C++ 初始化Vector
向量可以存储多个数据值,类似于数组,但它们只能存储对象引用而不是基本数据类型。它们存储对象的引用意味着它们指向包含数据的对象,而不是存储数据本身。与数组不同,向量不需要初始化大小。它们可以根据对象引用的数量自动调整大小,这是因为它们的存储由容器自动处理。容器将保留一个alloc的内部副本,用于分配存储器的生命周期。可以使用迭代器定位和遍历向量,因此它们放置在连续的存储空间中。向量还具有安全特性,可以避免程序崩溃,而数组则没有。我们可以为向量提供保留空间,但不能为数组提供。数组不是一个类,而向量是一个类。在向量中,可以删除元素,但在数组中不能。
使用父级’Collection class’,向量以模板类的形式发送。数组是具有特定属性的低级数据结构。向量具有函数和构造函数;它们不是基于索引的。它们是与数组相反的索引为基的数据结构。这里,最低地址提供给第一个元素,最高地址提供给最后一个元素。向量用于插入和删除对象,而数组用于频繁访问对象。数组是节约内存的数据结构,而向量利用更多内存来管理存储器并动态增长。访问元素时向量需要更多时间,但对于数组来说不是这样。
有四种初始化vector的方式:
- 逐个输入值
- 使用向量类的重载构造函数
- 使用数组的帮助
- 使用另一个初始化的向量
逐个输入值 –
可以使用向量类的方法’push_back’逐个插入向量中的所有元素。
算法
Begin
Declare v of vector type.
Then we call push_back() function. This is done to insert values into vector v.
Then we print "Vector elements: \n".
" for (int a: v)
print all the elements of variable a."
代码 –
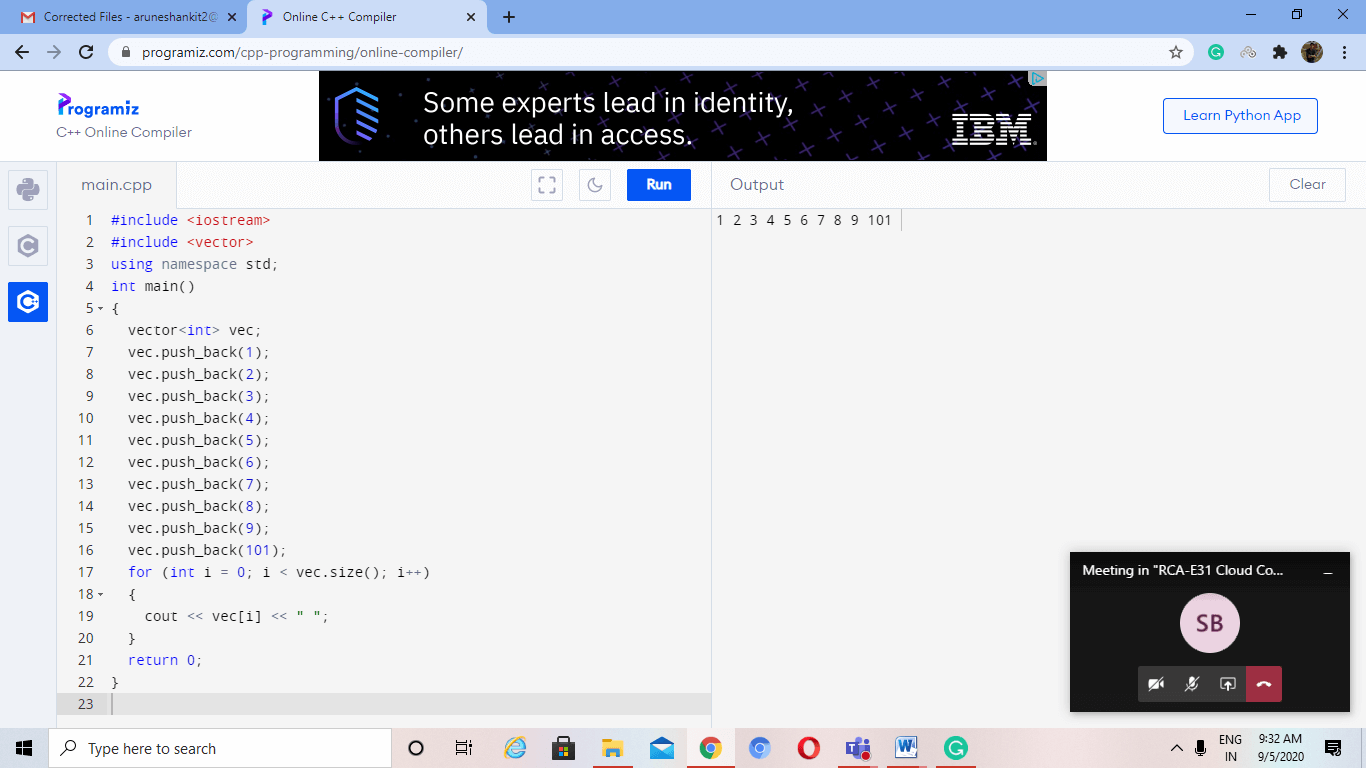
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int> vec;
vec.push_back(1);
vec.push_back(2);
vec.push_back(3);
vec.push_back(4);
vec.push_back(5);
vec.push_back(6);
vec.push_back(7);
vec.push_back(8);
vec.push_back(9);
vec.push_back(101);
for (int i = 0; i < vec.size(); i++)
{
cout << vec[i] << " ";
}
return 0;
}
输出
使用重载构造函数 –
当向量中有多个相同值的元素时,我们使用这个方法。
通过使用向量类的重载构造函数 –
这个方法主要用于向量被多个相同值的元素填充时使用。
算法
Begin
First, we initialize a variable say 's'.
Then we have to create a vector say 'v' with size's'.
Then we initialize vector v1.
Then initialize v2 by v1.
Then we print the elements.
End.
代码 –
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int elements = 12;
vector<int> vec(elements, 8);
for (int i = 0; i < vec.size(); i++)
{
cout << vec[i] << " \n";
}
return 0;
}
输出
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
通过数组的帮助 –
我们将一个数组传递给向量类的构造函数。数组包含将填充向量的元素。
算法 –
Begin
First, we create a vector say v.
Then, we initialize the vector.
In the end, print the elements.
End.
代码 –
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int> vectr{9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1,0};
for (int i = 0; i < vectr.size(); i++)
{
cout << vectr[i] << " \n";
}
return 0;
}
输出
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
使用另一个初始化的向量 –
在这里,我们需要将一个已初始化向量的begin()和end()迭代器传递给一个向量类构造函数。然后,我们初始化一个新的向量,并用旧的向量填充它。
算法 –
Begin
First, we have to create a vector v1.
Then, we have to initialize vector v1 by an array.
Then we initialize vector v2 by v1.
We have to print the elements.
End.
代码 –
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int> vec_1{1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8};
vector<int> vec_2(vec_1.begin(), vec_1.end());
for (int i = 0; i < vec_2.size(); i++)
{
cout << vec_2[i] << " \n";
}
return 0;
}
输出
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
 极客笔记
极客笔记