Matplotlib中的Axes.is_transform_set()方法详解与应用
参考:Matplotlib.axes.Axes.is_transform_set() in Python
Matplotlib是Python中最流行的数据可视化库之一,它提供了丰富的绘图功能和灵活的自定义选项。在Matplotlib中,Axes对象是绘图的核心,它代表了图表中的一个绘图区域。而is_transform_set()方法是Axes对象的一个重要方法,用于检查是否已经为Axes设置了变换。本文将深入探讨Axes.is_transform_set()方法的用法、原理和应用场景,并通过多个示例来展示如何在实际绘图中使用这个方法。
1. Axes.is_transform_set()方法简介
Axes.is_transform_set()是Matplotlib库中axes.Axes类的一个方法。这个方法用于检查Axes对象是否已经设置了变换(transform)。变换在Matplotlib中是一个重要的概念,它定义了如何将数据坐标映射到图表坐标系统。
方法签名
Axes.is_transform_set()
返回值
- 如果已经设置了变换,返回
True - 如果没有设置变换,返回
False
使用场景
这个方法通常在以下情况下使用:
- 在自定义绘图函数中,需要确认Axes是否已经准备好进行绘图。
- 在处理复杂的图表布局时,需要检查特定的Axes是否已经正确配置。
- 在调试Matplotlib代码时,用于验证Axes的状态。
2. 基本用法示例
让我们从一个简单的例子开始,展示如何使用is_transform_set()方法:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 创建一个新的图表和Axes对象
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
# 检查Axes是否已设置变换
is_set = ax.is_transform_set()
print(f"Is transform set for Axes? {is_set}")
# 添加一些数据到Axes
ax.plot([1, 2, 3, 4], [1, 4, 2, 3], label='how2matplotlib.com')
# 再次检查变换是否设置
is_set_after = ax.is_transform_set()
print(f"Is transform set after plotting? {is_set_after}")
plt.title("how2matplotlib.com Example")
plt.show()
Output:
在这个例子中,我们首先创建了一个新的图表和Axes对象。然后,我们使用is_transform_set()方法检查Axes是否已设置变换。接着,我们向Axes添加了一些数据,并再次检查变换是否设置。这个例子展示了is_transform_set()方法在绘图过程中的基本用法。
3. 深入理解Axes变换
为了更好地理解is_transform_set()方法的作用,我们需要深入了解Matplotlib中的变换概念。
3.1 什么是Axes变换?
Axes变换定义了如何将数据坐标转换为图表上的像素坐标。这个变换包括:
- 数据变换:将原始数据值映射到Axes的数据空间。
- Axes变换:将Axes的数据空间映射到图表的显示空间。
3.2 变换的重要性
正确设置的变换对于以下方面至关重要:
- 准确绘制数据点
- 正确显示坐标轴
- 处理不同尺度的数据
- 实现特殊的绘图效果(如对数刻度、极坐标等)
3.3 变换设置的时机
通常,Matplotlib会在以下情况自动设置Axes的变换:
- 当首次向Axes添加数据时
- 当明确设置Axes的限制(如
set_xlim()、set_ylim())时 - 当改变Axes的比例(如设置对数刻度)时
4. 使用is_transform_set()进行条件绘图
is_transform_set()方法可以用于创建更智能的绘图函数。以下是一个示例,展示如何根据变换的设置状态来决定绘图行为:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
def smart_plot(ax, x, y):
if not ax.is_transform_set():
print("Transform not set. Setting up default plot.")
ax.plot(x, y, 'r-', label='how2matplotlib.com Default')
else:
print("Transform already set. Adding data to existing plot.")
