try_module_get函数功能描述:该函数的功能是首先判断模块module是否处于活动状态,然后通过local_inc()宏操作将模块module的引用计数加1。
try_module_get文件包含
#include <linux/module.h>
try_module_get函数定义
在内核源码中的位置:linux-3.19.3/kernel/module.c
函数定义格式:
static inline int try_module_get(struct module *module)
try_module_get输入参数说明
module:指向模块结构体的指针,结构体中包含模块的名称、状态、所属的模块链表等。关于结构体struct module的定义,请参见find_module()函数的分析。
try_module_get返回参数说明
返回值为一个整型值,如果模块module处于活动状态且对其引用计数增加1的操作成功,则函数返回1,否则返回0。
try_module_get实例解析
编写测试文件:try_module_get.c
头文件及全局变量声明如下:
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
static int __init try_module_get_init(void);
static void __exit try_module_get_exit(void);
模块初始化函数:
int __init try_module_get_init(void)
{
int ret ;
const char * name;
struct module * fmodule;
name = "test_module"; //定义待查找的模块名为“test_module”
fmodule = find_module( name ); //调用查找模块函数
if( fmodule ! = NULL )
{
printk("before calling try_module_get, \n");
printk("refs of %s is: %d\n", name, module_refcount(fmodule));
ret = try_module_get(fmodule);
printk("after calling try_module_get, \n");
printk("ret = %d\n", ret);
printk("refs of %s is: %d\n", name, module_refcount(fmodule));
}
return 0;
}
模块退出函数:
void __exit try_module_get_exit(void)
{
printk("module exit ok! \n");
}
模块初始化及退出函数调用:
module_init(try_module_get_init);
module_exit(try_module_get_exit);
实例运行结果及分析:
首先执行命令lsmod | head -4,然后编译模块,执行命令insmod try_module_get.ko插入模块,再执行命令dmesg -c和lsmod | head -4,会出现如图所示的结果。
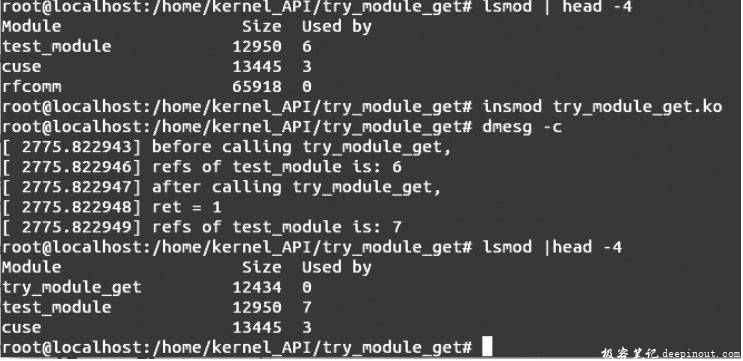
结果分析:
在该测试程序中,首先通过“ lsmod | head -4 ”命令获取一些模块的信息,这里主要关注模块“ test_module ”,该模块是笔者动态插入的模块。在图2-23中可以看到模块“ test_module ”的引用计数为6。
然后测试try_module_get( )函数的功能。首先调用find_module()内核函数查找名为“test_module ”的模块,查找模块返回不为空后,再调用try_module_get( )函数实现对模块“ test_module ”的引用计数减1。上图中中部为运行结果,从中可以看到,在调用try_module_get( )之前,引用计数为6,调用try_module_get()之后,模块“ test_module ”的引用计数因增加1而变为7,并且由于函数执行成功,返回值ret = 1。
最后,再通过“ lsmod | head -4 ”命令获取模块“ test_module ”的信息,从图中的显示信息可知,模块“ test_module ”的引用计数也变为7。
实例程序中调用了find_module()和module_refcount()函数,函数find_module( )是根据模块名查找模块并返回查找到的模块,函数module_refcount()则是用来获得模块被引用的次数。
 极客笔记
极客笔记