Matplotlib中的axis.Axis.get_clip_box()函数详解与应用
参考:Matplotlib.axis.Axis.get_clip_box() function in Python
Matplotlib是Python中最流行的数据可视化库之一,它提供了丰富的绘图功能和自定义选项。在Matplotlib中,axis.Axis.get_clip_box()函数是一个重要的方法,用于获取轴的裁剪框。本文将深入探讨这个函数的用法、特性以及在实际绘图中的应用。
1. get_clip_box()函数简介
get_clip_box()函数是Matplotlib库中axis.Axis类的一个方法。它的主要作用是返回轴的裁剪框,即一个Bbox对象。裁剪框定义了轴的可见区域,任何超出这个区域的内容都会被裁剪掉。
1.1 函数语法
Axis.get_clip_box()
这个函数不需要任何参数,直接调用即可。
1.2 返回值
函数返回一个matplotlib.transforms.Bbox对象,代表轴的裁剪框。
2. 理解裁剪框(Clip Box)
裁剪框是一个矩形区域,定义了图形元素的可见部分。在Matplotlib中,裁剪框通常用于限制绘图区域,确保图形内容不会超出指定的边界。
2.1 裁剪框的重要性
裁剪框在以下几个方面起着重要作用:
- 控制可见区域
- 优化渲染性能
- 创建特殊的视觉效果
2.2 示例:获取并打印裁剪框信息
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot([1, 2, 3, 4], [1, 4, 2, 3], label='how2matplotlib.com')
clip_box = ax.xaxis.get_clip_box()
print(f"X轴裁剪框: {clip_box}")
plt.title('How2Matplotlib.com - Clip Box Example')
plt.show()
Output:
在这个示例中,我们创建了一个简单的线图,然后使用get_clip_box()方法获取x轴的裁剪框信息并打印出来。这有助于我们理解裁剪框的具体位置和大小。
3. get_clip_box()的实际应用
get_clip_box()函数在许多场景下都非常有用,特别是当我们需要精确控制图形元素的可见区域时。
3.1 调整图形元素位置
通过获取裁剪框信息,我们可以精确地调整图形元素的位置,确保它们在可见区域内正确显示。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.patches as patches
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot([1, 2, 3, 4], [1, 4, 2, 3], label='how2matplotlib.com')
clip_box = ax.xaxis.get_clip_box()
rect = patches.Rectangle((clip_box.x0, clip_box.y0), clip_box.width, clip_box.height,
linewidth=2, edgecolor='r', facecolor='none')
ax.add_patch(rect)
plt.title('How2Matplotlib.com - Visualizing Clip Box')
plt.show()
Output:
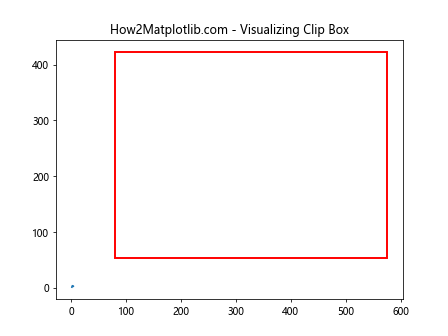
这个例子展示了如何使用get_clip_box()获取裁剪框信息,并在图上绘制一个矩形来可视化裁剪框的位置和大小。
3.2 创建自定义裁剪区域
我们可以利用get_clip_box()返回的信息来创建自定义的裁剪区域,从而实现更复杂的视觉效果。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
x = np.linspace(0, 10, 100)
y = np.sin(x)
ax.plot(x, y, label='how2matplotlib.com')
clip_box = ax.xaxis.get_clip_box()
custom_clip = plt.Rectangle((clip_box.x0, clip_box.y0), clip_box.width/2, clip_box.height,
facecolor='white', edgecolor='none')
ax.add_patch(custom_clip)
ax.set_clip_path(custom_clip)
plt.title('How2Matplotlib.com - Custom Clipping')
plt.show()
Output:
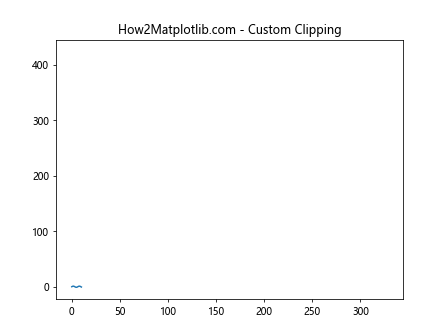
在这个示例中,我们使用get_clip_box()获取的信息创建了一个自定义的裁剪区域,只显示图表的左半部分。
4. 与其他Matplotlib函数的配合使用
get_clip_box()函数通常与其他Matplotlib函数结合使用,以实现更复杂的绘图效果。
4.1 与set_clip_box()配合
set_clip_box()函数可以设置新的裁剪框,与get_clip_box()配合使用可以实现动态调整裁剪区域。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.transforms as transforms
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot([1, 2, 3, 4], [1, 4, 2, 3], label='how2matplotlib.com')
original_clip_box = ax.xaxis.get_clip_box()
new_clip_box = transforms.Bbox([[1, 1], [3, 3]])
ax.set_clip_box(new_clip_box)
plt.title('How2Matplotlib.com - Modified Clip Box')
plt.show()
Output:
这个例子展示了如何获取原始裁剪框,然后设置一个新的裁剪框来限制图形的可见区域。
