函数unregister_chrdev()通过调用函数__unregister_chrdev()实现其功能,函数__unregister_chrdev()首先调用函数__unregister_chrdev_region()删除一个字符设备区,并更改文件/proc/devices的内容;然后将一个字符设备从Linux内核系统中删除,如果此字符设备是通过函数cdev_alloc()动态申请的,函数会释放其占用的内存空间。最后调用函数cdev_del()删除字符设备。
unregister_chrdev文件包含
#include <linux/fs.h>
unregister_chrdev函数定义
在内核源码中的位置:linux-3.19.3/include/linux/fs.h
函数定义格式:
static inline void unregister_chrdev(unsigned int major, const char *name)
{
__unregister_chrdev(major, 0, 256, name);
}
unregister_chrdev输入参数说明
- 函数
unregister_chrdev()有两个输入参数,第一个输入参数代表即将被删除的字符设备区及字符设备的主设备号,函数将根据此参数查找内核中的字符设备。 - 第二个输入参数代表设备名,但在函数的实现源码中没有用到,没有什么意义。
unregister_chrdev返回参数说明
- 函数
unregister_chrdev()的返回void类型的结果,即不返回任何类型的值。
unregister_chrdev实例解析
编写测试文件:register_unregister_chrdev.c
头文件引用、全局变量定义及相关函数声明:
/*头文件引用*/
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
#include <linux/vmalloc.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <asm/uaccess.h>
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <linux/moduleparam.h>
#include <linux/pci.h>
#include <asm/unistd.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
/*宏定义及全局变量定义*/
#define MEM_MALLOC_SIZE 4096 //缓冲区大小
#define MEM_MAJOR 245 //主设备号
#define MEM_MINOR 0 //次设备号
char *mem_spvm; //缓冲区指针,指向内存区
struct class *mem_class; //设备类指针
static int __init register_unregister_chrdev_init(void); //模块加载函数声明
static void __exit register_unregister_chrdev_exit(void); //模块卸载函数声明
static int mem_open(struct inode *ind, struct file *filp); //设备打开函数声明
static int mem_release(struct inode *ind, struct file *filp); //设备关闭函数声明
/*设备读函数声明*/
static ssize_t mem_read(struct file *filp, char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *fpos);
/*设备写函数声明*/
static ssize_t mem_write(struct file *filp, const char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *fpos);
/*定义设备驱动文件结构体*/
struct file_operations mem_fops =
{
.owner=THIS_MODULE, //驱动文件拥有者
.open = mem_open, //设备打开函数
.release = mem_release, //设备打开函数
.read = mem_read, //设备读函数
.write = mem_write, //设备写函数
};
模块加载函数定义:
/*模块加载函数定义*/
int __init register_unregister_chrdev_init(void)
{
int res;
printk("into register_unregister_chrdev_init\n");
mem_spvm = (char *)vmalloc(MEM_MALLOC_SIZE); //开辟内存缓冲区
res=register_chrdev(MEM_MAJOR, "my_char_dev", &mem_fops); // 注册一个字符设备
