prepare_to_wait函数功能描述:函数prepare_to_wait( )能够将第二个参数所代表的等待队列元素加入到第一个参数所代表的等待队列的头部,但此等待队列元素需要满足条件:wait->task_list.next = wait->task_list,即等待队列元素是一个单独的节点,并且task_list字段的next值指向其自身;函数能够更改当前进程的状态,将当前进程置于函数的第三个参数state所代表的状态;通过函数prepare_to_wait( )插入到等待队列中的等待队列元素的f lags字段的值一般为0,即对应的进程不是高优先级进程。
prepare_to_wait文件包含
#include <linux/wait.h>
prepare_to_wait函数定义
在内核源码中的位置:linux-3.19.3/kernel/sched/wait.c
函数定义格式:
void prepare_to_wait(wait_queue_head_t *q, wait_queue_t *wait, int state)
prepare_to_wait输入参数说明
函数有三个输入参数,分析说明如下:
- 第一个输入参数是wait_queue_head_t类型的指针,代表等待队列的头指针,其定义及详细信息参考__wake_up( )分析文档的输入参数说明部分。
- 第二个输入参数是wait_queue_t类型的指针,代表等待队列中的一个元素,其定义及详细信息参考abort_exclusive_wait( )分析文档的输入参数说明部分。
- 第三个输入参数是int型的变量,代表进程的状态,此状态值将被设为当前进程的状态,对于进程的状态参考__wake_up( )说明文档的进程状态说明部分。
prepare_to_wait返回参数说明
函数的返回值类型是void类型,即不返回任何类型的值。
prepare_to_wait实例解析
编写测试文件:prepare_to_wait.c
头文件引用:
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/sched.h>
#include <linux/list.h>
#include <linux/kthread.h>
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
子进程处理函数定义:
int my_function(void * argc)
{
printk("in the kernel thread function! \n");
printk("the current pid is:%d\n", current->pid); //显示当前进程的进程号
printk("out the kernel thread function\n");
return 0;
}
模块加载函数定义:
static int __init prepare_to_wait_init(void)
{
/*局部变量定义*/
struct task_struct * result, *result1;
int wait_queue_num=0;
wait_queue_head_t head;
wait_queue_t data, data1, *curr, *next;
printk("into prepare_to_wait_init.\n");
/*创建两个新进程*/
result=kthread_create_on_node(my_function, NULL, -1, "prepare_to_wait");
result1=kthread_create_on_node(my_function, NULL, -1, "prepare_to_wait1");
wake_up_process(result);
wake_up_process(result1);
init_waitqueue_head(&head); //初始化等待队列头指针
init_waitqueue_entry(&data, result); //用新进程初始化等待队列元素
data.task_list.next=&data.task_list; // 初始化等待队列元素的next字段
printk("the state of the current thread is:%ld\n", current->state);
//显示当前进程的状态
prepare_to_wait(&head, &data,130); //将新进程加入等待队列,并更改当前进程的状态
printk("the state of the current thread is:%ld\n", current->state);
//显示当前进程的状态
init_waitqueue_entry(&data1, result1); // 用新进程初始化等待队列元素
prepare_to_wait(&head, &data1,1); //将新进程加入等待队列,并更改当前进程的状态
printk("the state of the current thread is:%ld\n", current->state);
//显示当前进程的状态
/*循环显示等待队列中的等待元素的信息*/