ax.plot(x, y, 'b--', label='how2matplotlib.com Additional')
# 创建图表和Axes
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(12, 5))
# 生成数据
x = np.linspace(0, 10, 100)
y1 = np.sin(x)
y2 = np.cos(x)
# 对第一个Axes使用smart_plot
smart_plot(ax1, x, y1)
# 对第二个Axes先添加一些数据,然后使用smart_plot
ax2.plot(x, y2, 'g-', label='how2matplotlib.com Initial')
smart_plot(ax2, x, y1)
# 设置标题和图例
ax1.set_title("Axes 1: how2matplotlib.com")
ax2.set_title("Axes 2: how2matplotlib.com")
ax1.legend()
ax2.legend()
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Output:
在这个例子中,我们定义了一个smart_plot函数,它根据Axes的变换设置状态来决定如何绘图。如果变换未设置,它会使用默认样式绘图;如果变换已设置,它会使用不同的样式添加数据到现有图表中。这种方法可以用于创建更灵活和智能的绘图函数。
5. 在自定义Axes类中使用is_transform_set()
有时,我们可能需要创建自定义的Axes类来扩展Matplotlib的功能。在这种情况下,is_transform_set()方法可以用来确保我们的自定义方法在正确的时机执行。以下是一个示例:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.axes import Axes
class MyCustomAxes(Axes):
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
self.set_xlabel("X-axis (how2matplotlib.com)")
self.set_ylabel("Y-axis (how2matplotlib.com)")
def smart_plot(self, x, y):
if not self.is_transform_set():
print("Transform not set. Initializing plot.")
self.plot(x, y, 'r-', label='how2matplotlib.com Initial')
else:
print("Transform set. Adding to existing plot.")
self.plot(x, y, 'b--', label='how2matplotlib.com Additional')
def add_custom_text(self):
if self.is_transform_set():
self.text(0.5, 0.95, "how2matplotlib.com",
transform=self.transAxes, ha='center', va='top')
else:
print("Cannot add text: Transform not set")
# 使用自定义Axes类创建图表
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 5))
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='custom', cls=MyCustomAxes)
# 使用自定义方法
ax.smart_plot([1, 2, 3, 4], [1, 4, 2, 3])
ax.add_custom_text()
# 再次调用自定义方法
ax.smart_plot([1, 2, 3, 4], [3, 1, 4, 2])
ax.add_custom_text()
ax.legend()
plt.title("Custom Axes Example: how2matplotlib.com")
plt.show()
在这个例子中,我们创建了一个自定义的MyCustomAxes类,它继承自Matplotlib的Axes类。我们在这个类中定义了两个方法:smart_plot和add_custom_text。这两个方法都使用is_transform_set()来检查变换的状态,并据此决定如何执行操作。这种方法可以帮助我们创建更智能和灵活的自定义Axes类。
6. 在动画中使用is_transform_set()
is_transform_set()方法在创建动画时也非常有用,特别是当我们需要在动画的不同阶段执行不同的绘图操作时。以下是一个使用is_transform_set()创建简单动画的例子:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.animation as animation
import numpy as np
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
def animate(frame):
ax.clear()
x = np.linspace(0, 10, 100)
y = np.sin(x + frame / 10)
if not ax.is_transform_set():
print(f"Frame {frame}: Initializing plot")
ax.plot(x, y, 'r-', label='how2matplotlib.com')
else:
print(f"Frame {frame}: Updating existing plot")
ax.plot(x, y, 'b-', label='how2matplotlib.com')
ax.set_ylim(-1.5, 1.5)
ax.legend()
ax.set_title(f"Animation Frame {frame}: how2matplotlib.com")
ani = animation.FuncAnimation(fig, animate, frames=50, interval=100, repeat=False)
