Java 如何使用PreparedStatement
当在Java中使用数据库和SQL查询时,利用PreparedStatement来安全有效地运行参数化查询至关重要。
与数据库交互的能力是当今这个数据驱动世界中许多软件程序的重要需求。Java是一种多用途和强大的编程语言,提供了Java数据库连接(JDBC),这是一种有效的机制,可以实现与不同数据库系统的顺畅交互。
Java的PreparedStatement功能允许程序员在执行SQL查询之前预编译它们。通过减少解析时间和重用执行计划,与常规的Statement对象相比,PreparedStatement提高了数据库的性能。此外,它还提供了一种安全的处理动态输入的方法,以防止SQL注入攻击。
从上面的段落中,我们了解了使用PreparedStatement的定义和优点,现在我们将通过一些示例来了解PreparedStatement的使用。
首先,让我们在MYSQL数据库中创建一个表,或者您可以使用您熟悉的任何数据库。
创建表:-
打开Mysql数据库,现在我们将创建一个新的数据库并使用它。
create database Test;
use Test;
现在让我们创建一个拥有emp_id、emp_name和emo_email列的Employee表。
查询
create table Employee(emp_id int primary key,emp_name varchar(20), emp_email varchar(20));
desc Employee;
输出
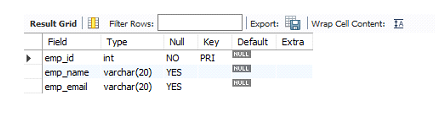
将一些记录插入到Employee表中:
insert into Employee values(1,"Hari","hari123@gmail.com");
insert into Employee values(2,"Syam","syam98@gmail.com");
insert into Employee values(3,"Revanth","Revanth53@gmail.com");
让我们检查数据是否已被插入到表中:
查询
select *from Employee;
输出
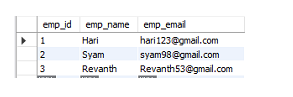
现在我们已经准备好了数据。让我们创建一个Java应用程序,尝试使用Eclipse IDE连接到这个数据库。PreparedStatement的使用主要包括5个步骤:
- 建立连接。
-
创建PreparedStatement。
-
设置参数。
-
执行查询。
-
关闭连接。
在建立数据库连接之前,我们需要加载JDBC驱动程序,或者只需从Maven存储库中添加mysql依赖项来建立连接。驱动程序类名将根据所使用的数据库而变化。
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
或者
依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.27</version>
</dependency>
现在我们将使用JDBC的URL、用户名和密码来建立与数据库的连接。
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection( "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/Test","root", "root");
一旦连接建立,我们可以使用< b >PreparedStatement< /b >类执行我们的SQL语句。
我们将使用< b >问号< /b >作为查询中的占位符。
select *from Employee where emp_name= ?
示例1
import java.net.ConnectException;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/Test";
String user ="root";
String password = "root";
Connection myConn = null;
ResultSet result = null;
try {
//We will provide the url,username and the password to establish the connection
myConn = DriverManager.getConnection(url,user,password);
//we will form our query and keep placeholders if we want to pass any paramters
String qp= "select * from Employee where emp_name =?";
//creation of PreparedStatement
PreparedStatement myStmnt = myConn.prepareStatement(qp);
//Now we will set the parameters
//depending upon the paramter type we will use different methods to set the values like
//myStmnt.setInt(),myStmnt.setFloat(),myStmnt.setDouble(),setString()
//first value in setString() represents paramterIndex and second will be the value
myStmnt.setString(1, "Hari");
//for executing the query we have mainly two methods
//1. executeQuery() - we need to use this when we are using select queries and it returns ResultSet
//2. executeUpdate()- we use this method when we need to perform operations like create, insert, drop, delete, update
result= myStmnt.executeQuery();
System.out.println("EmpID"+ " " + "EmpName");
System.out.println("=============");
while(result.next()) {
System.out.println(result.getInt("emp_id") + " \t " + result.getString("emp_name"));
}
}
catch(Exception e){
// this catch block is used to handle the exceptions
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
//close the connection
myConn=null;
result=null;
}
}
}
输出
EmpID EmpName
=============
1 Hari
示例2
现在我们将看一个使用PreparedStatement向我们的Employee表中插入记录的示例。
import java.net.ConnectException;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/Test";
String user ="root";
String password = "root";
Connection myConn = null;
ResultSet result = null;
try {
//We will provide the url,username and the password to establish the connection
myConn = DriverManager.getConnection(url,user,password);
//we will form our query and keep placeholders if we want to pass any paramters
String qp= "insert into Employee values(?,?,?)";
//creation of PreparedStatement
PreparedStatement myStmnt = myConn.prepareStatement(qp);
//Now we will set the parameters
//depending upon the paramter type we will use different methods to set the values like
//myStmnt.setInt(),myStmnt.setFloat(),myStmnt.setDouble(),setString()
myStmnt.setInt(1, 4);
myStmnt.setString(2, "Latha");
myStmnt.setString(3, "latha1210@gmail.com");
//for executing the query we have mainly two methods
//1. executeQuery() - we need to use this when we are using select queries and it returns ResultSet
//2. executeUpdate()- we use this method when we need to perform operations like create, insert, drop, delete, update
int recCount= myStmnt.executeUpdate();
System.out.println(recCount + " record(s) inserted");
}
catch(Exception e){
// this catch block is used to handle the exceptions
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
//close the connection
myConn=null;
result=null;
}
}
}
输出
在将数据插入表之前:
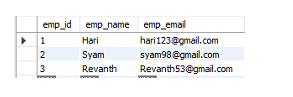
运行上述程序后,即插入一条记录后:
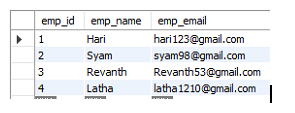
结论
在本文中,我们讨论了PreparedStatement的定义以及其相对于普通语句的优势,包括增强的效率和防止SQL注入。我们还使用JDBC的帮助在Java中看到了一些PreparedStatement的示例。
 极客笔记
极客笔记