list_for_each_entry_safe(curr, next, &(head.task_list), task_list)
{
wait_queue_num++; //累加等待队列中的元素个数
/*显示等待队列中当前等待元素的flags字段的值*/
printk("the flag value of the current data of the waitqueue is:%d\n", curr->flags);
/*显示等待队列中当前等待元素对应的进程的PID值*/
printk("the pid value of the current data of the waitqueue is:%d\n", ((struct task_struct *)(curr->private))->pid);
}
printk("the value of the wait_queue_num is :%d\n", wait_queue_num);
// 显示当前等待队列中的等待元素的个数
data1.task_list.next=&data1.task_list; // 初始化等待队列元素的next字段
prepare_to_wait(&head, &data1,1); //将新进程加入等待队列,并更改当前进程的状态
wait_queue_num=0;
/*循环显示等待队列中的等待元素的信息*/
list_for_each_entry_safe(curr, next, &(head.task_list), task_list)
{
wait_queue_num++; //累加等待队列中的元素个数
/*显示等待队列中当前等待元素的flags字段的值*/
printk("the flag value of the current data of the waitqueue is:%d\n", curr->flags);
/*显示等待队列中当前等待元素对应的进程的PID值*/
printk("the pid value of the current data of the waitqueue is:%d\n", ((struct task_struct *)(curr->private))->pid);
}
printk("the value of the wait_queue_num is :%d\n", wait_queue_num);
// 显示当前等待队列中的等待元素的个数
/*显示函数kernel_thread( )的返回结果*/
printk("the pid of new thread is :%d\n", result->pid);
printk("the pid of new thread1 is :%d\n", result1->pid);
printk("the current pid is:%d\n", current->pid); //显示当前进程的PID值
printk("out prepare_to_wait_init.\n");
return 0;
}
模块退出函数定义:
static void __exit prepare_to_wait_exit(void)
{
printk("Goodbye prepare_to_wait\n");
}
模块加载、退出函数调用:
module_init(prepare_to_wait_init);
module_exit(prepare_to_wait_exit);
实例运行结果及分析:
首先编译模块,执行命令insmod prepare_to_wait.ko插入内核模块,然后输入命令dmesg -c查看模块插入结果,会出现如图所示的结果。
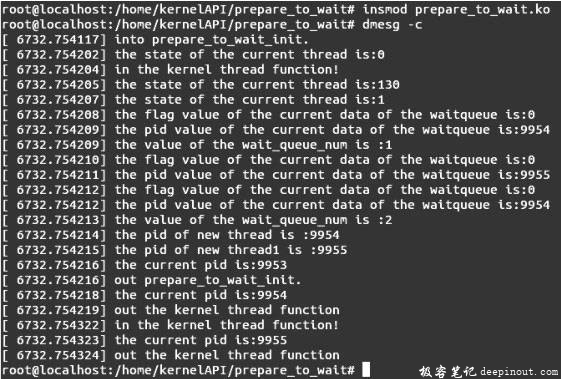
结果分析:
由上图可以看出函数prepare_to_wait( )能够将进程插入到等待队列中,在函数prepare_to_wait( )执行之前,当前进程的状态为0,处于TASK_RUNNING状态,函数执行之后,当前进程的状态更改为130,即处于TASK_KILLABLE状态;状态值是调用函数时传递的第三个参数的值,说明函数prepare_to_wait( )在执行时能更改当前进程的状态值。
由上图的输出结果可以看出第一次插入后只有一个进程插入等待队列,对于进程号为9955的进程没有被插入等待队列中,因为其不满足插入条件。对进程9955的next字段初始化之后,第二次进行插入后,等待队列中的进程数变为2,说明第二次插入成功,由此可以得出函数prepare_to_wait( )能将满足条件的等待队列元素插入到等待队列中,不满足条件的元素则不能插入等待队列中,此条件在函数功能描述中已经说明。
由函数的输出结果可以得出对于通过函数prepare_to_wait( )插入到等待队列中的等待队列元素的f lags值将被设为0,即对应的进程没有被设置为高优先级进程。
对于后插入的一个进程,进程号是9955的进程对应的等待队列元素位于等待队列的头部,可以得知函数prepare_to_wait( )将等待队列元素插入到等待队列的头部。
进程状态说明:
对于进程能够处于的状态,在函数__wake_up( )的进程状态说明部分有详细的说明。
 极客笔记
极客笔记