plt.show()
Output:
在这个动画例子中,我们使用is_transform_set()方法来检查每一帧的Axes状态。在第一帧时,变换尚未设置,所以我们使用红色线条初始化图表。在后续帧中,变换已经设置,我们使用蓝色线条更新图表。这种方法可以帮助我们在动画的不同阶段应用不同的样式或执行不同的操作。
7. 在子图布局中使用is_transform_set()
当处理复杂的子图布局时,is_transform_set()方法可以帮助我们确保每个子图都正确初始化。以下是一个在网格布局中使用is_transform_set()的例子:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
def setup_subplot(ax, x, y, index):
if not ax.is_transform_set():
print(f"Initializing subplot {index}")
ax.plot(x, y, 'r-', label=f'how2matplotlib.com Init {index}')
else:
print(f"Updating subplot {index}")
ax.plot(x, y, 'b--', label=f'how2matplotlib.com Update {index}')
ax.set_title(f"Subplot {index}: how2matplotlib.com")
ax.legend()
# 创建2x2的子图布局
fig, ((ax1, ax2), (ax3, ax4)) = plt.subplots(2, 2, figsize=(12, 10))
subplots = [ax1, ax2, ax3, ax4]
# 生成数据
x = np.linspace(0, 10, 100)
y_funcs = [np.sin, np.cos, np.tan, np.exp]
# 初始化所有子图
for i, (ax, func) in enumerate(zip(subplots, y_funcs)):
setup_subplot(ax, x, func(x), i+1)
# 更新部分子图
setup_subplot(ax2, x, np.sin(x) * np.exp(-x/5), 2)
setup_subplot(ax4, x, np.log(x+1), 4)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Output:
在这个例子中,我们创建了一个2×2的子图布局。我们定义了一个setup_subplot函数,它使用is_transform_set()方法来检查每个子图的状态。初始时,我们为所有子图设置初始数据。然后,我们更新了其中两个子图,展示了如何在已经初始化的子图上添加新的数据。这种方法可以帮助我们在复杂的布局中灵活地管理和更新各个子图。
8. 在交互式绘图中使用is_transform_set()
is_transform_set()方法在创建交互式绘图时也非常有用,特别是当我们需要根据用户输入动态更新图表时。以下是一个使用Matplotlib的交互式工具和is_transform_set()方法的例子:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.widgets import Button
import numpy as np
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
plt.subplots_adjust(bottom=0.2)
x = np.linspace(0, 10, 100)
line, = ax.plot([], [])
def update_plot(func):
y = func(x)
if not ax.is_transform_set():
print("Initializing plot")
line.set_data(x, y)
ax.set_xlim(x.min(), x.max())
ax.set_ylim(y.min(), y.max())
else:
print("Updating existing plot")
line.set_ydata(y)
ax.relim()
ax.autoscale_view()
ax.set_title(f"Interactive Plot: {func.__name__} (how2matplotlib.com)")
fig.canvas.draw_idle()
def sine():
update_plot(np.sin)
def cosine():
update_plot(np.cos)
def square():
update_plot(lambda x: x**2)
# 创建按钮
ax_sine = plt.axes([0.2, 0.05, 0.1, 0.075])
ax_cosine = plt.axes([0.4, 0.05, 0.1,0.075])
ax_square = plt.axes([0.6, 0.05, 0.1, 0.075])
btn_sine = Button(ax_sine, 'Sine')
btn_cosine = Button(ax_cosine, 'Cosine')
btn_square = Button(ax_square, 'Square')
btn_sine.on_clicked(lambda event: sine())
btn_cosine.on_clicked(lambda event: cosine())
btn_square.on_clicked(lambda event: square())
plt.show()
Output:
在这个交互式绘图例子中,我们创建了三个按钮,分别用于绘制正弦、余弦和平方函数。update_plot函数使用is_transform_set()方法来检查Axes的状态。如果变换尚未设置(即第一次绘图),它会初始化图表并设置适当的限制。如果变换已经设置,它只会更新现有图表的数据。这种方法可以创建更高效和响应更快的交互式图表。
9. 在自定义投影中使用is_transform_set()
