C++ 数组
像其他编程语言一样,C++中的数组是具有连续内存位置的相似类型元素的组。
在C++中, std::array 是一个封装了固定大小数组的容器。在C++中,数组的索引从0开始。我们可以在C++数组中仅存储固定集合的元素。
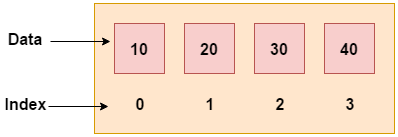
在C/C++编程语言或任何其他编程语言中,将相关数据项存储在相邻内存位置中称为数组。可以使用数组的索引任意访问数组的元素。它们可以用于存储任何类型的基本数据类型的集合,包括int、float、double、char等。在C/C++中,数组还可以存储派生数据类型,如结构、指针和其他数据类型,这是一个附加功能。下图显示了数组的表示形式。
C++数组的优势
- 代码优化(少量代码)
- 随机访问
- 易于遍历数据
- 易于操作数据
- 易于排序数据等等
C++数组的劣势
- 固定大小
C++数组类型
C++编程中有两种类型的数组:
- 单维数组
- 多维数组
C++单维数组
让我们看一个简单的C++数组示例,我们将创建、初始化和遍历数组。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int arr[5]={10, 0, 20, 0, 30}; //creating and initializing array
//traversing array
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
cout<<arr[i]<<"\n";
}
}
输出:
10
0
20
0
30
C++数组示例:使用foreach循环进行遍历
我们还可以使用foreach循环来遍历数组元素。它逐个返回数组元素。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int arr[5]={10, 0, 20, 0, 30}; //creating and initializing array
//traversing array
for (int i: arr)
{
cout<<i<<"\n";
}
}
输出:
10
20
30
40
50
我们为什么需要数组
当我们需要存储许多实例时,使用普通变量(v1、v2、v3…)管理它们变得困难。为了在一个变量中表示多个实例,我们使用数组。
如果我们尝试访问超出数组界限,会发生什么
如果我们定义了一个大小为10的数组,则数组的元素将从0到9进行编号。
然而,如果我们尝试访问索引大于10的元素,将会出现未定义行为。
具有空成员的C++数组
C++中数组最多可以存储n个元素。但是,如果我们存储少于n个元素会发生什么?
例如,
// store only 3 elements in the array
int x[6] = {19, 10, 8};
在这种情况下,数组x有6个元素的宽度。但我们只给它一个三元素的初始化。
当这种情况发生时,编译器会用随机值填充空白的位置。这个随机值经常出现为0。
在使用C++中的数组时需要记住的重要事项
- 数组的索引从0开始。意思是保存在索引0的第一项是x[0]。
- 大小为n的数组的最后一个元素保存在索引(n-1)处。这个例子的最后一个元素是x[5]。
- 数组的元素具有连续的地址。考虑x[0]的地址为2120的情况。
接下来的元素x[1]的地址将是2124,然后是x[2]的地址2128,以此类推。
在这种情况下,每个元素的大小增加了四倍。这是因为int类型具有4个字节的容量。
什么是二维数组
这种数组中的每个元素由两个索引描述,第一个索引表示行,第二个索引表示列。
正如你看到的,使用行和列来安排组成部分在二维数组中;有I行和j列。
什么是多维数组
二维数组是最基本的多维数组类型;它也符合多维数组的定义。对数组的维度没有限制。
如何在数组中插入它
int mark[5] = {19, 10, 8, 17, 9}
// change 4th element to 9
mark[3] = 9;
// take input from the user
// store the value at third position
cin >> mark[2];
// take input from the user
// insert at ith position
cin >> mark[i-1];
// print first element of the array
cout << mark[0];
// print ith element of the array
cout >> mark[i-1];
如何显示数组元素的总和和平均值
#include
using namespace std;
int main() {
// initialize an array without specifying the size
double numbers[] = {7, 5, 6, 12, 35, 27};
double sum = 0;
double count = 0;
double average;
cout << "The numbers are: ";
// print array elements
// use of range-based for loop
for (const double &n : numbers) {
cout << n << " ";
// calculate the sum
sum += n;
// count the no. of array elements
++count;
}
// print the sum
cout << "\nTheir Sum = " << sum << endl;
// find the average
average = sum / count;
cout << "Their Average = " << average << endl;
return 0;
}
输出:
The numbers are: 7 5 6 12 35 27
Their Sum = 92
Their Average = 15.3333
如何显示数组元素
#include
using namespace std;
int main() {
int numbers[5] = {7, 5, 6, 12, 35};
cout << "The numbers are: ";
// Printing array elements
// using range-based for loop
for (const int &n : numbers) {
cout << n << " ";
}
cout << "\nThe numbers are: ";
// Printing array elements
// using traditional for loop
for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i) {
cout << numbers[i] << " ";
}
return 0;
}
输出:
The numbers are: 7 5 6 12 35
The numbers are: 7 5 6 12 35
 极客笔记
极客笔记