if(res) //注册失败
{
unregister_chrdev(MEM_MAJOR, "my_char_dev"); //失败,删除注册的字符设备
printk("register char dev failed\n");
return -1;
}
printk("register char dev success\n");
mem_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "my_char_dev"); //创建设备类
if(IS_ERR(mem_class)) //判断创建是否成功
{
printk("failed in creating class.\n");
class_destroy(mem_class); //失败,销毁设备类
return -1;
}
printk("class create success\n");
device_create(mem_class, NULL, MKDEV(MEM_MAJOR, MEM_MINOR), NULL, "my_char_dev");
// 注册设备文件系统,并建立设备节点
printk("device create success\n");
printk("out register_unregister_chrdev_init\n");
return 0;
}
模块退出函数定义:
void __exit register_unregister_chrdev_exit (void)
{
printk("into register_unregister_chrdev_exit\n");
unregister_chrdev(MEM_MAJOR, "my_char_dev"); //删除字符设备
printk("unregister char dev success\n");
/*删除设备节点及目录*/
device_destroy(mem_class, MKDEV(MEM_MAJOR, MEM_MINOR));
printk("device destroy success\n");
class_destroy(mem_class); //删除设备类
printk("class destroy success\n");
if (mem_spvm ! = NULL)
vfree(mem_spvm); //释放缓冲区空间
printk("vfree ok! \n");
printk("out register_unregister_chrdev_exit\n");
}
相关函数定义:
/*设备打开函数定义*/
int mem_open(struct inode *ind, struct file *filp)
{
printk("open vmalloc space\n");
try_module_get(THIS_MODULE); //模块引用自加
printk("open vmalloc space success\n");
return 0;
}
/*设备读函数定义*/
ssize_t mem_read(struct file *filp, char *buf, size_t size, loff_t *lofp)
{
int res = -1;
char *tmp;
printk("copy data to the user space\n");
tmp = mem_spvm;
if (size > MEM_MALLOC_SIZE) //判断读取数据的大小
size = MEM_MALLOC_SIZE;
if (tmp ! = NULL)
res = copy_to_user(buf, tmp, size); //将内核输入写入用户空间
if (res == 0)
{
printk("copy data success and the data is:%s\n", tmp); //显示读取的数据
return size;
}
else
{
printk("copy data fail to the user space\n");
return 0;
}
}
/*设备写函数定义*/
ssize_t mem_write(struct file *filp, const char *buf, size_t size, loff_t *lofp)
{
int res = -1;
char *tmp;
printk("read data from the user space\n");
tmp = mem_spvm;
if (size > MEM_MALLOC_SIZE) //判断输入数据的大小
size = MEM_MALLOC_SIZE;
if (tmp ! = NULL)
res = copy_from_user(tmp, buf, size); //将用户输入数据写入内核空间
if (res == 0)
{
printk("read data success and the data is:%s\n", tmp); //显示写入的数据
return size;
}
else
{
printk("read data from user space fail\n");
return 0;
}
}
/*设备关闭函数定义*/