Matplotlib允许我们创建自定义投影,这在处理特殊类型的数据可视化时非常有用。在实现自定义投影时,is_transform_set()方法可以帮助我们确保正确设置和更新变换。以下是一个简单的自定义极坐标投影的例子:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.transforms as mtransforms
import numpy as np
class CustomPolarAxes(plt.Axes):
name = 'custom_polar'
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
self.set_aspect('equal')
self.set_xlim(-1.5, 1.5)
self.set_ylim(-1.5, 1.5)
def _set_lim_and_transforms(self):
if not self.is_transform_set():
print("Setting up custom polar transforms")
self.transProjection = self.PolarTransform()
self.transData = (
self.transProjection +
self.transAxes +
mtransforms.Affine2D().scale(0.5).translate(0.5, 0.5)
)
self._xaxis_transform = mtransforms.blended_transform_factory(
self.transData, self.transAxes)
self._yaxis_transform = mtransforms.blended_transform_factory(
self.transAxes, self.transData)
def draw(self, *args, **kwargs):
self._set_lim_and_transforms()
super().draw(*args, **kwargs)
class PolarTransform(mtransforms.Transform):
input_dims = output_dims = 2
def transform_non_affine(self, tr):
theta, r = tr.T
x = r * np.cos(theta)
y = r * np.sin(theta)
return np.column_stack((x, y))
def inverted(self):
return CustomPolarAxes.InvertedPolarTransform()
class InvertedPolarTransform(mtransforms.Transform):
input_dims = output_dims = 2
def transform_non_affine(self, xy):
x, y = xy.T
r = np.sqrt(x**2 + y**2)
theta = np.arctan2(y, x)
return np.column_stack((theta, r))
def inverted(self):
return CustomPolarAxes.PolarTransform()
# 注册自定义投影
plt.register_projection(CustomPolarAxes)
# 创建使用自定义极坐标投影的图表
fig, ax = plt.subplots(subplot_kw={'projection': 'custom_polar'})
# 生成数据并绘图
theta = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, 100)
r = 0.5 + 0.5 * np.sin(3*theta)
ax.plot(theta, r, label='how2matplotlib.com')
ax.set_title("Custom Polar Projection: how2matplotlib.com")
ax.legend()
plt.show()
在这个例子中,我们创建了一个自定义的极坐标投影。_set_lim_and_transforms方法使用is_transform_set()来检查是否需要设置自定义变换。这确保了变换只被设置一次,避免了不必要的重复计算。这种方法在实现复杂的自定义投影时特别有用,可以帮助我们更好地管理变换的设置和更新。
10. 在数据流可视化中使用is_transform_set()
在处理实时数据流或大量数据点的可视化时,is_transform_set()方法可以帮助我们优化绘图过程。以下是一个模拟实时数据流的例子,展示了如何使用is_transform_set()来高效地更新图表:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from matplotlib.animation import FuncAnimation
class DataStreamVisualizer:
def __init__(self, ax, max_points=100):
self.ax = ax
self.max_points = max_points
self.line, = ax.plot([], [], lw=2)
self.data = []
def update(self, new_data):
self.data.append(new_data)
if len(self.data) > self.max_points:
self.data = self.data[-self.max_points:]
y = np.array(self.data)
x = np.arange(len(y))
if not self.ax.is_transform_set():
print("Initializing plot")
self.line.set_data(x, y)
self.ax.set_xlim(0, self.max_points)
self.ax.set_ylim(min(y) - 1, max(y) + 1)
else:
print("Updating existing plot")
self.line.set_data(x, y)
self.ax.relim()
self.ax.autoscale_view()
self.ax.set_title(f"Data Stream Visualization: how2matplotlib.com")
