LeetCode 705题目描述:不使用任何内建的哈希表库设计一个哈希集合(HashSet)。
实现 MyHashSet 类:
void add(key)向哈希集合中插入值 key 。bool contains(key)返回哈希集合中是否存在这个值 key。void remove(key)将给定值 key 从哈希集合中删除。如果哈希集合中没有这个值,什么也不做。
示例:
输入:
["MyHashSet", "add", "add", "contains", "contains", "add", "contains", "remove", "contains"]
[[], [1], [2], [1], [3], [2], [2], [2], [2]]
输出:
[null, null, null, true, false, null, true, null, false]
解释:
MyHashSet myHashSet = new MyHashSet();
myHashSet.add(1); // set = [1]
myHashSet.add(2); // set = [1, 2]
myHashSet.contains(1); // 返回 True
myHashSet.contains(3); // 返回 False ,(未找到)
myHashSet.add(2); // set = [1, 2]
myHashSet.contains(2); // 返回 True
myHashSet.remove(2); // set = [1]
myHashSet.contains(2); // 返回 False ,(已移除)
提示:
0 <= key <= 10^6- 最多调用
10^4次 add、remove 和 contains 。
LeetCode 705概述
为了实现哈希集合这一数据结构,有以下几个关键问题需要解决:
- 哈希函数:能够将集合中任意可能的元素映射到一个固定范围的整数值,并将该元素存储到整数值对应的地址上。
- 冲突处理:由于不同元素可能映射到相同的整数值,因此需要在整数值出现「冲突」时,需要进行冲突处理。总的来说,有以下几种策略解决冲突:
- 链地址法:为每个哈希值维护一个链表,并将具有相同哈希值的元素都放入这一链表当中。
- 开放地址法:当发现哈希值 h 处产生冲突时,根据某种策略,从 h 出发找到下一个不冲突的位置。例如,一种最简单的策略是,不断地检查 h + 1,h + 2,h + 3,… 这些整数对应的位置。
- 再哈希法:当发现哈希冲突后,使用另一个哈希函数产生一个新的地址。
- 扩容:当哈希表元素过多时,冲突的概率将越来越大,而在哈希表中查询一个元素的效率也会越来越低。因此,需要开辟一块更大的空间,来缓解哈希表中发生的冲突。
以上内容读者可以自行翻阅数据结构的教材,本题解不再阐述,而是直接给出一个最简单的哈希表实现。
LeetCode 705解决方案
方法:链地址法
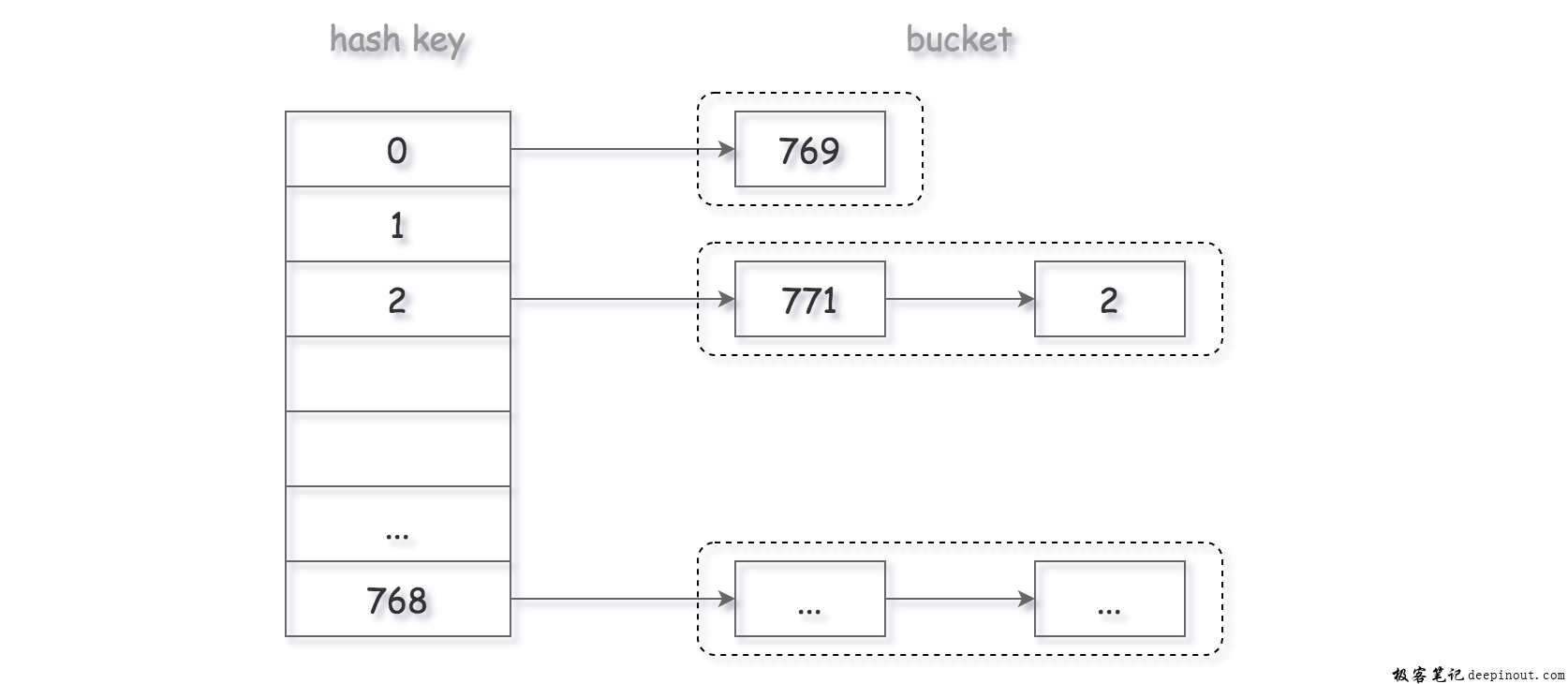
设哈希表的大小为 base,则可以设计一个简单的哈希函数:hash(x) = x mod base。
我们开辟一个大小为 base 的数组,数组的每个位置是一个链表。当计算出哈希值之后,就插入到对应位置的链表当中。
由于我们使用整数除法作为哈希函数,为了尽可能避免冲突,应当将 base 取为一个质数。在这里,我们取 base = 769。
LeetCode 705代码
C++语言
class MyHashSet {
private:
vector<list<int>> data;
static const int base = 769;
static int hash(int key) {
return key % base;
}
public:
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
MyHashSet(): data(base) {}
void add(int key) {
int h = hash(key);
for (auto it = data[h].begin(); it != data[h].end(); it++) {
if ((*it) == key) {
return;
}
}
data[h].push_back(key);
}
void remove(int key) {
int h = hash(key);
for (auto it = data[h].begin(); it != data[h].end(); it++) {
if ((*it) == key) {
data[h].erase(it);
return;
}
}
}
/** Returns true if this set contains the specified element */
bool contains(int key) {
int h = hash(key);
