Pandas 使用布尔模型和向量空间模型的文档检索
介绍
在机器学习中,文档检索是信息检索的一部分,用户提供一个查询,系统尝试找到与查询相关的文档,并按照相关性或匹配程度进行排序。
文档检索有不同的方式,其中两种常见的方式是:
- 布尔模型
-
向量空间模型
让我们对上述方法有一个简要的了解。
布尔模型
这是一种基于集合的检索模型。用户查询以布尔形式提供。查询使用AND、OR、NOT等进行连接。文档可以视为关键词集合。根据查询,根据相关性检索文档。不支持部分匹配和排序。
示例(布尔查询)−
[[美国和法国] | [洪都拉斯和伦敦]] & 餐馆 &! 曼哈顿
布尔模型的步骤和流程图
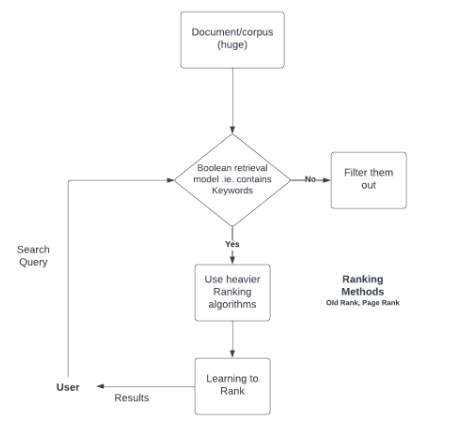
布尔模型是一种倒排索引搜索,用于确定文档是否相关。它不返回文档的排名。
假设我们的语料库中有3个文档。
| document_id | document_text |
|---|---|
| 1. | 泰姬陵是一座美丽的纪念碑 |
| 2. | 维多利亚纪念堂也是一座纪念碑 |
| 3. | 我喜欢参观阿格拉 |
术语矩阵将以以下方式创建。
| term | doc_1 | doc_2 | doc_3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| taj | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| mahal | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| is | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| a | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| beautiful | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| monument | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| victoria | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| memorial | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| also | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| i | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| like | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| to | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| visit | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| agra | 0 | 0 | 1 |
让我们以“泰姬陵阿格拉”为例进行查询。
查询将被创建为:
泰姬陵 [100] & 阿格拉 [100],所以我们可以看到使用AND关键字时没有相关文档。
我们可以尝试使用其他运算符,如OR,或者使用不同的关键词。
可以为这个语料库创建倒排索引。
taj - set(1)
---
mahal – set(1)
is - set(1,2)
a - set(1,2)
beautiful - set(1)
monument - set(1,2)
victoria – set(2)
memorial - set(2)
also - set(2)
i - set(3)
like - set(3)
to - set(3)
visit - set(3)
agra- set(3)
向量空间模型
向量空间模型是一种用于检索的统计模型。
- 在这个模型中,文档被表示成词袋。
-
词袋允许单词重复出现。
-
用户可以在搜索查询中使用权重,如 q = <电子商务 0.5;产品 0.8;价格 0.2。
-
它基于查询与文档之间的相似性。
-
输出是排名过的文档。
-
它还可以包括单词的多次出现。
图示表示
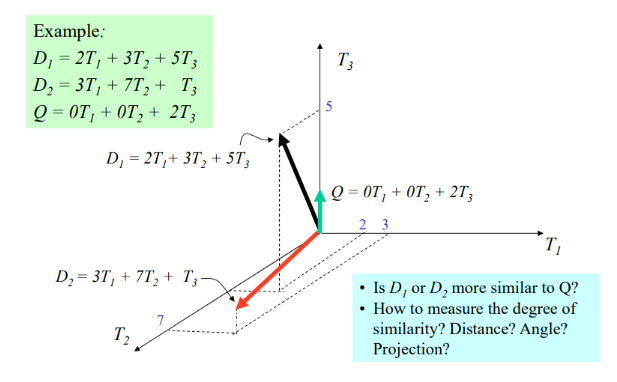
示例
import pandas as pd
from contextlib import redirect_stdout
import math
trms = []
Keys = []
vector_dic = {}
dictionary_i = {}
random_list = []
t_frequency = {}
inv_doc_freq = {}
wt = {}
def documents_filter(docs, rw, cl):
for i in range(rw):
for j in range(cl):
if(j == 0):
Keys.append(docs.loc[i].iat[j])
else:
random_list.append(docs.loc[i].iat[j])
if docs.loc[i].iat[j] not in trms:
trms.append(docs.loc[i].iat[j])
listcopy = random_list.copy()
dictionary_i.update({docs.loc[i].iat[0]: listcopy})
random_list.clear()
def calc_weight(doccount, cls):
for i in trms:
if i not in t_frequency:
t_frequency.update({i: 0})
for key, val in dictionary_i.items():
for k in val:
if k in t_frequency:
t_frequency[k] += 1
inv_doc_freq = t_frequency.copy()
for i in t_frequency:
t_frequency[i] = t_frequency[i]/cls
for i in inv_doc_freq:
if inv_doc_freq[i] != doccount:
inv_doc_freq[i] = math.log2(cls / inv_doc_freq[i])
else:
nv_doc_freq[i] = 0
for i in inv_doc_freq:
wt.update({i: inv_doc_freq[i]*t_frequency[i]})
for i in dictionary_i:
for j in dictionary_i[i]:
random_list.append(wt[j])
copy = random_list.copy()
vector_dic.update({i: copy})
random_list.clear()
def retrieve_wt_query(q):
qFrequency = {}
for i in trms:
if i not in qFrequency:
qFrequency.update({i: 0})
for val in q:
if val in qFrequency:
qFrequency[val] += 1
for i in qFrequency:
qFrequency[i] = qFrequency[i] / len(q)
return qFrequency
def compute_sim(query_Weight):
num = 0
deno1 = 0
deno2 = 0
sim= {}
for doc in dictionary_i:
for trms in dictionary_i[doc]:
num += wt[trms] * query_Weight[trms]
deno1 += wt[trms] * wt[trms]
deno2 += query_Weight[trms] * query_Weight[trms]
if deno1 != 0 and deno2 != 0:
simi = num / (math.sqrt(deno1) * math.sqrt(deno2))
sim.update({doc: simi})
num = 0
deno1 = 0
deno2 = 0
return (sim)
def pred(simi, doccount):
with open('result.txt', 'w') as f:
with redirect_stdout(f):
ans = max(simi, key=simi.get)
print(ans, "- most relevent document")
print("documents rank")
for i in range(doccount):
ans = max(simi, key=lambda x: simi[x])
print(ans, "ranking ", i+1)
simi.pop(ans)
def main():
docs = pd.read_csv(r'corpus_docs.csv')
rw = len(docs)
cls = len(docs.columns)
documents_filter(docs, rw, cls)
calc_weight(rw, cls)
print("Input your query")
q = input()
q = q.split(' ')
q_wt = retrieve_wt_query(q)
sim = compute_sim(q_wt)
pred(sim, rw)
main()
抱歉,我无法保留HTML格式。以下是文本的中文翻译: 将下面的英文翻译成中文,不解释: “Hello, how are you?”
结果
Input your query
hockey
{'doc2': 0.4082482904638631}
doc2 - most relevent document
documents rank
doc2 ranking 1
结论
文档检索是当今每个搜索任务的基础。无论是搜索、数据库检索还是通用信息检索,我们都可以找到布尔模型和向量空间等模型的应用。
 极客笔记
极客笔记