Spring Boot 如何实现简单的身份验证
Spring Boot被广泛认可为用于开发Java应用程序的框架,因其简单性和增加生产力的声誉而备受赞誉。在许多应用程序中,身份验证的实施是一个重要考虑因素,它可以确保只有经过授权的人员才能访问特定资源。
在Spring Boot中,通过利用其内置的安全特性和库,实现身份验证既高效又便捷。这种能力使开发人员可以专注于核心业务逻辑,而无需重新发明现有解决方案。
开发人员可以通过遵循一些简单的步骤来确保其Spring Boot应用程序的安全性并保护敏感数据。这些步骤包括在Spring Boot中实现身份验证,为应用程序开发奠定安全基础。通过这样做,用户在访问受保护的资源之前将需要对自己进行身份验证。本文探讨了在Spring Boot中实现简单身份验证的过程,并提供了有价值的见解,以有效保护您的应用程序。
Spring Boot
Spring Boot是基于Java的开源框架,用于轻松开发和部署强大的独立应用程序。
Spring Boot旨在最小化配置和样板代码,使开发人员能够快速构建强大和可伸缩的应用程序。凭借其主观的方法和自动设置功能,Spring Boot避免了手动配置的需要,并为开发基于Spring的应用程序提供了一个和谐的环境。
该句子展示了一系列功能,包括嵌入式服务器、依赖管理和强大的安全选项。凭借这些功能,它已成为构建微服务、Web应用程序和RESTful API的流行选择。
方法
在Spring Boot中,可以找到多种实现简单身份验证的方法。让我们来探索三种常见方法:
- 使用内存中的身份验证
-
使用数据库身份验证
-
使用LDAP身份验证
使用内存中的身份验证
在此方法中,应用程序将用户凭证存储在内存中。为了定义用户详细信息,如用户名、密码和角色,需要实现UserDetailsService接口。在进行身份验证时,Spring Security将提供的凭据与内存中保存的凭据进行比较。根据匹配情况,它授予或拒绝用户访问权限。
步骤
- 创建一个实现UserDetailsService接口的配置类。
-
在配置类中定义用户详细信息(用户名、密码、角色)。
-
在身份验证期间,Spring Security将提供的凭据与内存中的用户详细信息进行比较。
-
根据匹配情况授予或拒绝访问权限。
示例
//pom.xml
<dependencies>
<!-- Other dependencies -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
// WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter.java
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.authentication.
builde
rs.AuthenticationManagerBuilder;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.
HttpSecu
rity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.
Ena
bleWebSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.
Web
SecurityConfigurerAdapter;
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth)
throws Exception {
auth.inMemoryAuthentication()
.withUser("admin").password("{noop}password").roles("ADMIN")
.and()
.withUser("user").password("{noop}password").roles("USER");
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/admin").hasRole("ADMIN")
.antMatchers("/user").hasRole("USER")
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin();
}
}
输出
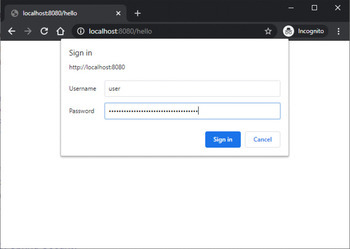
使用数据库认证
采用这种方法,用户凭证被存储在数据库中。创建一个用户实体,并带有一个与数据库交互的存储库。在认证过程中,Spring Security利用UserDetailsService接口从数据库中加载用户详细信息,将其与提供的凭证进行比较,以授予或拒绝访问权限。
步骤
- 创建一个用户实体并定义与数据库交互的存储库。
-
实现UserDetailsService接口以从数据库中加载用户详细信息。
-
在认证过程中,Spring Security根据提供的凭证从数据库中检索用户详细信息。
-
将检索到的凭证与提供的凭证进行比较,并根据情况授予或拒绝访问权限。
示例
//pom.xml
<dependencies>
<!-- Other dependencies -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Add your database driver dependency -->
</dependencies>
// application.properties
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:<localhost:8080/hello>
spring.datasource.username=<user>
spring.datasource.password=<password>
spring.jpa.show-sql=true
//User.java
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
@Entity
public class User {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
private String username;
private String password;
private boolean enabled;
// Getters and setters
// Constructors
}
// UserDetailsService.java
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.