for (auto it = data[h].begin(); it != data[h].end(); it++) {
if ((*it) == key) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
};
java语言
class MyHashSet {
private static final int BASE = 769;
private LinkedList[] data;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public MyHashSet() {
data = new LinkedList[BASE];
for (int i = 0; i < BASE; ++i) {
data[i] = new LinkedList<Integer>();
}
}
public void add(int key) {
int h = hash(key);
Iterator<Integer> iterator = data[h].iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Integer element = iterator.next();
if (element == key) {
return;
}
}
data[h].offerLast(key);
}
public void remove(int key) {
int h = hash(key);
Iterator<Integer> iterator = data[h].iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Integer element = iterator.next();
if (element == key) {
data[h].remove(element);
return;
}
}
}
/** Returns true if this set contains the specified element */
public boolean contains(int key) {
int h = hash(key);
Iterator<Integer> iterator = data[h].iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Integer element = iterator.next();
if (element == key) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
private static int hash(int key) {
return key % BASE;
}
}
Javascript语言
var MyHashSet = function() {
this.BASE = 769;
this.data = new Array(this.BASE).fill(0).map(() => new Array());
};
MyHashSet.prototype.add = function(key) {
const h = this.hash(key);
for (const element of this.data[h]) {
if (element === key) {
return;
}
}
this.data[h].push(key);
};
MyHashSet.prototype.remove = function(key) {
const h = this.hash(key);
const it = this.data[h];
for (let i = 0; i < it.length; ++i) {
if (it[i] === key) {
it.splice(i, 1);
return;
}
}
};
MyHashSet.prototype.contains = function(key) {
const h = this.hash(key);
for (const element of this.data[h]) {
if (element === key) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
};
MyHashSet.prototype.hash = function(key) {
return key % this.BASE;
}
Go语言
const base = 769
type MyHashSet struct {
data []list.List
}
func Constructor() MyHashSet {
return MyHashSet{make([]list.List, base)}
}
