inode_set_bytes()函数的功能是设置inode节点的字节数,设置的字节数由参数loff_t bytes决定。函数执行过程是首先把要设置的量右移9位然后赋值给inode->i_blocks,设置节点的扇区数,然后将参数bytes与511相“与”,获取不足一个扇区的字节数,赋值给inode->i_bytes,完成对节点的字节数的设置。
inode_set_bytes文件包含
#include <linux/fs.h>
inode_set_bytes函数定义
在内核源码中的位置:linux-3.19.3/fs/stat.c
函数定义格式:
void inode_set_bytes(struct inode *inode, loff_t bytes)
inode_set_bytes输入参数说明
inode:要被设置字节数的inode结构体,对于inode结构体,其定义及详细说明参考极客笔记中d_find_alias()函数的参数说明部分。bytes:是loff_t类型的变量,代表要设置的字节数,其定义如下:
typedef __kernel_loff_t loff_t;
其中__kernel_loff_t定义如下:
typedef long long __kernel_loff_t;
inode_set_bytes返回参数说明
inode_set_bytes()函数无返回值。
inode_set_bytes实例解析
编写测试文件:inode_set_bytes.c
头文件声明如下:
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/fs_struct.h>
#include <linux/path.h>
#include <linux/sched.h>
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
模块初始化函数:
int inode_set_bytes_init(void)
{
struct dentry *dentry;
struct inode *inode;
loff_t num1 = 8192;
dentry = current->fs->pwd.dentry; //获取当前文件的入口目录
inode = dentry->d_inode; //获取当前文件的inode节点
unsigned long data1 = inode_get_bytes(inode); //获取inode节点的字节数
printk("The result of \"inode_get_bytes\" is :%ld\n", data1);
//显示节点的当前字节数
inode_set_bytes(inode, num1); //设置当前节点的字节数
printk("Exec \"inode_set_bytes\" begins:\n");
printk("After Exec, The result is :%ld\n", inode_get_bytes(inode));
//显示函数调用之后节点的字节数
return 0;
}
模块退出函数:
void inode_set_bytes_exit(void)
{
printk("Goodbye inode_set_bytes\n");
}
模块初始化及退出函数调用:
module_init(inode_set_bytes_init);
module_exit(inode_set_bytes_exit);
实例运行结果及分析:
首先编译模块,执行命令insmod inode_set_bytes.ko插入模块,然后执行命令dmesg -c,会出现如图所示的结果。
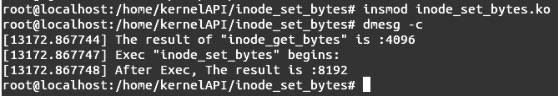
结果分析:
函数inode_set_bytes()执行之前当前文件对应的节点字节数是4096。函数执行时,将当前节点所对应的文件大小设置为字节数为8192。如图所示,从模块插入后系统输出信息可以看出,当前文件对应的inode节点的字节数是8192,说明函数inode_set_bytes()设置当前节点文件的字节数成功执行。
 极客笔记
极客笔记