UsernameNotFoundExcept
ion;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class UserDetailsServiceImpl implements UserDetailsService {
private UserRepository userRepository;
@Autowired
public UserDetailsServiceImpl(UserRepository userRepository) {
this.userRepository = userRepository;
}
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
User user = userRepository.findByUsername(username)
.orElseThrow(() -> new UsernameNotFoundException("User not found with username: " + username));
return new org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User(
user.getUsername(),
user.getPassword(),
user.isEnabled(),
true,
true,
true,
Collections.emptyList()
);
}
}
// UserRepository.java
import java.util.Optional;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository<User, Long> {
Optional<User> findByUsername(String username);
}
// WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter.java
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.authentication.
builde
rs.AuthenticationManagerBuilder;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.
HttpSecu
rity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.
Ena
bleWebSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.
Web
SecurityConfigurerAdapter;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.password.PasswordEncoder;
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
private UserDetailsServiceImpl userDetailsService;
private PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder;
@Autowired
public SecurityConfig(UserDetailsServiceImpl userDetailsService, PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder) {
this.userDetailsService = userDetailsService;
this.passwordEncoder = passwordEncoder;
}
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.userDetailsService(userDetailsService).passwordEncoder(passwordEncoder);
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/admin").hasRole("ADMIN")
.antMatchers("/user").hasAnyRole("ADMIN", "USER")
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin();
}
}
输出
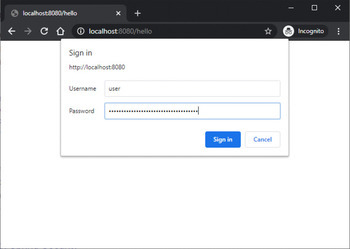
使用LDAP认证
当使用LDAP服务器进行用户管理时,LDAP认证是适用的。Spring Security与LDAP服务器集成,允许对其进行认证。配置涉及指定LDAP服务器连接详情,包括主机、端口和凭据。另外,定义了搜索基础和过滤器,以在LDAP目录中定位用户条目。Spring Security然后通过与LDAP服务器验证所提供的凭据进行身份认证。
步骤
- 配置LDAP服务器的连接详情,包括主机、端口和凭据。
-
定义搜索基础和过滤器,以在LDAP目录中定位用户条目。
-
在认证过程中,Spring Security通过与LDAP服务器验证所提供的凭据。
-
根据认证结果授予或拒绝访问权限。
示例
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.ldapAuthentication()
.userDnPatterns("uid={0},ou=users")
.groupSearchBase("ou=groups")
.contextSource()
.url("ldap://localhost:389/dc=mycompany,dc=com")
.managerDn("cn=admin,dc=mycompany,dc=com")
.managerPassword("admin");
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/user").hasRole("USER")
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SecurityConfig.class, args);
}
}
输出
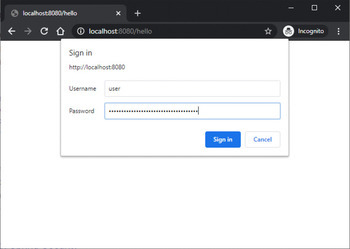
结论
在这个教程中,使用Spring Boot实现简单的身份验证对于保护应用程序和确保只有授权用户能够访问受保护的资源是至关重要的。无论是使用内存身份验证、数据库身份验证还是LDAP身份验证,Spring Boot都通过Spring Security提供了便捷的功能来简化身份验证过程。通过选择最合适的方法并配置必要的组件,开发人员可以建立一个强大的身份验证系统,保护他们的应用程序并防止未经授权的访问敏感数据。
 极客笔记
极客笔记