func (s *MyHashSet) hash(key int) int {
return key % base
}
func (s *MyHashSet) Add(key int) {
if !s.Contains(key) {
h := s.hash(key)
s.data[h].PushBack(key)
}
}
func (s *MyHashSet) Remove(key int) {
h := s.hash(key)
for e := s.data[h].Front(); e != nil; e = e.Next() {
if e.Value.(int) == key {
s.data[h].Remove(e)
}
}
}
func (s *MyHashSet) Contains(key int) bool {
h := s.hash(key)
for e := s.data[h].Front(); e != nil; e = e.Next() {
if e.Value.(int) == key {
return true
}
}
return false
}
C语言
struct List {
int val;
struct List* next;
};
void listPush(struct List* head, int x) {
struct List* tmp = malloc(sizeof(struct List));
tmp->val = x;
tmp->next = head->next;
head->next = tmp;
}
void listDelete(struct List* head, int x) {
for (struct List* it = head; it->next; it = it->next) {
if (it->next->val == x) {
struct List* tmp = it->next;
it->next = tmp->next;
free(tmp);
break;
}
}
}
bool listContains(struct List* head, int x) {
for (struct List* it = head; it->next; it = it->next) {
if (it->next->val == x) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
void listFree(struct List* head) {
while (head->next) {
struct List* tmp = head->next;
head->next = tmp->next;
free(tmp);
}
}
const int base = 769;
int hash(int key) {
return key % base;
}
typedef struct {
struct List* data;
} MyHashSet;
MyHashSet* myHashSetCreate() {
MyHashSet* ret = malloc(sizeof(MyHashSet));
ret->data = malloc(sizeof(struct List) * base);
for (int i = 0; i < base; i++) {
ret->data[i].val = 0;
ret->data[i].next = NULL;
}
return ret;
}
void myHashSetAdd(MyHashSet* obj, int key) {
int h = hash(key);
if (!listContains(&(obj->data[h]), key)) {
listPush(&(obj->data[h]), key);
}
}
void myHashSetRemove(MyHashSet* obj, int key) {
int h = hash(key);
listDelete(&(obj->data[h]), key);
}
bool myHashSetContains(MyHashSet* obj, int key) {
int h = hash(key);
return listContains(&(obj->data[h]), key);
}
void myHashSetFree(MyHashSet* obj) {
for (int i = 0; i < base; i++) {
listFree(&(obj->data[i]));
}
free(obj->data);
}
LeetCode 705复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(n/b)。其中 n 为哈希表中的元素数量,b 为链表的数量。假设哈希值是均匀分布的,则每个链表大概长度为 n/b。
空间复杂度:O(n + b)。
 极客笔记
极客笔记