int mem_release(struct inode *ind, struct file *filp)
{
printk("close vmalloc space\n");
module_put(THIS_MODULE); //模块引用自减
printk("close vmalloc space success\n");
return 0;
}
模块加载、退出函数调用:
module_init(register_unregister_chrdev_init); //模块加载
module_exit(register_unregister_chrdev_exit); //模块卸载
用户态测试函数:
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <linux/fcntl.h>
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int fd, cnt;
char buf[256];
printf("char device testing.\n");
fd = open("/dev/my_char_dev", O_RDWR); //打开字符设备
if (fd == 0)
{
printf("the char dev file cannot be opened.\n");
return 1;
}
printf("input the data for kernel: ");
scanf("%s", buf); //输入数据
cnt = write(fd, buf, 256); //将输入数据写入设备
if (cnt == 0)
printf("Write Error! \n");
cnt = read(fd, buf, 256); //从设备中读取数据
if (cnt > 0)
printf("read data from kernel is: %s\n", buf);
else
printf("read data error\n");
close(fd); //关闭设备
printf("close the char dev file and test over\n");
return 0;
}
实例运行结果及分析
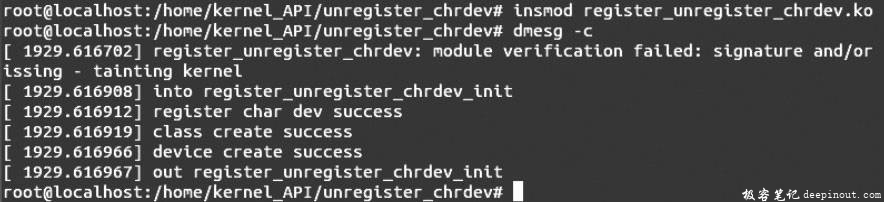
首先编译模块,执行命令insmod register_unregister_chrdev.ko插入内核模块,然后输入命令dmesg -c查看模块插入结果,会出现如图A所示的结果。
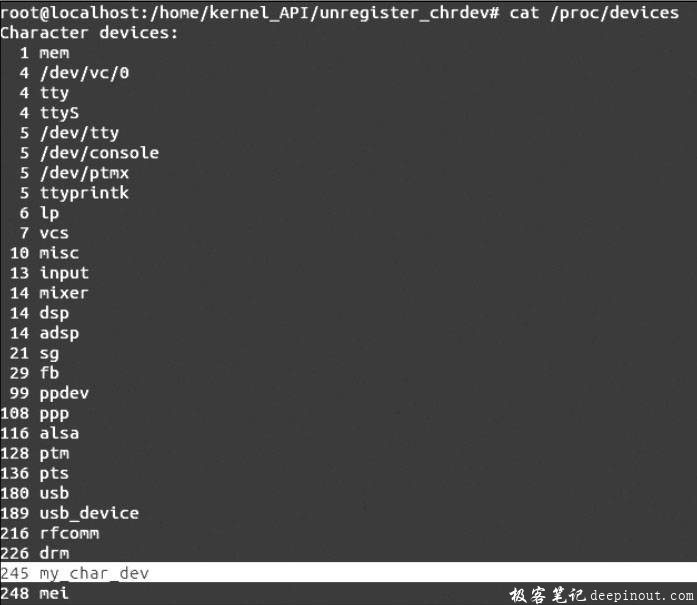
执行命令cat /proc/devices查看注册的字符设备,出现如图B所示的结果。
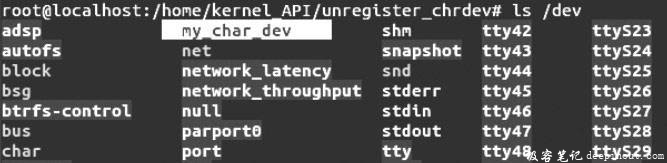
执行命令ls /dev查看当前系统的设备文件,出现如图C所示的结果。
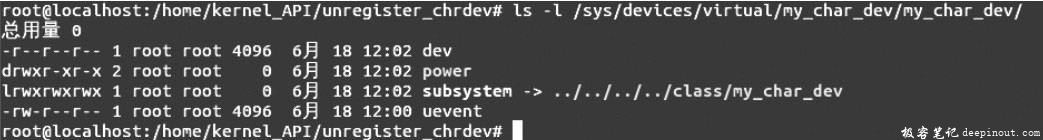
执行命令ls -l /sys/devices/virtual/my_char_dev/my_char_dev查看逻辑设备目录,出现如图D所示的结果。
用gcc编译器编译用户驱动测试文件,运行编译之后的可执行文件,出现如图E所示的结果。
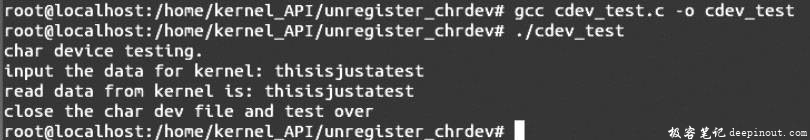
用户测试程序执行完之后,输入命令dmesg -c,出现如图F所示的执行结果。
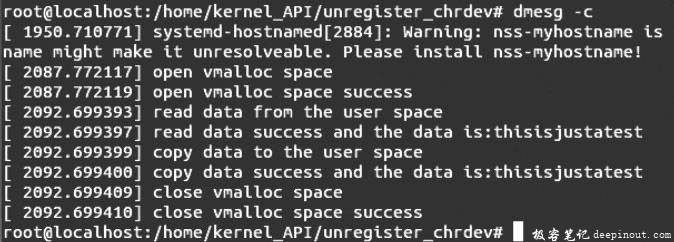
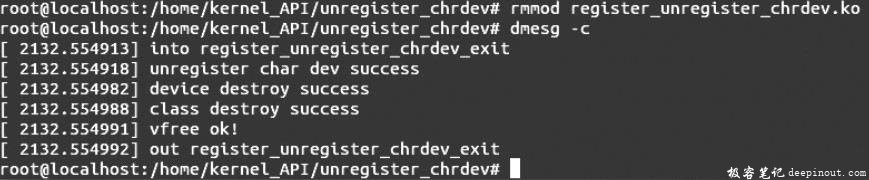
卸载内核模块,执行命令rmmod register_unregister_chrdev.ko,然后输入命令dmesg -c,出现如图G所示的信息。
结果分析:
由图A和图B的显示结果可以判断添加字符设备区及字符设备成功;图E和图F的显示信息说明用户程序能够成功的访问新字符设备,并且字符设备能够正常的工作,正好说明了添加的字符设备是成功的,函数register_chrdev()能够向Linux内核系统添加字符设备。执行完命令rmmod register_unregister_chrdev.ko之后,重新查看文件/proc/devices的内容,可以发现没有出现图B的记录表项,说明设备被函数unregister_chrdev()成功删除。
函数比较:
对于用函数cdev_init()、cdev_alloc()、cdev_add()向Linux内核系统中添加的字符设备,在文件/proc/devices中没有出现新添加的设备的记录表项,而用函数register_chrdev()向Linux内核系统中添加的字符设备,在文件/proc/devices中有新添加的字符设备的记录表项,但通过第一种方法添加的字符设备是完全好用的,与第二种方法没有什么区别。函数register_chrdev()在实现过程中调用了函数__register_chrdev_region(),此函数的作用是注册一个字符设备区,控制对应主设备号的次设备号的变化范围,这是文件/proc/devices中出现新设备记录表项的原因。
 极客笔记
极客笔记