completion_done函数功能描述:此函数用于判读参数completion变量中的等待队列是否有等待者,即是否有进程处于阻塞状态,等待此等待队列中的进程执行完毕。函数通过返回bool类型的变量来通知调用者。
completion_done文件包含
#include <linux/completion.h>
completion_done函数定义
在内核源码中的位置:linux-3.19.3/kernel/sched/completion.c
函数定义格式:
bool completion_done(struct completion *x)
completion_done输入参数说明
此函数的输入参数是struct completion结构体类型的指针,包含一个等待队列信息及等待队列的状态信息,等待队列的状态代表此等待队列是否被唤醒过,其定义及详细解释参考complete( )。
completion_done返回参数说明
此函数的返回结果是bool类型的变量,结果可能的取值是0或1,返回1代表等待队列没有等待者,返回0代表等待队列有等待者。
completion_done实例解析
编写测试文件:complete_done.c
头文件引用及全局变量定义:
/*头文件引用*/
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/sched.h>
#include <linux/pid.h>
#include <linux/completion.h>
#include <linux/wait.h>
#include <linux/list.h>
#include <linux/kthread.h>
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
/*全局变量定义*/
static struct completion comple; //用于保存completion的状态
struct task_struct * old_thread;
子进程处理函数定义:
int my_function(void * argc)
{
int result=-1;
wait_queue_head_t head;
wait_queue_t data;
printk("in the kernel thread function! \n");
init_waitqueue_head(&head); //初始化等待队列头元素
init_waitqueue_entry(&data, current); // 用当前进程初始化等待队列元素
add_wait_queue(&head, &data); //将当前进程插入到等待队列中
schedule_timeout_uninterruptible(100); //将等待队列置于不可中断的等待状态
complete(&comple); //调用函数唤醒进程,并更改done字段的值
printk("the value of done of the comple is:%d\n", comple.done); //显示字段done的值
result=completion_done(&comple); //测试completion是否有等待者
printk("the return result of the completion_done is:%d\n", result);
//显示函数调用结果
printk("the current pid is:%d\n", current->pid); //显示当前进程的PID值
printk("the state of the init function is :%ld\n", old_thread->state);
// 显示父进程的状态
//complete(&comple); //调用函数唤醒进程,并更改done字段的值
printk("out the kernel thread function\n");
return 0;
}
模块加载函数定义:
static int __init completion_done_init(void)
{
char namefrm[] = "complete.c";
struct task_struct * result;
wait_queue_t data;
printk("into completion_done_init.\n");
old_thread = current;
result=kthread_create_on_node(my_function, NULL, -1, namefrm); //创建新进程
wake_up_process(result);
init_completion(&comple); //初始化completion变量
init_waitqueue_entry(&data, result); //用新进程初始化等待队列元素
__add_wait_queue_tail(&(comple.wait), &data); // 将新进程加入等待队列的尾部
wait_for_completion(&comple); //阻塞进程,等待新进程的结束
printk("the pid of result is :%d\n", result->pid);
//显示函数kernel_thread( )函数的返回结果
printk("the current pid is:%d\n", current->pid); //显示当前进程的PID值
printk("out completion_done_init.\n");
return 0;
}
模块退出函数定义:
static void __exit completion_done_exit(void)
{
printk("Goodbye completion_done\n");
}
模块加载、退出函数调用:
module_init(completion_done_init);
module_exit(completion_done_exit);
实例运行结果及分析:
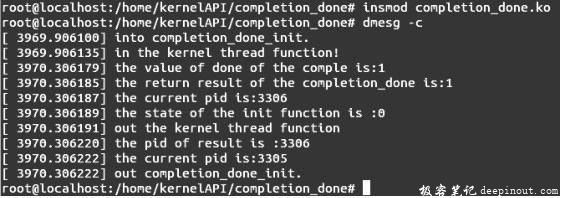
首先编译模块,执行命令insmod complete_done.ko插入内核模块,然后输入命令dmesg -c查看模块插入结果,会出现如图A所示的结果。
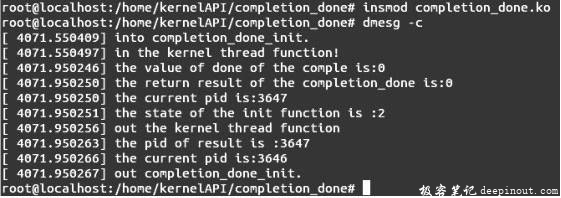
注释掉子进程处理函数中的第一处“complete(&comple); ”,去掉第二处“complete (&comple); ”的注释;然后保存文件,重新编译、加载模块,输入命令dmesg -c会出现如图B所示的结果。
结果分析:
对于图A的测试程序,函数complete( )的执行在函数completion_done( )之前,等待队列在函数执行之前被唤醒,所以当函数执行时函数wait_for_completion( )设置的等待者被解除,即变量comple没有了等待者,函数completion_done( )的返回结果是1正好与之对应。
对于图B的测试程序,函数complete( )的执行在函数completion_done( )之后,等待队列在函数执行之前没有被唤醒,所以当函数complete( )执行时函数wait_for_completion( )设置的等待者仍存在,函数completion_done( )的返回结果是0正好与之对应。
 极客笔记
极客笔记