20
在上面的例子中,类A是私有继承的。因此,类B的对象无法访问类A的mul()函数。它只能被类B的成员函数访问。
如何使私有成员可继承
私有成员是不可继承的。如果我们通过将其修改为公有来改变可见性模式,但这会带走数据隐藏的优点。
C++引入了第三个可见性修饰符,即 protected 。声明为protected的成员将对类内所有成员函数以及直接派生自它的类可访问。
可见性模式可以分为三类:
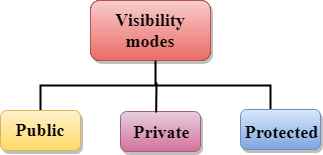
- 公共 :当成员被声明为
public时,可以被程序中的所有函数访问。 - 私有 :当成员被声明为
private时,只能在类内部访问。 - 受保护 :当成员被声明为
protected时,可以在自身类以及直接派生类中访问。
继承成员的可见性
| Base class visibility | Derived class visibility |
|---|---|
| Public | Private | Protected |
| Private | Not Inherited | Not Inherited | Not Inherited |
| Protected | Protected | Private | Protected |
| Public | Public | Private | Protected |
C++ 多级继承
多级继承 是从另一个派生类派生出一个类的过程。

C++多级继承示例
当一个类继承另一个类,而后者又被另一个类继承时,在C++中称为多级继承。继承是传递性的,因此最后一个派生类会继承所有其基类的成员。
让我们看一个C++中的多级继承示例。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Animal {
public:
void eat() {
cout<<"Eating..."<<endl;
}
};
class Dog: public Animal
{
public:
void bark(){
cout<<"Barking..."<<endl;
}
};
class BabyDog: public Dog
{
public:
void weep() {
cout<<"Weeping...";
}
};
int main(void) {
BabyDog d1;
d1.eat();
d1.bark();
d1.weep();
return 0;
}
输出:
Eating...
Barking...
Weeping...
C++多重继承
多重继承 是从两个或更多的类继承属性来派生一个新类的过程。
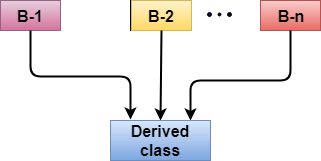
派生类的语法:
class D : visibility B-1, visibility B-2, ?
{
// Body of the class;
}
让我们来看一个多重继承的简单示例。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A
{
protected:
int a;
public:
void get_a(int n)
{
a = n;
}
};
class B
{
protected:
int b;
public:
void get_b(int n)
{
b = n;
}
};
class C : public A,public B
{
public:
void display()
{
std::cout << "The value of a is : " <<a<< std::endl;
std::cout << "The value of b is : " <<b<< std::endl;
cout<<"Addition of a and b is : "<<a+b;
}
};
int main()
{
C c;
c.get_a(10);
c.get_b(20);
c.display();
return 0;
}
输出:
The value of a is : 10
The value of b is : 20
Addition of a and b is : 30
在上面的例子中,类’C’以公共模式继承了两个基类’A’和’B’。
继承中的歧义解决
在使用多重继承时,当一个函数在多个基类中出现相同的名称时,就会发生歧义。
让我们通过一个例子来理解:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A
{
public:
void display()
{
std::cout << "Class A" << std::endl;
}
};
class B
{
public:
void display()
{
std::cout << "Class B" << std::endl;
}
};
class C : public A, public B
{
void view()
{
display();
}
};
int main()
{
C c;
c.display();
return 0;
}
输出:
error: reference to 'display' is ambiguous
display();
- 解决上述问题可以使用类解析操作符来处理函数。在上面的示例中,派生类的代码可以重写为:
class C : public A, public B
{
void view()
{
A :: display(); // Calling the display() function of class A.
B :: display(); // Calling the display() function of class B.
}
};
单继承中也可能出现歧义。
考虑以下情况:
class A
{
public:
void display()
{
cout<<?Class A?;
}
} ;
class B
{
public:
void display()
{
cout<<?Class B?;
}
} ;
在上述情况下,派生类的函数覆盖了基类的方法。因此,对display()函数的调用将只是调用派生类中定义的函数。如果我们想调用基类函数,可以使用类解析运算符。
int main()
{
B b;
b.display(); // Calling the display() function of B class.
b.B :: display(); // Calling the display() function defined in B class.
}
C++混合继承
混合继承是多种类型继承的组合。
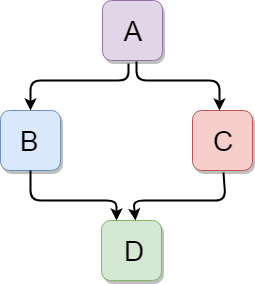
让我们来看一个简单的例子:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A
{
protected:
int a;
public:
void get_a()
{
std::cout << "Enter the value of 'a' : " << std::endl;
cin>>a;
}
};
class B : public A
{
protected:
int b;
public:
void get_b()
{
std::cout << "Enter the value of 'b' : " << std::endl;
cin>>b;
}
};
class C
{
protected:
int c;
public:
void get_c()
{
std::cout << "Enter the value of c is : " << std::endl;
cin>>c;
}
};
class D : public B, public C
{
protected:
int d;
public:
void mul()
{
get_a();
get_b();
get_c();
std::cout << "Multiplication of a,b,c is : " <<a*b*c<< std::endl;
}
};
int main()
{
D d;
d.mul();
return 0;
}
输出:
Enter the value of 'a' :
10
Enter the value of 'b' :
20
Enter the value of c is :
30
Multiplication of a,b,c is : 6000
C++ 层次化继承
层次化继承被定义为从一个基类派生出多个子类的过程。
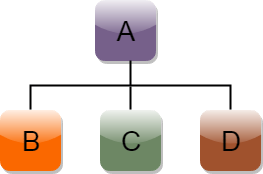
Hierarchical inheritance的语法:
class A
{
// body of the class A.
}
class B : public A
{
// body of class B.
}
class C : public A
{
// body of class C.
}
class D : public A
{
// body of class D.
}
让我们看一个简单的例子:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Shape // Declaration of base class.
{
public:
int a;
int b;
void get_data(int n,int m)
{
a= n;
b = m;
}
};
class Rectangle : public Shape // inheriting Shape class
{
public:
int rect_area()
{
int result = a*b;
return result;
}
};
class Triangle : public Shape // inheriting Shape class
{
public:
int triangle_area()
{
float result = 0.5*a*b;
return result;
}
};
int main()
{
Rectangle r;
Triangle t;
int length,breadth,base,height;
std::cout << "Enter the length and breadth of a rectangle: " << std::endl;
cin>>length>>breadth;
r.get_data(length,breadth);
int m = r.rect_area();
std::cout << "Area of the rectangle is : " <<m<< std::endl;
std::cout << "Enter the base and height of the triangle: " << std::endl;
cin>>base>>height;
t.get_data(base,height);
float n = t.triangle_area();
std::cout <<"Area of the triangle is : " << n<<std::endl;
return 0;
}
输出:
Enter the length and breadth of a rectangle:
23
20
Area of the rectangle is : 460
Enter the base and height of the triangle:
2
5
Area of the triangle is : 5
 极客笔记
极客笔记