4.2 与get_clip_path()和set_clip_path()配合
结合使用get_clip_box()和get_clip_path()/set_clip_path()可以创建更复杂的裁剪效果。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.path as mpath
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot([1, 2, 3, 4], [1, 4, 2, 3], label='how2matplotlib.com')
clip_box = ax.xaxis.get_clip_box()
circle = mpath.Path.circle(center=(0, 0), radius=1)
circle_patch = mpath.PathPatch(circle, transform=ax.transData)
ax.set_clip_path(circle_patch)
plt.title('How2Matplotlib.com - Circular Clipping')
plt.show()
这个示例展示了如何使用get_clip_box()获取裁剪框信息,然后创建一个圆形的裁剪路径来限制图形的可见区域。
5. get_clip_box()在不同类型图表中的应用
get_clip_box()函数可以应用于各种类型的Matplotlib图表,包括散点图、柱状图、饼图等。
5.1 在散点图中的应用
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
x = np.random.rand(50)
y = np.random.rand(50)
scatter = ax.scatter(x, y, label='how2matplotlib.com')
clip_box = ax.xaxis.get_clip_box()
ax.set_xlim(clip_box.x0, clip_box.x0 + clip_box.width / 2)
plt.title('How2Matplotlib.com - Scatter Plot with Clipping')
plt.show()
Output:
这个例子展示了如何在散点图中使用get_clip_box()来限制x轴的显示范围。
5.2 在柱状图中的应用
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
x = ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E']
y = np.random.randint(1, 10, 5)
bars = ax.bar(x, y, label='how2matplotlib.com')
clip_box = ax.xaxis.get_clip_box()
for bar in bars[3:]:
bar.set_clip_on(True)
bar.set_clip_box(plt.Rectangle((clip_box.x0, clip_box.y0), clip_box.width/2, clip_box.height))
plt.title('How2Matplotlib.com - Bar Chart with Partial Clipping')
plt.show()
这个示例展示了如何在柱状图中使用get_clip_box()来部分裁剪某些柱子。
6. get_clip_box()在动画中的应用
get_clip_box()函数也可以在Matplotlib动画中发挥作用,用于创建动态的裁剪效果。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.animation as animation
import numpy as np
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
x = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, 100)
line, = ax.plot(x, np.sin(x), label='how2matplotlib.com')
clip_box = ax.xaxis.get_clip_box()
rect = plt.Rectangle((clip_box.x0, clip_box.y0), 0, clip_box.height, facecolor='white')
ax.add_patch(rect)
def animate(frame):
rect.set_width(frame * clip_box.width / 100)
return rect,
ani = animation.FuncAnimation(fig, animate, frames=100, interval=50, blit=True)
plt.title('How2Matplotlib.com - Animated Clipping')
plt.show()
Output:
这个例子展示了如何使用get_clip_box()创建一个动画效果,逐渐显示正弦波图形。
7. get_clip_box()在3D图形中的应用
虽然get_clip_box()主要用于2D图形,但它在3D图形中也有一些应用。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
import numpy as np
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
x = np.random.rand(100)
y = np.random.rand(100)
z = np.random.rand(100)
scatter = ax.scatter(x, y, z, label='how2matplotlib.com')
clip_box = ax.xaxis.get_clip_box()
ax.set_xlim(clip_box.x0, clip_box.x0 + clip_box.width / 2)
plt.title('How2Matplotlib.com - 3D Scatter Plot with Clipping')
plt.show()
