Java 数组旋转
数组是一种线性数据结构,用于存储具有相似数据类型的一组元素。它以顺序的方式存储数据。一旦我们创建了一个数组,就无法改变它的大小,即它可以存储固定数量的元素。数组有广泛的应用和用途。此外,我们可以对数组执行许多操作。本文将帮助您了解数组的基础知识,并且我们也将编写Java程序来执行数组的右旋转和左旋转操作。
Java数组旋转的程序
首先,让我们了解在数组的上下文中什么是右旋转和左旋转。
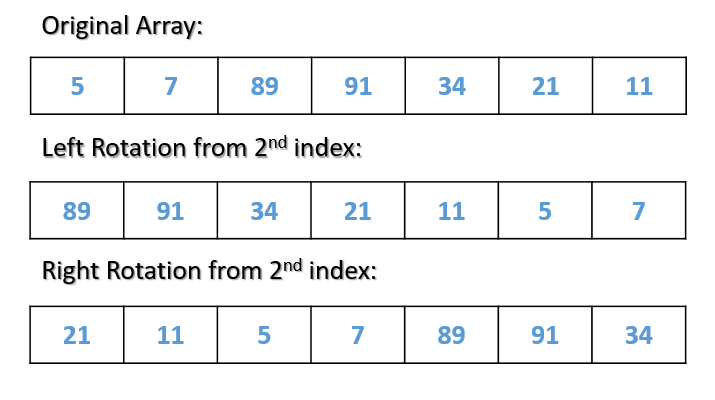
在数组的右旋转中,我们只是将数组的元素向右移动指定的位置,左旋转的情况则相反,如下一个示例所示。
实例
声明数组的语法
Data_Type nameOfarray[]; // declaration
Or,
// declaration with size
Data_Type nameOfarray[] = new Data_Type[sizeofarray];
在我们的程序中,我们可以使用以上任何一种语法。
在直接进入程序之前,让我们先了解一下一个内置方法,名为 ‘System.arraycopy()’,我们将在示例程序中使用它。
System.arraycopy() 方法
java.lang.System.arraycopy() 是 Java System 类的静态方法,用于将源数组从指定索引复制到目标数组的指定索引。
语法
System.arraycopy(srcArray, index1, destArray, index2, length);
在这里,
- srcArray − 要复制的数组。
-
index1 − 需要复制的源数组的起始索引。
-
index2 − 目标数组的起始索引,元素将复制到这里。
-
destArray − 元素将被复制到的数组。
-
length − 要复制的元素数量。
示例1
在下面的示例中,我们将从第二个索引开始将数组向左旋转两次。
方法
- 首先,定义一个带有两个参数的方法,接受一个整数和一个索引作为参数。
-
在这个方法中,创建一个临时数组来存储旋转后的元素。然后,使用 ‘arraycopy()’ 方法从指定的索引将原始数组复制到临时数组中。
-
再次使用 ‘arraycopy()’ 方法将原始数组的剩余元素复制到临时数组中,使得元素左移。现在,使用 ‘arraycopy()’ 方法将所有旋转后的元素从临时数组复制到原始数组中。
-
在 main() 方法中,声明并初始化一个整数数组,然后初始化一个整数变量以指定要旋转的索引。然后,调用用户定义的方法来旋转数组。
import java.util.Arrays;
public class ArrayRotationleft {
// user-defined method to rotate the given array
public static void rotateArray(int[] arr, int rotateBy) {
int length = arr.length;
// Calculate the effective rotation value
int rotation = rotateBy % length;
// Create a temporary array to store rotated elements
int[] temp = new int[rotation];
// Copy elements till the rotateBy to the temporary array
System.arraycopy(arr, 0, temp, 0, rotation);
// Shift the remaining elements to the left
System.arraycopy(arr, rotation, arr, 0, length - rotation);
// Copy the rotated elements from the temporary array to the original array
System.arraycopy(temp, 0, arr, length - rotation, rotation);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// declaring and initializing an array
int[] arr = { 5, 7, 89, 91, 34, 21, 11, 0 };
int rotateBy = 2;
System.out.println("The original array is as follows: ");
// for-each loop to print original array
for(int print : arr) {
System.out.print(print + " ");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("The array after left rotation: ");
// calling the method to rotate the array
rotateArray(arr, rotateBy);
// for-each loop to print rotated array
for(int print : arr) {
System.out.print(print + " ");
}
}
}
输出
The original array is as follows:
5 7 89 91 34 21 11 0
The array after left rotation:
89 91 34 21 11 0 5 7
示例2
进行正确旋转时,我们不需要从第0个索引拷贝原始数组,而是需要从我们希望旋转的位置开始拷贝元素。
import java.util.Arrays;
public class ArrayRotationright {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// declaring and initializing an array
int[] arr = { 5, 7, 89, 91, 34, 21, 11, 0 };
int rotateBy = 2;
System.out.println("The original array is as follows: ");
// for-each loop to print original array
for(int print : arr) {
System.out.print(print + " ");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("The array after right rotation: ");
// calling the method to rotate the array
rotateArray(arr, rotateBy);
// for-each loop to print rotated array
for(int print : arr) {
System.out.print(print + " ");
}
}
// user-defined method to rotate the given array
public static void rotateArray(int[] arr, int rotateBy) {
int length = arr.length;
// Calculate the effective rotation value
int rotation = rotateBy % length;
// Create a temporary array to store rotated elements
int[] temp = new int[rotation];
// Copy the elements till rotateBy to the temporary array
System.arraycopy(arr, length - rotation, temp, 0, rotation);
// Shift the remaining elements to the right
System.arraycopy(arr, 0, arr, rotation, length - rotation);
// Copy the rotated elements from the temporary array to the original array
System.arraycopy(temp, 0, arr, 0, rotation);
}
}
输出
The original array is as follows:
5 7 89 91 34 21 11 0
The array after right rotation:
11 0 5 7 89 91 34 21
结论
在本文中,我们了解了什么是数组,并讨论了两个Java程序来执行数组的右旋转和左旋转。同时,我们还发现了arraycopy()方法,在将元素从一个数组复制到另一个数组时非常有用。
 极客笔记
极客笔记