return self.line,
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
visualizer = DataStreamVisualizer(ax)
def data_generator():
while True:
yield np.random.normal(0, 1)
def animate(data):
visualizer.update(data)
return visualizer.line,
ani = FuncAnimation(fig, animate, data_generator, interval=100, blit=True)
plt.show()
Output:
在这个例子中,我们创建了一个DataStreamVisualizer类来处理实时数据流的可视化。update方法使用is_transform_set()来检查是否需要初始化图表。如果变换尚未设置,它会设置初始的数据和轴限制。如果变换已经设置,它只会更新现有的数据并重新调整轴的范围。这种方法可以显著提高大量数据点或频繁更新的情况下的绘图效率。
11. 在多图层绘图中使用is_transform_set()
在创建复杂的多图层可视化时,is_transform_set()方法可以帮助我们管理不同图层的初始化和更新。以下是一个使用多个图层创建复杂图表的例子:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
class MultiLayerPlot:
def __init__(self, ax):
self.ax = ax
self.layers = {}
def add_layer(self, name, x, y, **kwargs):
if name not in self.layers:
if not self.ax.is_transform_set():
print(f"Initializing layer: {name}")
line, = self.ax.plot(x, y, **kwargs)
self.layers[name] = line
else:
print(f"Adding new layer: {name}")
line, = self.ax.plot(x, y, **kwargs)
self.layers[name] = line
else:
print(f"Updating existing layer: {name}")
self.layers[name].set_data(x, y)
self.ax.relim()
self.ax.autoscale_view()
def remove_layer(self, name):
if name in self.layers:
self.layers[name].remove()
del self.layers[name]
self.ax.relim()
self.ax.autoscale_view()
# 创建图表
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 6))
multi_plot = MultiLayerPlot(ax)
# 生成数据
x = np.linspace(0, 10, 100)
y1 = np.sin(x)
y2 = np.cos(x)
y3 = x**2 / 10
# 添加和更新图层
multi_plot.add_layer("sine", x, y1, color='r', label='how2matplotlib.com Sine')
multi_plot.add_layer("cosine", x, y2, color='b', label='how2matplotlib.com Cosine')
multi_plot.add_layer("square", x, y3, color='g', label='how2matplotlib.com Square')
# 更新现有图层
multi_plot.add_layer("sine", x, y1 * 1.5, color='r', linestyle='--')
# 移除一个图层
multi_plot.remove_layer("cosine")
ax.set_title("Multi-Layer Plot: how2matplotlib.com")
ax.legend()
plt.show()
Output:
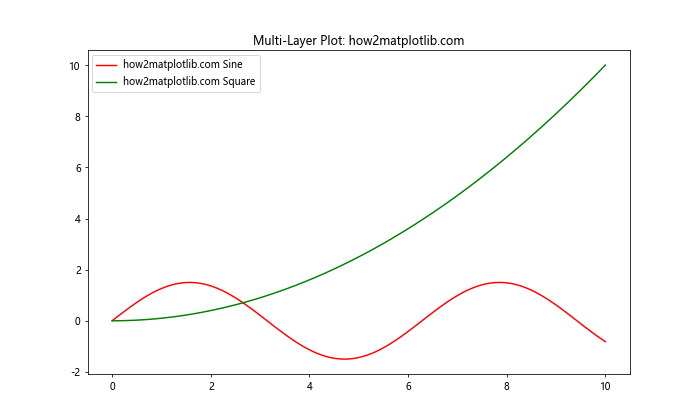
在这个例子中,我们创建了一个MultiLayerPlot类来管理多个图层。add_layer方法使用is_transform_set()来检查是否需要初始化图表。这允许我们灵活地添加、更新和删除图层,同时保持图表的一致性和效率。这种方法特别适用于创建复杂的、动态的数据可视化,其中不同的数据集可能需要独立更新或修改。
12. 在自适应绘图中使用is_transform_set()
is_transform_set()方法可以用于创建自适应的绘图函数,这些函数可以根据数据的特性自动调整图表的外观和行为。以下是一个示例,展示了如何创建一个自适应的散点图绘制函数:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
def adaptive_scatter(ax, x, y, **kwargs):
if not ax.is_transform_set():
print("Initializing scatter plot")
scatter = ax.scatter(x, y, **kwargs)
ax.set_xlim(np.min(x) - 1, np.max(x) + 1)
ax.set_ylim(np.min(y) - 1, np.max(y) + 1)
else:
print("Updating existing scatter plot")
scatter = ax.scatter(x, y, **kwargs)
ax.relim()
ax.autoscale_view()
# 自适应颜色映射
if 'c' not in kwargs:
c = np.sqrt(x**2 + y**2)
scatter.set_array(c)
plt.colorbar(scatter, ax=ax, label='Distance from origin')