Output:
这个示例展示了如何在3D散点图中使用get_clip_box()来限制x轴的显示范围。
8. get_clip_box()在子图中的应用
当使用子图时,get_clip_box()可以帮助我们精确控制每个子图的显示区域。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(10, 5))
x = np.linspace(0, 10, 100)
y1 = np.sin(x)
y2 = np.cos(x)
ax1.plot(x, y1, label='how2matplotlib.com - Sin')
ax2.plot(x, y2, label='how2matplotlib.com - Cos')
clip_box1 = ax1.xaxis.get_clip_box()
clip_box2 = ax2.xaxis.get_clip_box()
ax1.set_xlim(clip_box1.x0, clip_box1.x0 + clip_box1.width / 2)
ax2.set_xlim(clip_box2.x0 + clip_box2.width / 2, clip_box2.x1)
plt.suptitle('How2Matplotlib.com - Subplots with Different Clipping')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Output:
这个例子展示了如何在两个子图中分别使用get_clip_box()来设置不同的显示范围。
9. get_clip_box()与自定义样式的结合
get_clip_box()可以与Matplotlib的自定义样式功能结合使用,创造出独特的视觉效果。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
plt.style.use('seaborn')
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
x = np.linspace(0, 10, 100)
y = np.sin(x)
ax.plot(x, y, label='how2matplotlib.com')
clip_box = ax.xaxis.get_clip_box()
custom_clip = plt.Rectangle((clip_box.x0, clip_box.y0), clip_box.width, clip_box.height/2,
facecolor='lightgray', alpha=0.5)
ax.add_patch(custom_clip)
plt.title('How2Matplotlib.com - Custom Style with Clipping')
plt.show()
这个示例展示了如何结合自定义样式和get_clip_box()来创建一个半透明的遮罩效果。
10. 处理get_clip_box()的常见问题
在使用get_clip_box()时,可能会遇到一些常见问题。以下是一些解决方案:
10.1 裁剪框不准确
有时get_clip_box()返回的裁剪框可能不够准确。这通常是因为图形还没有完全渲染。解决方法是在获取裁剪框之前调用fig.canvas.draw()。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot([1, 2, 3, 4], [1, 4, 2, 3], label='how2matplotlib.com')
fig.canvas.draw()
clip_box = ax.xaxis.get_clip_box()
print(f"更准确的裁剪框: {clip_box}")
plt.title('How2Matplotlib.com - Accurate Clip Box')
plt.show()
Output:
10.2 与tight_layout()的兼容性
使用tight_layout()可能会影响裁剪框的位置。在这种情况下,可以在调用tight_layout()后再获取裁剪框。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot([1, 2, 3, 4], [1, 4, 2, 3], label='how2matplotlib.com')
plt.tight_layout()
clip_box = ax.xaxis.get_clip_box()
print(f"tight_layout后的裁剪框: {clip_box}")
plt.title('How2Matplotlib.com - Clip Box with Tight Layout')
plt.show()
Output:
11. get_clip_box()在不同Matplotlib版本中的变化
Matplotlib的不同版本可能会对get_clip_box()的行为有细微的改变。了解这些变化对于维护跨版本兼容的代码很重要。
11.1 版本兼容性检查
import matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot([1, 2, 3, 4], [1, 4, 2, 3], label='how2matplotlib.com')
clip_box = ax.xaxis.get_clip_box()
print(f"Matplotlib版本: {matplotlib.__version__}")
print(f"裁剪框: {clip_box}")
plt.title(f'How2Matplotlib.com - Version {matplotlib.__version__}')
plt.show()
Output:
这个示例可以帮助你检查不同版本的Matplotlib中get_clip_box()的行为。
12. get_clip_box()与其他图形库的对比
虽然get_clip_box()是Matplotlib特有的方法,但其他图形库也有类似的功能。了解这些差异可以帮助我们在不同库之间进行选择。
12.1 与Plotly的对比
Plotly是另一个流行的Python绘图库,它使用不同的方法来处理裁剪。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import plotly.graph_objects as go
