Swift 递归
一个反复调用自身的函数被称为递归函数,而这种技术被称为递归。当你创建一个递归函数时,你必须创建一个条件来确保函数不会无限调用自身。
示例
func recurse() {
//statements
recurse()
}
recurse()
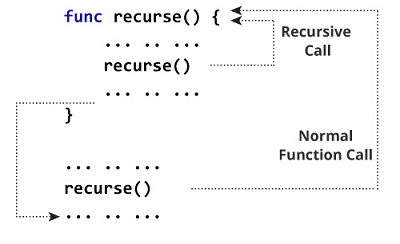
从上面的图表中可以看出,递归是无限执行的。为了摆脱这种无限递归的类型,我们使用控制语句。
示例:Swift 4程序打印N个正数
func countDownToZero(num: Int) {
print(num)
if num > 0 {
countDownToZero(num: num - 1)
}
}
print("Countdown:")
countDownToZero(num:6)
输出:
Countdown:
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
在上面的程序中,print(“Countdown:”)语句会输出结果,而countDownToZero(num:3)语句会调用一个接受一个整数参数的函数。
在countDownToZero()函数内部的语句会执行,如果条件num > 0满足,函数会再次被调用,即countDownToZero(num: num – 1)。
当条件不满足时,函数调用不再进行,递归停止。
执行步骤
| Steps | Function call | Printed | Is num > 0 ? |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | countDownToZero(6) | 6 | Yes |
| 2 | countDownToZero(5) | 5 | Yes |
| 3 | countDownToZero(4) | 4 | Yes |
| 4 | countDownToZero(3) | 3 | Yes |
| 5 | countDownToZero(2) | 2 | Yes |
| 6 | countDownToZero(1) | 1 | Yes |
| 7 | countDownToZero(0) | 0 | No (Recursion Ends) |
示例2:Swift 4程序计算一个数的阶乘
func findFactorial(of num: Int) -> Int {
if num == 1 {
return 1
} else {
return num * findFactorial(of:num - 1)
}
}
let x = 6
let result = findFactorial(of: x)
print("The factorial of \(x) is \(result)")
输出:
The factorial of 6 is 720
执行步骤
| 步骤 | 传入参数 | 返回语句 | 值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6 | 返回 6 * findFactorial(of:5) | 6 * findFactorial(of:5) |
| 2 | 5 | 返回 5 * findFactorial(of:4) | 6 *5 findFactorial(of:4) |
| 3 | 4 | 返回 4 * findFactorial(of:3) | 6 54 findFactorial(of:3) |
| 4 | 3 | 返回 3 * findFactorial(of:2) | 6 54*3 findFactorial(of:2) |
| 5 | 2 | 返回 2 * findFactorial(of:1) | 65432 findFactorial(of:1) |
| 6 | 1 | 返回 1 | 65432*1 |
 极客笔记
极客笔记