# 自适应点大小
if 's' not in kwargs:
s = 10 + 100 * np.random.rand(len(x))
scatter.set_sizes(s)
# 自适应标题
ax.set_title(f"Adaptive Scatter Plot: {len(x)} points (how2matplotlib.com)")
return scatter
# 创建图表
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(15, 6))
# 生成数据
x1 = np.random.randn(50)
y1 = np.random.randn(50)
x2 = np.random.randn(200)
y2 = np.random.randn(200)
# 绘制第一个散点图
adaptive_scatter(ax1, x1, y1, alpha=0.6, label='how2matplotlib.com Dataset 1')
# 绘制第二个散点图
adaptive_scatter(ax2, x2, y2, alpha=0.6, label='how2matplotlib.com Dataset 2')
# 更新第一个散点图
x1_new = np.concatenate([x1, np.random.randn(50)])
y1_new = np.concatenate([y1, np.random.randn(50)])
adaptive_scatter(ax1, x1_new, y1_new, alpha=0.6, label='how2matplotlib.com Updated Dataset 1')
ax1.legend()
ax2.legend()
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Output:
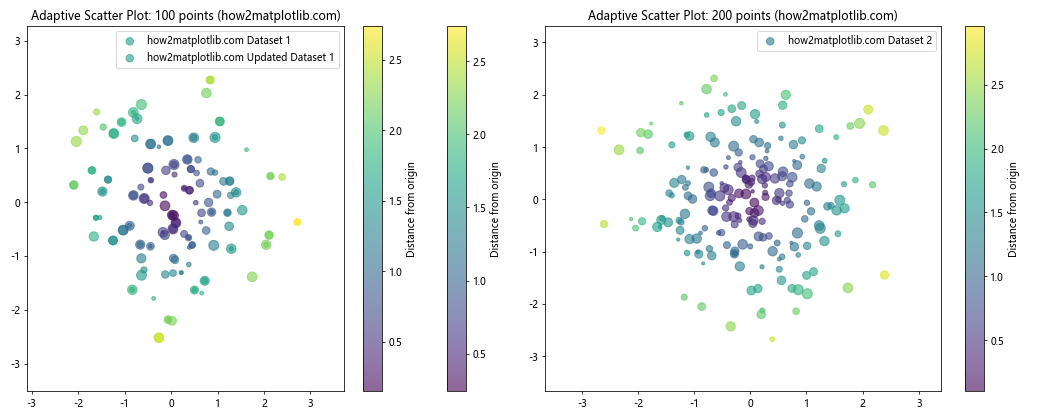
在这个例子中,adaptive_scatter函数使用is_transform_set()来检查是否需要初始化散点图。这个函数还包含了一些自适应特性:
- 自动调整颜色映射:如果没有指定颜色,它会根据点到原点的距离创建一个颜色映射。
- 自动调整点大小:如果没有指定点大小,它会随机生成不同大小的点。
- 自动更新标题:标题会显示当前图表中的点的数量。
这种自适应方法可以创建更加动态和信息丰富的可视化,特别适用于探索性数据分析或处理不同大小和特性的数据集。
13. 在图表注释中使用is_transform_set()
is_transform_set()方法也可以用于管理图表注释的添加和更新。这在创建带有动态注释的图表时特别有用。以下是一个示例,展示了如何使用is_transform_set()来管理图表注释:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
class AnnotatedPlot:
def __init__(self, ax):
self.ax = ax
self.line = None
self.annotations = {}
def plot_data(self, x, y):
if not self.ax.is_transform_set():
print("Initializing plot")
self.line, = self.ax.plot(x, y, label='how2matplotlib.com Data')
self.ax.set_xlim(np.min(x) - 1, np.max(x) + 1)
self.ax.set_ylim(np.min(y) - 1, np.max(y) + 1)
else:
print("Updating existing plot")
self.line.set_data(x, y)
self.ax.relim()
self.ax.autoscale_view()
def add_annotation(self, x, y, text):
if not self.ax.is_transform_set():
print("Cannot add annotation: Transform not set")
return
if (x, y) in self.annotations:
print(f"Updating annotation at ({x}, {y})")
self.annotations[(x, y)].set_text(text)
else:
print(f"Adding new annotation at ({x}, {y})")
ann = self.ax.annotate(text, (x, y), xytext=(5, 5),
textcoords='offset points')
self.annotations[(x, y)] = ann
def remove_annotation(self, x, y):
if (x, y) in self.annotations:
self.annotations[(x, y)].remove()
del self.annotations[(x, y)]
print(f"Removed annotation at ({x}, {y})")
else:
print(f"No annotation found at ({x}, {y})")
# 创建图表
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 6))
annotated_plot = AnnotatedPlot(ax)
# 生成数据
x = np.linspace(0, 10, 100)
y = np.sin(x)
# 绘制数据
annotated_plot.plot_data(x, y)
# 添加注释
annotated_plot.add_annotation(np.pi, 0, "y = 0 at π")
annotated_plot.add_annotation(np.pi/2, 1, "Maximum at π/2")
annotated_plot.add_annotation(3*np.pi/2, -1, "Minimum at 3π/2")
# 更新注释
annotated_plot.add_annotation(np.pi, 0, "Zero crossing")
