在有向图中找到长度为K的路径数
给定一个有向无权图G和一个整数K。您需要找到这个图中长度为K的路径的数量。这里的图以邻接矩阵的形式给出。从顶点i到j,如果存在一条边,则表示为G[i][j]=1,否则表示为G[i][j]=0。
输入
- 一个由邻接矩阵表示的有向无权图
-
一个整数K,表示要找到的路径的长度
输出
长度为K的路径的总数
案例I K=3
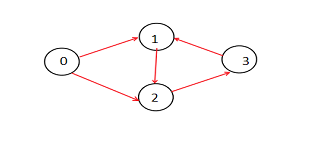
输出
路径总数= 2
解释
在上面的图中,有两条长度为3的路径。它们是:
- 0->1->2->3
-
0->2->3->1
案例II K=2
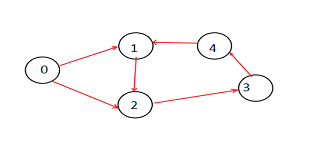
输出
路径总数= 6
解释
在上面的图中,有六条长度为2的路径。它们是:
- 0->1->2
-
0->2->3
-
1->2->3
-
2->3->4
-
3->4->1
-
4->1->2
示例
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] G = {
{0, 1, 1, 0},
{0, 0, 1, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 1},
{0, 1, 0, 0}
};
int K = 3;
List<List<Integer>> paths = fpath(G, K);
System.out.println("Paths of length are");
int count=0;
for (List<Integer> path : paths) {
count++;
System.out.println(path);
}
System.out.println("Total number of paths "+count);
}
public static List<List<Integer>> fpath(int[][] G, int K) {
List<List<Integer>> paths = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
boolean[] visited = new boolean[G.length];
// Start the search from each vertex
for (int i = 0; i < G.length; i++) {
dfs(G, i, K, path, visited, paths);
}
return paths;
}
private static void dfs(int[][] G, int vertex, int K,
List<Integer> path, boolean[] visited,
List<List<Integer>> paths) {
visited[vertex] = true;
path.add(vertex);
if (K == 0) {
paths.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
} else {
for (int n = 0; n < G.length; n++) {
if (G[vertex][n] == 1 && !visited[n]) {
dfs(G, n, K - 1, path, visited, paths);
}
}
}
visited[vertex] = false;
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
}
输出
Paths of length are
[0, 1, 2, 3]
[0, 2, 3, 1]
Total number of paths 2
解释
为了找到长度等于K的路径,我们将使用DFS(深度优先搜索)方法。有两个辅助函数- fpath()和dfs()。
fpath()函数
-
在fpath()函数中,将邻接矩阵G和K作为参数传递。它返回一个包含路径的列表。并且打印长度为K的路径的总数。
-
初始化一个包含路径的列表的列表,并初始化当前路径列表。创建一个布尔数组来标记访问过的顶点。对于每个顶点,调用dfs()方法,检查其是否包含长度为K的路径。
dfs()函数
-
dfs()函数用于执行深度优先搜索操作。这是一个递归函数。我们将传递图,当前顶点,剩余长度K,访问过的路径,跟踪访问过的顶点的布尔数组visited和包含路径的列表的列表paths。
-
在给定的dfs()函数中,我们将顶点标记为已访问并添加到访问过的路径中。然后访问相邻的顶点。如果相邻顶点未被访问,则递归调用dfs()函数,传递新的顶点和剩余长度K-1。
-
如果K的值为0,即我们的基本情况,将当前访问过的路径添加到“paths”中。否则,如果存在从顶点到相邻顶点的路径,并且相邻顶点未被访问,则递归调用函数。
-
在访问完所有邻居之后,将顶点标记为未访问并从当前访问过的路径列表中删除。这也被称为回溯。
 极客笔记
极客笔记