d_alloc()函数的功能是分配一个目录项缓存的入口目录。如果没有足够有效的内存,则返回NULL。如果分配成功分配则返回的是一个dentry结构体。
d_alloc文件包含
#include <linux/dcache.h>
d_alloc函数定义
在内核源码中的位置:linux-3.19.3/fs/dcache.c
函数定义格式:
struct dentry *d_alloc(struct dentry * parent, const struct qstr *name)
d_alloc输入参数说明
parent:要被分配的dentry结构体的父dentry结构体,定义见文件linux-3.19.3/include/linux/dcache.h,结构如下:
struct dentry {
unsigned int d_flags; /*目录项高速缓存标志*/
seqcount_t d_seq; /*dentry的seqlock*/
struct hlist_node d_hash; /*指向散列表表项链表的指针*/
struct dentry *d_parent; /*父目录的目录项对象*/
struct qstr d_name; /*文件名*/
struct inode *d_inode; /*与文件名关联的索引节点*/
unsigned char d_iname[DNAME_INLINE_LEN_MIN]; /*存放短文件名的空间*/
struct lockref d_lockref; /*dentry的锁和引用数*/
const struct dentry_operations *d_op; /*目录项的操作函数*/
struct super_block *d_sb; /*文件的超级块对象*/
unsigned long d_time; /*由d_revalidate方法调用*/
void *d_fsdata; /*文件系统各自独特的数据*/
struct list_head d_lru; /*对于未使用目录项链表的指针*/
struct list_head d_child; /*对目录而言,用于同一父目录中的目录项链表指针*/
struct list_head d_subdirs; /*对目录而言,子目录项链表的头*/
union {
struct hlist_node d_alias; /*用于与同一索引节点(别名)相关的目录项链表的指针*/
struct rcu_head d_rcu; /*回收目录项对象时,由RCU描述符使用*/
} d_u;
};
name:包含要被分配的dentry结构体名字的qstr结构体,qstr结构定义见文件linux-3.19.3/include/linux/dcache.h,如下:
struct qstr {
union {
struct {
HASH_LEN_DECLARE;
};
u64 hash_len; /*dentry结构体的hash序号的长度*/
};
const unsigned char *name; /* dentry结构体的名字*/
};
d_alloc返回参数说明
- 此函数的返回值是struct dentry结构体类型的指针变量,如果函数d_alloc()返回值为NULL,则说明没有足够的内存空间;如果返回值是dentry结构体,则说明在父dentry结构体下分配了一个dentry结构体。
d_alloc实例解析
编写测试文件:d_alloc.c
头文件声明如下:
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/fs_struct.h>
#include <linux/path.h>
#include <linux/sched.h>
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
模块初始化函数:
int d_alloc_init(void)
{
struct dentry *dentry_pwd = current->fs->pwd.dentry; //获取当前文件的入口目录
struct dentry *dentry_parent = current->fs->pwd.dentry->d_parent;
// 获取当前文件的上一级入口目录
struct qstr name = current->fs->pwd.dentry->d_name;
// 获取当前文件的入口目录名结构体
struct dentry *dentry=NULL;
// 分配一个目录项缓存结构体
dentry = d_alloc(dentry_parent, &name);
printk("The name of current dentry is %s\n", dentry_pwd->d_name.name);
// 显示当前文件名
printk("After \"d_alloc\" the name of the dentry is %s\n", dentry->d_name.name);
// 显示返回结果文件名
return 0;
}
模块退出函数:
void d_alloc_exit(void)
{
printk("Goodbye d_alloc\n");
}
模块初始化及退出函数调用:
module_init(d_alloc_init);
module_exit(d_alloc_exit);
实例运行结果及分析:
首先编译模块,执行命令insmod d_alloc.ko插入模块,然后执行命令dmesg -c,会出现如图所示的结果。
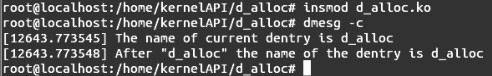
结果分析:
首先显示当前目录的目录名为d_alloc,在函数d_alloc中传入当前目录的父dentry结构体和当前目录的qstr结构体,得到的返回值是一个dentry结构体,显示名字也为d_alloc,因此该函数成功地分配一个目录缓存的入口结构体。
 极客笔记
极客笔记