Java 检查输入元素到数组时的数组边界
数组是一种线性数据结构,用于存储具有相似数据类型的一组元素。它按顺序存储数据。一旦我们创建了一个数组,就无法改变它的大小,即它是固定长度的。
本文将帮助您了解数组和数组边界的基本概念。此外,我们将讨论检查输入元素到数组时的Java程序的数组边界。
数组和数组边界
我们可以通过索引来访问数组元素。假设我们有一个长度为N的数组,则
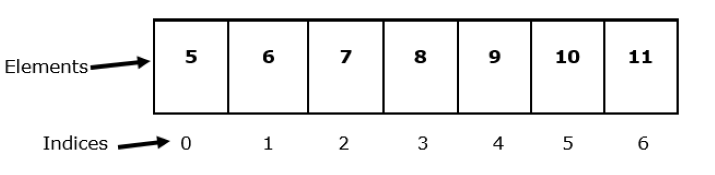
我们可以看到上图中数组有7个元素,但索引值是从0到6,即0到7-1。
数组的范围称为其边界。上述数组的范围从0到6,因此我们也可以说0到6是给定数组的边界。如果尝试访问超出范围的索引值或负索引,将会得到ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException。这是一种在运行时发生的错误。
声明数组的语法
Data_Type[] nameOfarray;
// declaration
Or,
Data_Type nameOfarray[];
// declaration
Or,
// declaration with size
Data_Type nameOfarray[] = new Data_Type[sizeofarray];
// declaration and initialization
Data_Type nameOfarray[] = {values separated with comma};
我们可以在程序中使用上述任何一种语法。
在将元素输入到数组时检查数组边界
示例1
如果我们在数组的边界内访问数组的元素,就不会出现任何错误。程序将成功执行。
public class Main {
public static void main(String []args) {
// declaration and initialization of array ‘item[]’ with size 5
String[] item = new String[5];
// 0 to 4 is the indices
item[0] = "Rice";
item[1] = "Milk";
item[2] = "Bread";
item[3] = "Butter";
item[4] = "Peanut";
System.out.print(" Elements of the array item: " );
// loop will iterate till 4 and will print the elements of ‘item[]’
for(int i = 0; i <= 4; i++) {
System.out.print(item[i] + " ");
}
}
}
输出
Elements of the array item: Rice Milk Bread Butter Peanut
示例2
让我们尝试打印给定数组范围之外的值。
public class Tutorialspoint {
public static void main(String []args) {
String[] item = new String[5];
item[0] = "Rice";
item[1] = "Milk";
item[2] = "Bread";
item[3] = "Butter";
item[4] = "Peanut";
// trying to run the for loop till index 5
for(int i = 0; i <= 5; i++) {
System.out.println(item[i]);
}
}
}
输出
Rice
Milk
Bread
Butter
Peanut
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: Index 5 out of bounds for length 5
at Tutorialspoint.main(Tutorialspoint.java:11)
正如我们之前讨论的那样,如果我们尝试访问一个数组的索引值超出其范围或为负数的话,我们会得到一个ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException。
在上面的程序中,我们尝试执行一个for循环直到数组’item[]’的索引5,但是它的范围只有从0到4。因此,在打印出4之后,我们得到了一个错误。
示例3
在这个示例中,我们尝试使用try和catch块来处理ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException异常。我们将在用户输入数组元素时检查数组边界。
import java.util.*;
public class Tutorialspoint {
public static void main(String []args) throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException {
// Here ‘sc’ is the object of scanner class
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter number of items: ");
int n = sc.nextInt();
// declaration and initialization of array ‘item[]’
String[] item = new String[n];
// try block to test the error
try {
// to take input from user
for(int i =0; i<= item.length; i++) {
item[i] = sc.nextLine();
}
}
// We will handle the exception in catch block
catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException exp) {
// Printing this message to let user know that array bound exceeded
System.out.println(
" Array Bounds Exceeded \n Can't take more inputs ");
}
}
}
输出
Enter number of items: 3
结论
在这篇文章中,我们学习了数组和数组边界。我们讨论了为什么如果我们试图在数组范围之外访问数组元素,我们会得到一个错误,以及我们如何使用try和catch块来处理这个错误。
 极客笔记
极客笔记