C++ 由最多 M 个连续节点组成的从根到叶路径的数量,节点值为 K
介绍
二叉树是计算机科学和编程中有着许多应用的迷人数据结构。一个有趣的问题是从给定的由父节点和其子节点组成的树中找到路径数量。二叉树由节点组成,根节点是确定的,子节点可以根据用户的需要给出。选择遍历方式是根据 M 值决定的,而 K 值也是确定的。
从根到叶路径的数量
以整数形式创建了包含各种值的图。本文主要关注从起始或根节点到叶子节点或子节点的计数。
示例
以下二叉树的图是由各种节点创建的。
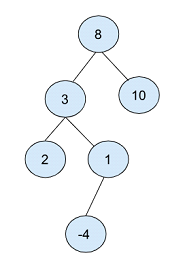
- 在上面的二叉树中,根节点被选择为’8’。
-
然后创建了两个节点,一个值为3,另一个值为10,分别占据了根节点的左侧和右侧。
-
以值为2的节点作为根节点,创建了一个子节点,其中值为2,分别为左侧和右侧。
-
最后一个值为1的子节点创建了一个值为-4的子节点。
方法1:使用递归函数计算由最多 M 个连续节点组成的从根到叶节点的值为 K 的路径的数量
为了高效解决这个问题,我们将利用树遍历算法和递归等基本概念。
步骤
步骤1 :创建一个表示树节点的结构,包括两个指针(左子节点和右子节点)和一个用于存储节点值的整数字段。
步骤2 :设计一个递归函数,从根节点开始遍历二叉树,同时维护当前路径长度(初始化为0)、连续出现次数计数(初始为0)、目标值 K 和允许的最大连续出现次数 M。
步骤3 :递归调用函数对每个左子树和右子树进行处理,传递更新后的参数,例如增加的路径长度和连续出现次数。
步骤4 :对于每个在遍历过程中访问的非空节点:
a)如果节点的值等于 K,则两个变量都增加1。
b)如果节点的值不匹配 K 或超过路径中已经遇到的 M 个连续出现次数,将变量重置为零。
步骤5 :在遍历过程中,如果子节点在左侧和右侧两种情况下的值都为零,我们可以通过以下两种方式之一进行处理:
a)检查变量是否不超过 M。
b)如果是,则将满足条件的从起始到结束的路径总数增加1。
示例
//including the all in one header
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
//creating structure with two pointers as up and down
struct Vertex {
int data;
struct Vertex* up;
struct Vertex* down;
};
//countPaths function declared with five arguments ; with root = end; Node= vertex; left = up; right = down
int countPaths(Vertex* end, int K, int M, int currCount, int
consCount) {
//To check the condition when the root is equal to 1 and greater than the maximum value, the values is incremented
if (end == NULL || consCount > M) {
return 0;
}
//To check when the root is equal to the K value, increment by 1
if (end->data == K) {
currCount++;
consCount++;
} else {
//If it is not equal, it will return 0
currCount = 0;
}
if (end->up == NULL && end->down == NULL) {
if (currCount <= M) {
return 1;
} else {
return 0;
}
}
return countPaths(end->up, K, M, currCount, consCount) + countPaths(end->down, K, M, currCount, consCount);
}
//Main function to test the implementation
int main() {
Vertex* end = new Vertex();
end->data = 8;
end->up = new Vertex();
end->up->data = 3;
end->down = new Vertex();
end->down->data = 10;
end->up->up = new Vertex();
end->up->up->data = 2;
end->up->down = new Vertex();
end->up->down->data = 1;
end->up->down->up = new Vertex();
end->up->down->up->data = -4;
int K = 1; // Value of node
int M = 2; // Maximum consecutive nodes
int currCount = -1; // Current count
int consCount = -1; // Consecutive count
cout << "The number of paths obtained from the given graph of" << M << "nodes with a value of " << K << " is " << countPaths(end, K, M, currCount, consCount) << endl;
return 0;
}
输出
The number of paths obtained from the given graph of 2 nodes with a value of 1 is 3
结论
在本文中,我们探讨了从顶部开始计算到末尾或根部的叶子路径数量的问题。通过在C++中运用树遍历算法和递归技术,可以有效地解决这类问题。通过遍历二叉树的过程看起来很困难,但通过示例变得简单明了。
 极客笔记
极客笔记