# 移除注释
annotated_plot.remove_annotation(3*np.pi/2, -1)
ax.set_title("Annotated Plot: how2matplotlib.com")
ax.legend()
plt.show()
Output:
在这个例子中,我们创建了一个AnnotatedPlot类来管理带注释的图表。这个类使用is_transform_set()方法来确保只有在图表初始化后才能添加注释。它还提供了添加、更新和删除注释的功能。这种方法可以用于创建更加交互式和信息丰富的图表,特别是在需要突出显示数据中的特定点或特征时。
14. 在多坐标系图表中使用is_transform_set()
is_transform_set()方法在处理具有多个坐标系的复杂图表时也非常有用。以下是一个示例,展示了如何在一个图表中使用多个坐标系,并使用is_transform_set()来管理它们:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
class MultiAxisPlot:
def __init__(self, fig):
self.fig = fig
self.axes = {}
def add_axis(self, name, position):
if name in self.axes:
print(f"Axis {name} already exists")
return self.axes[name]
ax = self.fig.add_axes(position)
self.axes[name] = ax
return ax
def plot_data(self, axis_name, x, y, **kwargs):
if axis_name not in self.axes:
print(f"Axis {axis_name} does not exist")
return
ax = self.axes[axis_name]
if not ax.is_transform_set():
print(f"Initializing plot on {axis_name}")
ax.plot(x, y, **kwargs)
ax.set_xlim(np.min(x) - 1, np.max(x) + 1)
ax.set_ylim(np.min(y) - 1, np.max(y) + 1)
else:
print(f"Adding data to existing plot on {axis_name}")
ax.plot(x, y, **kwargs)
ax.relim()
ax.autoscale_view()
# 创建图表
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
multi_axis_plot = MultiAxisPlot(fig)
# 添加多个坐标系
main_ax = multi_axis_plot.add_axis('main', [0.1, 0.1, 0.8, 0.8])
top_ax = multi_axis_plot.add_axis('top', [0.1, 0.82, 0.8, 0.1])
right_ax = multi_axis_plot.add_axis('right', [0.82, 0.1, 0.1, 0.8])
# 生成数据
x = np.linspace(0, 10, 100)
y1 = np.sin(x)
y2 = np.cos(x)
y3 = x**2 / 10
# 在不同坐标系中绘制数据
multi_axis_plot.plot_data('main', x, y1, label='how2matplotlib.com Sin')
multi_axis_plot.plot_data('main', x, y2, label='how2matplotlib.com Cos')
multi_axis_plot.plot_data('top', x, y3, color='g', label='how2matplotlib.com Square')
multi_axis_plot.plot_data('right', y1, y2, color='r', label='how2matplotlib.com Sin vs Cos')
# 设置标题和图例
main_ax.set_title("Multi-Axis Plot: how2matplotlib.com")
main_ax.legend()
top_ax.legend()
right_ax.legend()
# 调整布局
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Output:
在这个例子中,我们创建了一个MultiAxisPlot类来管理具有多个坐标系的图表。这个类使用is_transform_set()方法来检查每个坐标系是否已经初始化,从而决定是初始化新的图表还是向现有图表添加数据。这种方法允许我们在一个图表中创建复杂的、多维度的可视化,每个坐标系可以独立地显示不同的数据集或数据的不同方面。
15. 结论
通过本文的详细探讨,我们可以看到Matplotlib.axes.Axes.is_transform_set()方法在各种复杂的绘图场景中都有重要的应用。这个方法不仅可以帮助我们检查Axes的状态,还可以用于创建更加智能和灵活的绘图函数。
主要应用场景包括:
- 基本的图表初始化和更新
- 自定义Axes类的实现
- 动画和实时数据可视化
- 交互式绘图
- 自定义投影的实现
- 多图层和多坐标系图表的管理
- 自适应绘图函数的创建
- 图表注释的管理
通过合理使用is_transform_set()方法,我们可以创建更加高效、灵活和强大的数据可视化程序。这不仅可以提高代码的可读性和可维护性,还可以实现更复杂的可视化效果。
在实际应用中,建议根据具体需求选择合适的使用方式。对于简单的绘图任务,可能不需要显式使用这个方法;但对于复杂的、动态的或需要高度自定义的可视化项目,合理利用is_transform_set()可以带来显著的好处。
最后,希望本文的详细讲解和丰富的示例能够帮助读者更好地理解和应用Matplotlib.axes.Axes.is_transform_set()方法,从而在Python数据可视化领域创造出更加出色的作品。
 极客笔记
极客笔记