# Matplotlib
fig_mpl, ax_mpl = plt.subplots()
ax_mpl.plot([1, 2, 3, 4], [1, 4, 2, 3], label='how2matplotlib.com')
clip_box_mpl = ax_mpl.xaxis.get_clip_box()
print(f"Matplotlib裁剪框: {clip_box_mpl}")
# Plotly
fig_plotly = go.Figure(data=go.Scatter(x=[1, 2, 3, 4], y=[1, 4, 2, 3], name='how2matplotlib.com'))
layout = fig_plotly.layout
print(f"Plotly布局: {layout}")
plt.title('How2Matplotlib.com - Matplotlib vs Plotly')
plt.show()
Output:
这个例子展示了Matplotlib和Plotly在处理图形边界和裁剪方面的不同方法。
13. get_clip_box()在数据可视化项目中的实际应用
在实际的数据可视化项目中,get_clip_box()可以用于创建更复杂和交互式的图表。
13.1 创建可缩放的图表
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
x = np.linspace(0, 10, 100)
y = np.sin(x)
line, = ax.plot(x, y, label='how2matplotlib.com')
clip_box = ax.xaxis.get_clip_box()
zoom_factor = 0.5
def zoom(event):
global zoom_factor
if event.button == 'up':
zoom_factor *= 1.1
elif event.button == 'down':
zoom_factor /= 1.1
new_width = clip_box.width * zoom_factor
new_height = clip_box.height * zoom_factor
ax.set_xlim(clip_box.x0, clip_box.x0 + new_width)
ax.set_ylim(clip_box.y0, clip_box.y0 + new_height)
fig.canvas.draw_idle()
fig.canvas.mpl_connect('scroll_event', zoom)
plt.title('How2Matplotlib.com - Zoomable Plot')
plt.show()
Output:
这个示例创建了一个可以通过鼠标滚轮缩放的图表,利用get_clip_box()来获取初始的图表边界。
14. get_clip_box()在科学计算中的应用
在科学计算和数据分析中,get_clip_box()可以用于精确控制数据的显示范围,特别是在处理大量数据时。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
# 生成大量数据点
x = np.linspace(0, 100, 10000)
y = np.sin(x) + np.random.normal(0, 0.1, 10000)
ax.plot(x, y, label='how2matplotlib.com', alpha=0.5)
clip_box = ax.xaxis.get_clip_box()
# 只显示中间20%的数据
ax.set_xlim(clip_box.x0 + 0.4*clip_box.width, clip_box.x0 + 0.6*clip_box.width)
plt.title('How2Matplotlib.com - Data Subset Visualization')
plt.show()
Output:
这个例子展示了如何使用get_clip_box()来只显示大量数据中的一个子集。
15. 结合get_clip_box()和自定义绘图函数
我们可以结合get_clip_box()和自定义绘图函数来创建更复杂的可视化效果。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
def custom_plot(ax, x, y, clip_box):
line, = ax.plot(x, y, label='how2matplotlib.com')
mask = (x >= clip_box.x0) & (x <= clip_box.x1)
ax.fill_between(x[mask], y[mask], alpha=0.3)
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
x = np.linspace(0, 10, 100)
y = np.sin(x)
clip_box = ax.xaxis.get_clip_box()
custom_plot(ax, x, y, clip_box)
plt.title('How2Matplotlib.com - Custom Plot with Clip Box')
plt.show()
Output:
这个示例展示了如何创建一个自定义绘图函数,该函数使用get_clip_box()返回的信息来决定填充区域的范围。
总结
axis.Axis.get_clip_box()函数是Matplotlib中一个强大而灵活的工具,它允许我们精确控制图形的可见区域和裁剪效果。通过本文的详细介绍和丰富的示例,我们探讨了这个函数的各种应用场景,从基本用法到高级技巧,从2D图形到3D可视化,从静态图表到动画效果。
掌握get_clip_box()的使用可以帮助我们创建更精确、更专业的数据可视化作品。无论是在科学计算、数据分析还是创意设计领域,这个函数都能为我们的Matplotlib图表添加独特的魅力和功能性。
通过实践和探索,你会发现get_clip_box()在Matplotlib生态系统中的重要性,以及它如何与其他函数和方法协同工作,以实现复杂的可视化需求。希望这篇文章能够启发你在未来的数据可视化项目中更好地利用这个强大的工具。
 极客笔记
极客笔记