Android Service教程
Android服务 是一个组件,用于在后台执行操作,例如播放音乐,处理网络事务,与内容提供程序交互等。它没有任何用户界面(UI)。
即使应用程序被销毁,该服务也会在后台无限期运行。
此外,服务可以由组件绑定,以进行交互和进程间通信(IPC)。
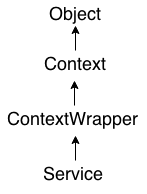
android.app.Service是ContextWrapper类的子类。
注意:Android服务不是线程或单独的进程。
Android服务的生命周期
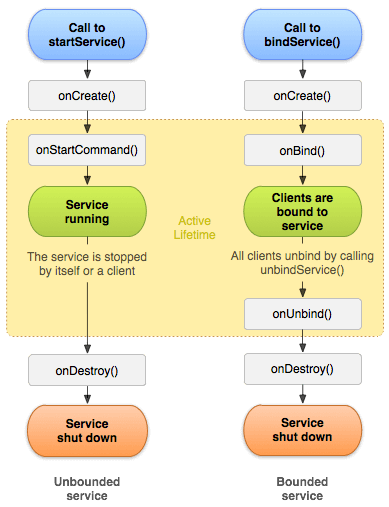
服务有两种形式。服务的生命周期可以遵循两条不同的路径:启动或绑定。
- 启动
- 绑定
1)启动的服务
当组件(如活动)调用 startService() 方法时,服务会启动,现在它在后台无限期运行。通过 stopService() 方法可以停止服务。服务可以通过调用 stopSelf() 方法来停止自身。
2)绑定的服务
当另一个组件(例如客户端)调用 bindService() 方法时,服务会绑定。客户端可以通过调用 unbindService() 方法解绑服务。
只有当所有客户端解绑服务后,服务才能停止。
理解通过背景音乐示例开始和绑定服务
假设我想在后台播放音乐,所以调用startService()方法。但是我想获得当前播放的歌曲的信息,我将绑定提供有关当前歌曲信息的服务。
Android服务示例
让我们看一个在Android中在后台播放音频的服务示例。即使您切换到另一个活动,音频也不会停止。要停止音频,您需要停止服务。
activity_main.xml
从工具箱中拖动3个按钮,现在activity_main.xml文件的样子如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context="example.javatpoint.com.androidservice.MainActivity">
<Button
android:id="@+id/buttonStart"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_marginTop="74dp"
android:text="Start Service" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/buttonStop"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_centerVertical="true"
android:text="Stop Service" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/buttonNext"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_marginBottom="63dp"
android:text="Next Page" />
</RelativeLayout>
activity_next.xml
这是下一个活动的布局文件。
它只包含一个文本视图,显示消息”下一页”
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context="example.javatpoint.com.androidservice.NextPage">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginEnd="8dp"
android:layout_marginStart="8dp"
android:layout_marginTop="200dp"
android:text="Next Page"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
</android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout>
服务类
现在通过继承服务类并重写其回调方法来创建服务实现类。
package example.javatpoint.com.androidservice;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.media.MediaPlayer;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.support.annotation.Nullable;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class MyService extends Service {
MediaPlayer myPlayer;
@Nullable
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return null;
}
@Override
public void onCreate() {
Toast.makeText(this, "Service Created", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
myPlayer = MediaPlayer.create(this, R.raw.sun);
myPlayer.setLooping(false); // Set looping
}
@Override
public void onStart(Intent intent, int startid) {
Toast.makeText(this, "Service Started", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
myPlayer.start();
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
Toast.makeText(this, "Service Stopped", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
myPlayer.stop();
}
}
Activity类
现在创建MainActivity类来执行事件处理。在这里,我们编写代码来启动和停止服务。此外,通过buttonNext调用第二个活动。
package example.javatpoint.com.androidservice;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements View.OnClickListener{
Button buttonStart, buttonStop,buttonNext;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
buttonStart = findViewById(R.id.buttonStart);
buttonStop = findViewById(R.id.buttonStop);
buttonNext = findViewById(R.id.buttonNext);
buttonStart.setOnClickListener(this);
buttonStop.setOnClickListener(this);
buttonNext.setOnClickListener(this);
}
public void onClick(View src) {
switch (src.getId()) {
case R.id.buttonStart:
startService(new Intent(this, MyService.class));
break;
case R.id.buttonStop:
stopService(new Intent(this, MyService.class));
break;
case R.id.buttonNext:
Intent intent=new Intent(this,NextPage.class);
startActivity(intent);
break;
}
}
}
NextPage类
现在,创建另一个活动。
package example.javatpoint.com.androidservice;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
public class NextPage extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_next);
}
}
声明服务在AndroidManifest.xml文件中
最后,在清单文件中声明服务。
让我们看看完整的AndroidManifest.xml文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="example.javatpoint.com.androidservice">
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:roundIcon="@mipmap/ic_launcher_round"
android:supportsRtl="true"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme">
<activity android:name=".MainActivity">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
<activity android:name=".NextPage"></activity>
<service
android:name=".MyService"
android:enabled="true" />
</application>
</manifest>
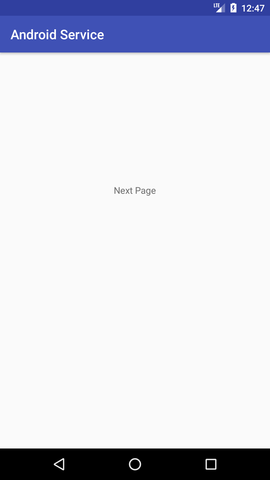
输出:
 极客笔记
极客笔记